|
Space–time Tradeoff
space–time trade-off, also known as time–memory trade-off or the algorithmic space-time continuum in computer science is a case where an algorithm or program trades increased space usage with decreased time. Here, ''space'' refers to the data storage consumed in performing a given task ( RAM, HDD, etc.), and ''time'' refers to the time consumed in performing a given task (computation time or response time). The utility of a given space–time tradeoff is affected by related fixed and variable costs (of, e.g., CPU speed, storage space), and is subject to diminishing returns. History Biological usage of time–memory tradeoffs can be seen in the earlier stages of animal behavior. Using stored knowledge or encoding stimuli reactions as "instincts" in the DNA avoids the need for "calculation" in time-critical situations. More specific to computers, look-up tables have been implemented since the very earliest operating systems. In 1980 Martin Hellman first proposed usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Index
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time said table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records. An index is a copy of selected columns of data, from a table, that is designed to enable very efficient search. An index normally includes a "key" or direct link to the original row of data from which it was copied, to allow the complete row to be retrieved efficiently. Some databases extend the power of indexing by letting developers create indexes on column values that have been transformed by functions or expressions. For example, an index could be created on upper(last_name), which would o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptographic Hash Function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: * the probability of a particular n-bit output result (hash value) for a random input string ("message") is 2^ (as for any good hash), so the hash value can be used as a representative of the message; * finding an input string that matches a given hash value (a ''pre-image'') is infeasible, ''assuming all input strings are equally likely.'' The ''resistance'' to such search is quantified as security strength: a cryptographic hash with n bits of hash value is expected to have a ''preimage resistance'' strength of n bits, unless the space of possible input values is significantly smaller than 2^ (a practical example can be found in ); * a ''second preimage'' resistance strength, with the same expectations, refers to a similar problem of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
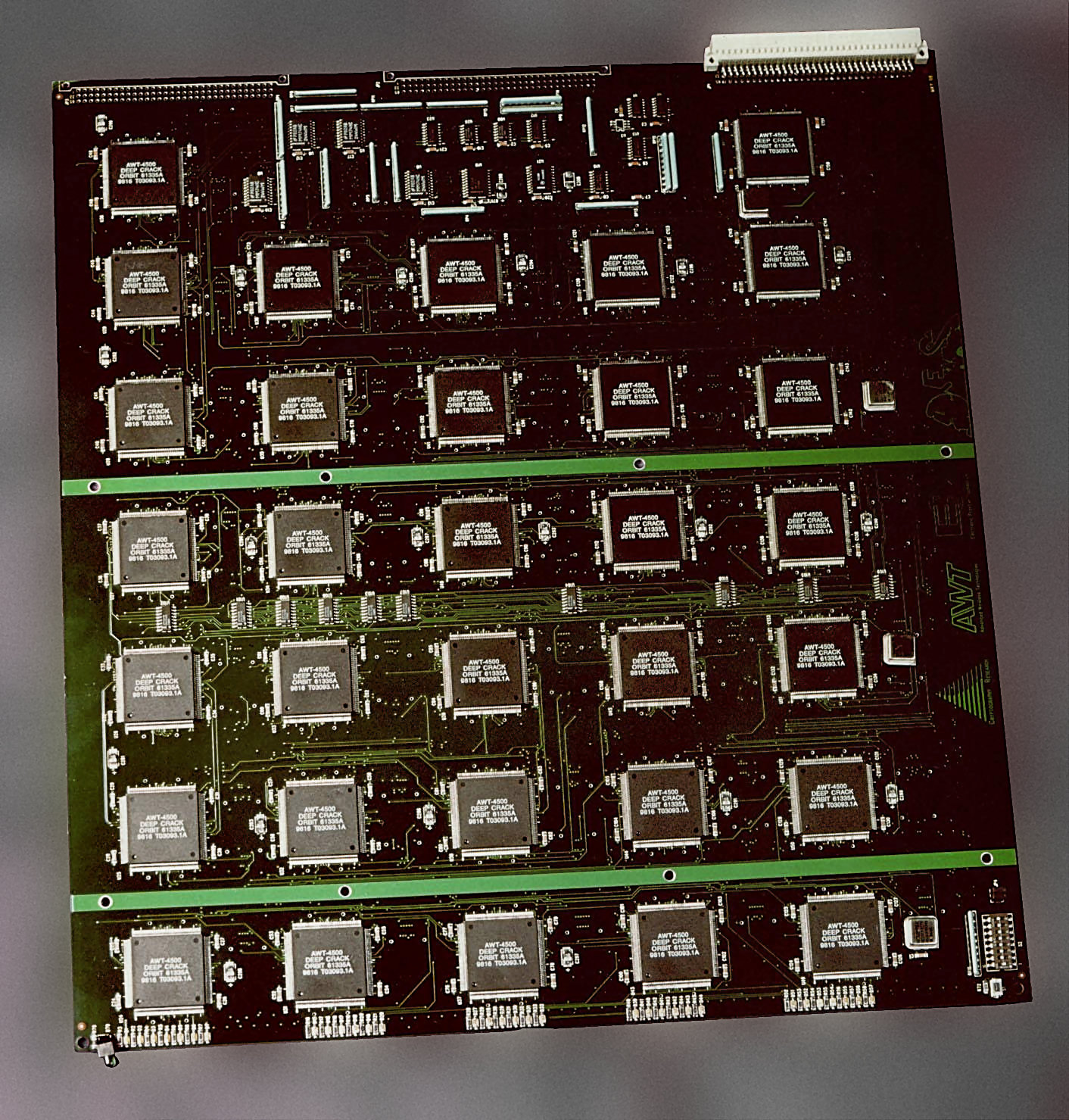
Brute-force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack or exhaustive key search is a cryptanalytic attack that consists of an attacker submitting many possible keys or passwords with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. This strategy can theoretically be used to break any form of encryption that is not information-theoretically secure. However, in a properly designed cryptosystem the chance of successfully guessing the key is negligible. When cracking passwords, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force search takes too long. Longer passwords, passphrases and keys have more possible values, making them exponentially more difficult to crack than shorter ones due to diversity of characters. Brute-force attacks can be made less effective by obfuscating the data to be encoded making it more difficult for an attacker to recognize when the code has been cracked or by ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Table
A rainbow table is a precomputed table for caching the outputs of a cryptographic hash function, usually for cracking password hashes. Passwords are typically stored not in plain text form, but as hash values. If such a database of hashed passwords falls into the hands of attackers, they can use a precomputed rainbow table to recover the plaintext passwords. A common defense against this attack is to compute the hashes using a key derivation function that adds a "salt" to each password before hashing it, with different passwords receiving different salts, which are stored in plain text along with the hash. Rainbow tables are a practical example of a space–time tradeoff: they use less computer processing time and more storage than a brute-force attack which calculates a hash on every attempt, but more processing time and less storage than a simple table that stores the hash of every possible password. Rainbow tables were invented by Philippe Oechslin as an application of an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Logarithm
In mathematics, for given real numbers a and b, the logarithm \log_b(a) is a number x such that b^x=a. Analogously, in any group G, powers b^k can be defined for all integers k, and the discrete logarithm \log_b(a) is an integer k such that b^k=a. In arithmetic modulo an integer m, the more commonly used term is index: One can write k=\mathbb_b a \pmod (read "the index of a to the base b modulo m") for b^k \equiv a \pmod if b is a primitive root of m and \gcd(a,m)=1. Discrete logarithms are quickly computable in a few special cases. However, no efficient method is known for computing them in general. In cryptography, the computational complexity of the discrete logarithm problem, along with its application, was first proposed in the Diffie–Hellman problem. Several important algorithms in public-key cryptography, such as ElGamal, base their security on the hardness assumption that the discrete logarithm problem (DLP) over carefully chosen groups has no efficient solution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baby-step Giant-step
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, the baby-step giant-step is a meet-in-the-middle algorithm for computing the discrete logarithm or order of an element in a finite abelian group by Daniel Shanks. The discrete log problem is of fundamental importance to the area of public key cryptography. Many of the most commonly used cryptography systems are based on the assumption that the discrete log is extremely difficult to compute; the more difficult it is, the more security it provides a data transfer. One way to increase the difficulty of the discrete log problem is to base the cryptosystem on a larger group. Theory The algorithm is based on a space–time tradeoff. It is a fairly simple modification of trial multiplication, the naive method of finding discrete logarithms. Given a cyclic group G of order n, a generator \alpha of the group and a group element \beta, the problem is to find an integer x such that : \alpha^x = \beta\,. The baby-step giant-step algorithm is based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Unrolling
Loop unrolling, also known as loop unwinding, is a loop transformation technique that attempts to optimize a program's execution speed at the expense of its binary size, which is an approach known as space–time tradeoff. The transformation can be undertaken manually by the programmer or by an optimizing compiler. On modern processors, loop unrolling is often counterproductive, as the increased code size can cause more cache misses; ''cf.'' Duff's device. The goal of loop unwinding is to increase a program's speed by reducing or eliminating instructions that control the loop, such as pointer arithmetic and "end of loop" tests on each iteration; reducing branch penalties; as well as hiding latencies, including the delay in reading data from memory. To eliminate this computational overhead, loops can be re-written as a repeated sequence of similar independent statements. Loop unrolling is also part of certain formal verification techniques, in particular bounded model chec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache (computing)
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs. To be cost-effective, caches must be relatively small. Nevertheless, caches are effective in many areas of computing because typical Application software, computer applications access data with a high degree of locality of reference. Such access patterns exhibit temporal locality, where data is requested that has been recently requested, and spatial locality, where data is requested that is stored near dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitmap
In computing, a bitmap (also called raster) graphic is an image formed from rows of different colored pixels. A GIF is an example of a graphics image file that uses a bitmap. As a noun, the term "bitmap" is very often used to refer to a particular bitmapping application: the pix-map, which refers to a map of pixels, where each pixel may store more than two colors, thus using more than one bit per pixel. In such a case, the domain in question is the array of pixels which constitute a digital graphic output device (a screen or monitor). In some contexts, the term ''bitmap'' implies one bit per pixel, whereas ''pixmap'' is used for images with multiple bits per pixel. A bitmap is a type of memory organization or image file format used to store digital images. The term ''bitmap'' comes from the computer programming terminology, meaning just a ''map of bits'', a spatially mapped array of bits. Now, along with ''pixmap'', it commonly refers to the similar concept of a spatially mapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are a form of computer graphics in which visual images are created directly from geometric shapes defined on a Cartesian plane, such as points, lines, curves and polygons. The associated mechanisms may include vector display and printing ''hardware'', vector ''data models'' and file formats, as well as the ''software'' based on these data models (especially graphic design software, computer-aided design, and geographic information systems). Vector graphics are an alternative to raster or bitmap graphics, with each having advantages and disadvantages in specific situations. While vector hardware has largely disappeared in favor of raster-based monitors and printers, vector data and software continue to be widely used, especially when a high degree of geometric precision is required, and when complex information can be decomposed into simple geometric primitives. Thus, it is the preferred model for domains such as engineering, architecture, surveying, 3D r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalable Vector Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector graphics format for defining two-dimensional graphics, having support for interactivity and animation. The SVG specification is an open standard developed by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999. SVG images are defined in a vector graphics format and stored in XML text files. SVG images can thus be scaled in size without loss of quality, and SVG files can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed. The XML text files can be created and edited with text editors or vector graphics editors, and are rendered by most web browsers. If used for images, SVG can host scripts or CSS, potentially leading to cross-site scripting attacks or other security vulnerabilities. History SVG has been in development within the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) since 1999 after six competing proposals for vector graphics languages had been submitted to the consortium during 1998 (see below). The early SVG Working Group decided not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |