|
Sonic Black Holes
A sonic black hole, sometimes called a dumb hole or acoustic black hole, is a phenomenon in which phonons (sound perturbations) are unable to escape from a region of a fluid that is flowing more quickly than the local speed of sound. They are called sonic, or acoustic, black holes because these trapped phonons are analogous to light in astrophysical (gravitational) black holes. Physicists are interested in them because they have many properties similar to astrophysical black holes and, in particular, emit a phononic version of Hawking radiation. This Hawking radiation can be spontaneously created by quantum vacuum fluctuations, in close analogy with Hawking radiation from a real black hole. On the other hand, the Hawking radiation can be stimulated in a classical process. The boundary of a sonic black hole, at which the flow speed changes from being greater than the speed of sound to less than the speed of sound, is called the event horizon. A rotating sonic black hole was used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical Quantization (physics), quantization of the mode of vibration, modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet Union, Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name ''phonon'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word (), which translates to ''so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slow Light
Slow light is the propagation of an optical pulse or other modulation of an optical carrier at a very low group velocity. Slow light occurs when a propagating pulse is substantially slowed by the interaction with the medium in which the propagation takes place. Group velocities below c were known to be possible as far back as 1880, but could not be realized in a useful manner until 1991, when Stephen Harris and collaborators demonstrated electromagnetically induced transparency in trapped strontium atoms. Reduction of the speed of light by a factor of 165 was reported in 1995. In 1998, Danish physicist Lene Vestergaard Hau led a combined team from Harvard University and the Rowland Institute for Science which realized much lower group velocities of light. They succeeded in slowing a beam of light to about 17 meters per second. In 2004, researchers at UC Berkeley first demonstrated slow light in a semiconductor, with a group velocity 9.6 kilometers per second. Hau and her colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Gravity
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics; it deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects, such as neutron stars. Three of the four fundamental forces of physics are described within the framework of quantum mechanics and quantum field theory. The current understanding of the fourth force, gravity, is based on Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which is formulated within the entirely different framework of classical physics. However, that description is incomplete: describing the gravitational field of a black hole in the general theory of relativity leads physical quantities, such as the spacetime curvature, to diverge at the center of the black hole. This signals the breakdown of the general theory of relativity and the need for a theory that goes b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Black Hole
An optical black hole is a phenomenon in which slow light is passed through a Bose–Einstein condensate that is itself spinning faster than the local speed of light within to create a vortex capable of trapping the light behind an event horizon just as a gravitational black hole would. Unlike other black hole analogs such as a sonic black hole in a Bose–Einstein condensate, a slow light black hole analog is not expected to mimic the quantum In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantizati ... effects of a black hole, and thus not emit Hawking radiation. It does, however, mimic the classical properties of a gravitational black hole, making it potentially useful in studying other properties of black holes. More recently, some physicists have developed a fiber optic based system wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Metric
In mathematical physics, a metric describes the arrangement of relative distances within a surface or volume, usually measured by signals passing through the region – essentially describing the intrinsic geometry of the region. An acoustic metric will describe the signal-carrying properties characteristic of a given particulate medium in acoustics, or in fluid dynamics. Other descriptive names such as sonic metric are also sometimes used, interchangeably. A simple fluid example For simplicity, we will assume that the underlying background geometry is Euclidean, and that this space is filled with an isotropic inviscid fluid at zero temperature (e.g. a superfluid). This fluid is described by a density field ''ρ'' and a velocity field \vec. The speed of sound at any given point depends upon the compressibility which in turn depends upon the density at that point. It requires much work to compress anything more into an already compacted space. This can be specified by the "sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasing
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Gravity
The surface gravity, ''g'', of an astronomical object is the gravitational acceleration experienced at its surface at the equator, including the effects of rotation. The surface gravity may be thought of as the acceleration due to gravity experienced by a hypothetical test particle which is very close to the object's surface and which, in order not to disturb the system, has negligible mass. For objects where the surface is deep in the atmosphere and the radius not known, the surface gravity is given at the 1 bar pressure level in the atmosphere. Surface gravity is measured in units of acceleration, which, in the SI system, are meters per second squared. It may also be expressed as a multiple of the Earth's standard surface gravity, which is equal to :''g'' = In astrophysics, the surface gravity may be expressed as log ''g'', which is obtained by first expressing the gravity in cgs units, where the unit of acceleration and surface gravity is centimeters per seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Unruh
William George "Bill" Unruh (; born August 28, 1945) is a Canadian physicist at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver who described the hypothetical Unruh effect in 1976. Early life and education Unruh was born into a Mennonite family in Winnipeg, Manitoba. His parents were Benjamin Unruh, a refugee from Russia, and Anna Janzen, who was born in Canada. He obtained his B.Sc. from the University of Manitoba in 1967, followed by an M.A. (1969) and Ph.D. (1971) from Princeton University, New Jersey, under the direction of John Archibald Wheeler. Areas of research Unruh has made seminal contributions to our understanding of gravity, black holes, cosmology, and quantum fields in curved spaces, including the discovery of what is now known as the Unruh effect. Unruh has contributed to the foundations of quantum mechanics in areas such as decoherence and the question of time in quantum mechanics. He has helped to clarify the meaning of nonlocality in a quantum context, in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Gravity
Induced gravity (or emergent gravity) is an idea in quantum gravity that spacetime curvature and its dynamics emerge as a mean field approximation of underlying microscopic degrees of freedom, similar to the fluid mechanics approximation of Bose–Einstein condensates. The concept was originally proposed by Andrei Sakharov in 1967. Overview Sakharov observed that many condensed matter systems give rise to emergent phenomena that are analogous to general relativity. For example, crystal defects can look like curvature and torsion in an Einstein–Cartan spacetime. This allows one to create a theory of gravity with torsion from a world crystal model of spacetime in which the lattice spacing is of the order of a Planck length. Sakharov's idea was to start with an arbitrary background pseudo-Riemannian manifold (in modern treatments, possibly with torsion) and introduce quantum fields (matter) on it but not introduce any gravitational dynamics explicitly. This gives rise to an effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
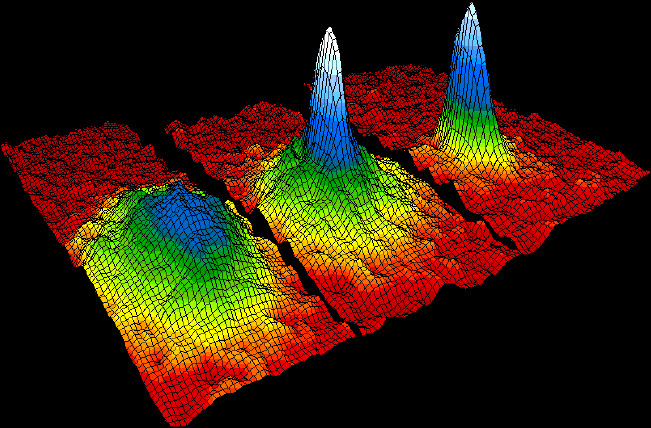
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which point microscopic quantum mechanical phenomena, particularly wavefunction interference, become apparent macroscopically. A BEC is formed by cooling a gas of extremely low density (about 100,000 times less dense than normal air) to ultra-low temperatures. This state was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein following and crediting a pioneering paper by Satyendra Nath Bose on the new field now known as quantum statistics. In 1995, the Bose-Einstein condensate was created by Eric Cornell and Carl Wieman of the University of Colorado at Boulder using rubidium atoms; later that year, Wolfgang Ketterle of MIT produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as well as the medium through which a sound wave is propagating. At , the speed of sound in air is about . The speed of sound in an ideal gas depends only on its temperature and composition. The speed has a weak dependence on frequency and pressure in ordinary air, deviating slightly from ideal behavior. In colloquial speech, ''speed of sound'' refers to the speed of sound waves in air. However, the speed of sound varies from substance to substance: typically, sound travels most slowly in gases, faster in liquids, and fastest in solids. For example, while sound travels at in air, it travels at in water (almost 4.3 times as fast) and at in iron (almost 15 times as fast). In an exceptionally stiff material such as diamond, sound travels a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_filtered.jpg)