|
Sol–gel Process
In materials science, the sol–gel process is a method for producing solid materials from small molecules. The method is used for the fabrication of metal oxides, especially the oxides of silicon (Si) and titanium (Ti). The process involves conversion of monomers into a colloidal solution (''sol'') that acts as the precursor for an integrated network (or '' gel'') of either discrete particles or network polymers. Typical precursors are metal alkoxides. Sol-gel process is used to produce ceramic nanoparticles. Stages In this chemical procedure, a "sol" (a colloidal solution) is formed that then gradually evolves towards the formation of a gel-like diphasic system containing both a liquid phase and solid phase whose morphologies range from discrete particles to continuous polymer networks. In the case of the colloid, the volume fraction of particles (or particle density) may be so low that a significant amount of fluid may need to be removed initially for the gel-like properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrinkage (casting)
In metalworking and jewelry making, casting is a process in which a liquid metal is delivered into a mold (usually by a crucible) that contains a negative impression (i.e., a three-dimensional negative image) of the intended shape. The metal is poured into the mold through a hollow channel called a sprue. The metal and mold are then cooled, and the metal part (the ''casting'') is extracted. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Casting processes have been known for thousands of years, and have been widely used for sculpture (especially in bronze), jewelry in precious metals, and weapons and tools. Highly engineered castings are found in 90 percent of durable goods, including cars, trucks, aerospace, trains, mining and construction equipment, oil wells, appliances, pipes, hydrants, wind turbines, nuclear plants, medical devices, defense products, toys, and more. Traditional techniques include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerogel
Aerogels are a class of synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas, without significant collapse of the gel structure. The result is a solid with extremely low density and extremely low thermal conductivity. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds. Silica aerogels feel like fragile expanded polystyrene to the touch, while some polymer-based aerogels feel like rigid foams. The first documented example of an aerogel was created by Samuel Stephens Kistler in 1931, as a result of a bet with Charles Learned over who could replace the liquid in "jellies" with gas without causing shrinkage. Aerogels are produced by extracting the liquid component of a gel through supercritical drying or freeze-drying. This allows the liquid to be slowly dried off without causing the solid matrix in the gel to collapse from capillary action, as would happen with conventional evaporation. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Membrane
An artificial membrane, or synthetic membrane, is a synthetically created membrane which is usually intended for separation purposes in laboratory or in industry. Synthetic membranes have been successfully used for small and large-scale industrial processes since the middle of twentieth century.Pinnau, I., Freeman, B.D., ''Membrane Formation and Modification'', ACS, 1999. A wide variety of synthetic membranes is known.Osada, Y., Nakagawa, T., ''Membrane Science and Technology'', New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc,1992. They can be produced from organic materials such as polymers and liquids, as well as inorganic materials. The most of commercially utilized synthetic membranes in separation industry are made of polymeric structures. They can be classified based on their surface chemistry, bulk structure, morphology, and production method. The chemical and physical properties of synthetic membranes and separated particles as well as a choice of driving force define a particular membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Wool
Mineral wool is any fibrous material formed by spinning or drawing molten mineral or rock materials such as slag and ceramics. Applications of mineral wool include thermal insulation (as both structural insulation and pipe insulation), filtration, soundproofing, and hydroponic growth medium. Naming Mineral wool is also known as ''mineral fiber'', ''mineral cotton'', ''mineral fibre'', ''man-made mineral fibre'' (MMMF), and ''man-made vitreous fiber'' (MMVF). Specific mineral wool products are ''stone wool'' and ''slag wool''. Europe also includes glass wool which, together with ceramic fiber, are entirely artificial fibers that can be made into different shapes and are spiky to touch. History Slag wool was first made in 1840 in Wales by Edward Parry, "but no effort appears to have been made to confine the wool after production; consequently it floated about the works with the slightest breeze, and became so injurious to the men that the process had to be abandoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silicon dioxide, silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and glasses, eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "'' ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process. Casting materials are usually metals or various ''time setting'' materials that cure after mixing two or more components together; examples are epoxy, concrete, plaster and clay. Casting is most often used for making complex shapes that would be otherwise difficult or uneconomical to make by other methods. Heavy equipment like machine tool beds, ships' propellers, etc. can be cast easily in the required size, rather than fabricating by joining several small pieces. Casting is a 7,000-year-old process. The oldest surviving casting is a copper frog from 3200 BC. History Throughout history, metal casting has been used to make tools, weapons, and religious objects. Metal casting history and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
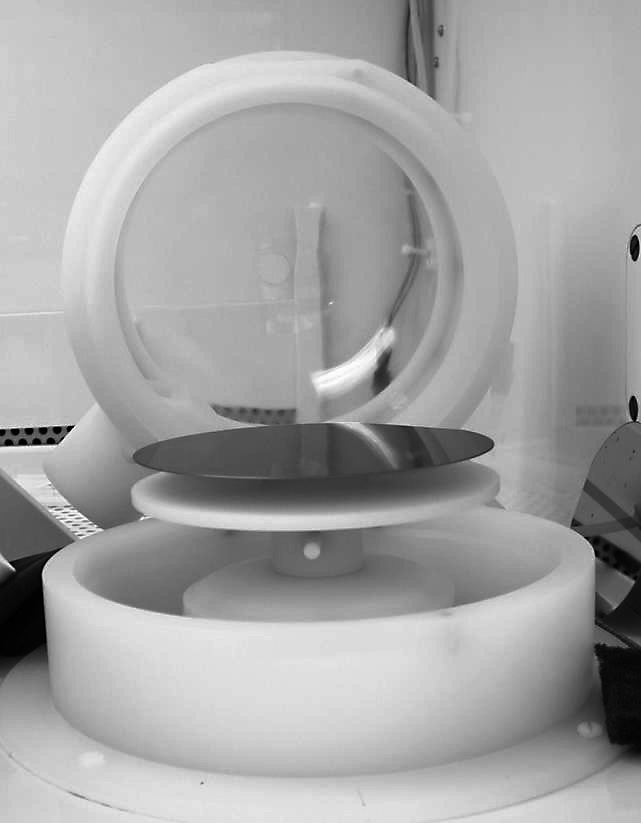
Spin Coating
Spin coating is a procedure used to deposit uniform thin films onto flat substrates. Usually a small amount of coating material is applied on the center of the substrate, which is either spinning at low speed or not spinning at all. The substrate is then rotated at speed up to 10,000 rpm to spread the coating material by centrifugal force. A machine used for spin coating is called a spin coater, or simply spinner. Rotation is continued while the fluid spins off the edges of the substrate, until the desired thickness of the film is achieved. The applied solvent is usually volatile, and simultaneously evaporates. The higher the angular speed of spinning, the thinner the film. The thickness of the film also depends on the viscosity and concentration of the solution, and the solvent. Pioneering theoretical analysis of spin coating was undertaken by Emslie et al., and has been extended by many subsequent authors (including Wilson et al., who studied the rate of spreading in spin coat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dip-coating
image:Dip coating.svg, A schematic of the continuous dip coating process. Roll of coarse cloth Cloth Bath Liquid material Rollers Oven Scrapers Excess liquid falls back A coating remains on the fabric cloth. Dip coating is an industrial coating process which is used, for example, to manufacture bulk products such as coated fabrics and condoms and specialised coatings for example in the biomedical field. Dip coating is also commonly used in academic research, where many chemical and nano material engineering research projects use the dip coating technique to create thin-film coatings. The earliest dip-coated products may have been candles. For flexible laminar substrates such as fabrics, dip coating may be performed as a continuous roll-to-roll process. For coating a 3D object, it may simply be inserted and removed from the bath of coating. For condom-making, a former is dipped into the coating. For some products, such as early methods of making candles, the process is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (materials Science)
Substrate is a term used in materials science and engineering to describe the base material on which processing is conducted. This surface could be used to produce new film or layers of material such as deposited coatings. It could be the base to which paint, adhesives, or adhesive tape is bonded. A typical substrate might be rigid such as metal, concrete, or glass, onto which a coating might be deposited. Flexible substrates are also used. With all coating processes, the condition of the surface of the substrate can strongly affect the bond of subsequent layers. This can include cleanliness, smoothness, surface energy, moisture, etc. Some substrates are anisotropic with surface properties being different depending on the direction: examples include wood and paper products. Coatings Coating can be by a variety of processes: * Adhesives and Adhesive tapes * Coating and printing processes * Chemical vapor deposition and physical vapor deposition * Conversion coating :* ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain Growth
In materials science, grain growth is the increase in size of grains (crystallites) in a material at high temperature. This occurs when recovery and recrystallisation are complete and further reduction in the internal energy can only be achieved by reducing the total area of grain boundary. The term is commonly used in metallurgy but is also used in reference to ceramics and minerals. The behaviors of grain growth is analogous to the coarsening behaviors of grains, which implied that both of grain growth and coarsening may be dominated by the same physical mechanism. Importance of grain growth The practical performances of polycrystalline materials are strongly affected by the formed microstructure inside, which is mostly dominated by grain growth behaviors. For example, most materials exhibit the Hall–Petch effect at room-temperature and so display a higher yield stress when the grain size is reduced (assuming abnormal grain growth has not taken place). At high temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)