|
Software-defined Storage
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots, copy-on-write clones, tiering and backup. Software-defined storage (SDS) hardware may or may not also have abstraction, pooling, or automation software of its own. When implemented as software only in conjunction with commodity servers with internal disks, it may suggest software such as a virtual or global file system or distributed block storage. If it is software layered over sophisticated large storage arrays, it suggests software such as storage virtualization or stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Data Storage
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and Data storage, recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast technologies are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
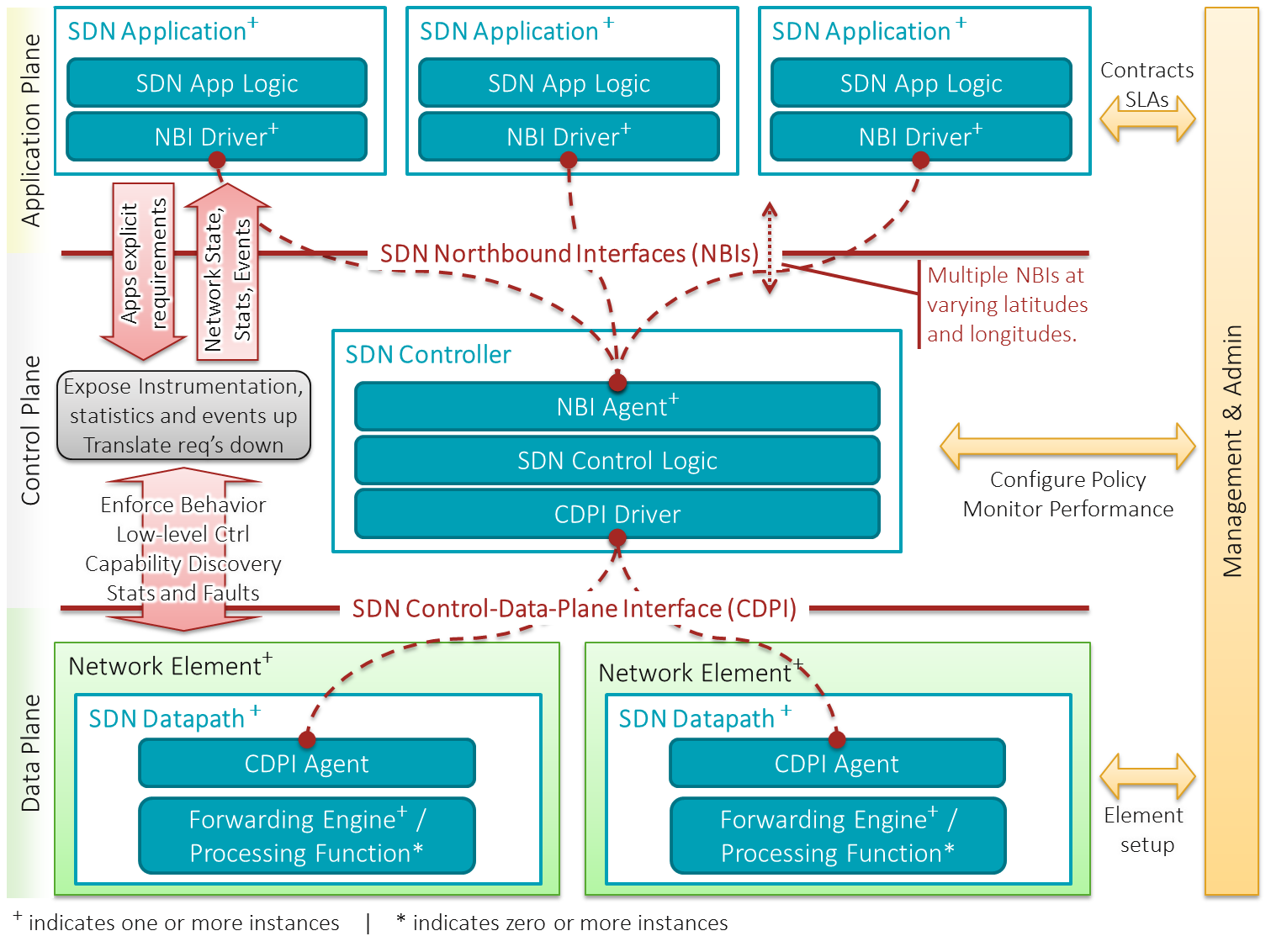
Software-defined Networking
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an approach to network management that uses abstraction to enable dynamic and programmatically efficient network configuration to create grouping and segmentation while improving network performance and monitoring in a manner more akin to cloud computing than to traditional network management. SDN is meant to improve the static architecture of traditional networks and may be employed to centralize network intelligence in one network component by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets ( data plane) from the routing process ( control plane). The control plane consists of one or more controllers, which are considered the brains of the SDN network, where the whole intelligence is incorporated. However, centralization has certain drawbacks related to security, scalability and elasticity. SDN was commonly associated with the OpenFlow protocol for remote communication with network plane elements to determine the path of network pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenFlow
OpenFlow is a communications protocol that gives access to the forwarding plane of a network switch or router (computing), router over the network. Description OpenFlow enables network controllers to determine the path of network packets across a network of switches. The controllers are distinct from the switches. This separation of the control from the forwarding allows for more sophisticated traffic management than is feasible using access control lists (ACLs) and routing protocols. Also, OpenFlow allows switches from different vendors — often each with their own proprietary interfaces and scripting languages — to be managed remotely using a single, open protocol. The protocol's inventors consider OpenFlow an enabler of software-defined networking (SDN). OpenFlow allows remote administration of a layer 3 switch's packet forwarding tables, by adding, modifying and removing packet matching rules and actions. This way, routing decisions can be made periodically or ''ad hoc'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service-level Agreement
A service-level agreement (SLA) is an agreement between a service provider and a customer. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user. The most common component of an SLA is that the services should be provided to the customer as agreed upon in the contract. As an example, Internet service providers and telcos will commonly include service level agreements within the terms of their contracts with customers to define the level(s) of service being sold in plain language terms. In this case, the SLA will typically have a technical definition of '' mean time between failures'' (MTBF), '' mean time to repair'' or '' mean time to recovery'' (MTTR); identifying which party is responsible for reporting faults or paying fees; responsibility for various data rates; throughput; jitter; or similar measurable details. Overview A service-level agreement is an agreement between two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustered File System
A clustered file system (CFS) is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system (only direct attached storage for each node). Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance. Shared-disk file system A shared-disk file system uses a storage area network (SAN) to allow multiple computers to gain direct disk access at the block level. Access control and translation from file-level operations that applications use to block-level operations used by the SAN must take place on the client node. The most common type of clustered file system, the shared-disk file systemby addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluster
Gluster Inc. (formerly known as Z RESEARCH) was a software company that provided an open source platform for scale-out public and private cloud storage. The company was privately funded and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, with an engineering center in Bangalore, India. Gluster was funded by Nexus Venture Partners and Index Ventures. Gluster was acquired by Red Hat on October 7, 2011. History The name ''Gluster'' comes from the combination of the terms ''GNU'' and ''cluster''. Despite the similarity in names, Gluster is not related to the Lustre (file system), Lustre file system and does not incorporate any Lustre code. Gluster based its product on ''GlusterFS'', an open-source software-based Network-attached storage, network-attached filesystem that deploys on commodity hardware. The initial version of GlusterFS was written by Anand Babu Periasamy, Gluster's founder and CTO. In May 2010 Ben Golub became the president and chief executive officer. Red Hat became the primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scality
Scality is a global technology provider of software-defined storage (SDS) solutions, specializing in distributed file and object storage with cloud data management. Scality maintains offices in Paris (France), London (UK), San Francisco and Washington DC (USA), and Tokyo (Japan) and has employees in 14 countries. History Scality was founded in 2009 by Jérôme Lecat, Giorgio Regni, Daniel Binsfeld, Serge Dugas, and Brad King. Scality raised $7 million of venture capital funding in March 2011. A C-round of $22 million was announced in June 2013, led by Menlo Ventures and Iris Capital with participation from FSN PME and all existing investors, including Idinvest Partners, OMNES Capital and Galileo Partners. Scality raised $45 million in August 2015. This Series D funding was led by Menlo Ventures with participation from all existing investors and one new strategic investor, BroadBand Tower. In 2016, HPE made a strategic investment in the company. In April, 2018, the company ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceph (software)
Ceph (pronounced ) is a Free software, free and open-source software, open-source software-defined Computer data storage, storage computing platform, platform that provides object storage, Block-level_storage, block storage, and File system, file storage built on a common computer cluster, distributed cluster foundation. Ceph provides distributed operation without a single point of failure and scalability to the exabyte level. Since version 12 (Luminous), Ceph does not rely on any other conventional filesystem and directly manages Hard disk drive, HDDs and Solid-state drive, SSDs with its own storage backend BlueStore and can expose a POSIX filesystem. Ceph replication (computer science), replicates data with fault tolerance, using commodity hardware and Ethernet IP and requiring no specific hardware support. Ceph is High_availability, highly available and ensures strong data durability through techniques including replication, Erasure_code, erasure coding, snapshots and clones. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenStack
OpenStack is a free, open standard cloud computing platform. It is mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) in both public and private clouds where virtual servers and other resources are made available to users. The software platform consists of interrelated components that control diverse, multi-vendor hardware pools of processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center. Users manage it either through a web-based dashboard, through command-line tools, or through RESTful web services. OpenStack began in 2010 as a joint project of Rackspace Hosting and NASA. , it was managed by the OpenStack Foundation, a non-profit corporate entity established in September 2012 to promote OpenStack software and its community. By 2018, more than 500 companies had joined the project. In 2020 the foundation announced it would be renamed the Open Infrastructure Foundation in 2021. History In July 2010, Rackspace Hosting and NASA announced an open-source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in , March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example) implement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to Server (computing), servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers. Fibre Channel networks form a switched fabric because the switches in a network operate in unison as one big switch. Fibre Channel typically runs on optical fiber cables within and between data centers, but can also run on copper cabling. Supported data rates include 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 gigabit per second resulting from improvements in successive technology generations. The industry now notates this as Gigabit Fibre Channel (GFC). There are various upper-level protocols for Fibre Channel, including two for block storage. Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a protocol that transports Small Computer System Interface, SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks. FICON is a protocol that transports ESCON comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISCSI
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI ( ) is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval. The protocol allows clients (called ''initiators'') to send SCSI commands (''CDBs'') to storage devices (''targets'') on remote servers. It is a storage area network (SAN) protocol, allowing organizations to consolidate storage into storage arrays while providing clients (such as database and web servers) with the illusion of locally attached SCSI disks. It mainly competes with Fibre Channel, but unlike traditional Fibre Channel which usually requires dedicated cabling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |