|
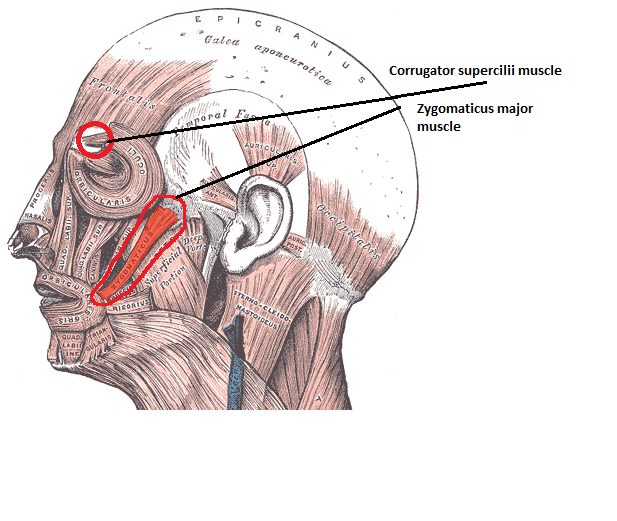
Smile Detection
Affective computing is the study and development of systems and devices that can recognize, interpret, process, and simulate human affects. It is an interdisciplinary field spanning computer science, psychology, and cognitive science. While some core ideas in the field may be traced as far back as to early philosophical inquiries into emotion, the more modern branch of computer science originated with Rosalind Picard's 1995 paper entitled "Affective Computing" and her 1997 book of the same name published by MIT Press. One of the motivations for the research is the ability to give machines emotional intelligence, including to simulate empathy. The machine should interpret the emotional state of humans and adapt its behavior to them, giving an appropriate response to those emotions. Areas Detecting and recognizing emotional information Detecting emotional information usually begins with passive sensors that capture data about the user's physical state or behavior without inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophia At The AI For Good Global Summit 2018 (27254369347) (cropped)
Sophia most commonly refers to: * Sophia (wisdom), a central idea in Hellenistic philosophy and religion * Sophia (Gnosticism), a feminine figure in Gnosticism * Sophia (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters named Sophia or Sofia Sophia or SOPHIA may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Sophia (Japanese band) * Sophia (singer) or Sophia Abrahão, pop singer from Brazil * Sophia (The Crüxshadows EP), ''Sophia'' (The Crüxshadows EP) * Sophia (Sophia Abrahão EP), ''Sophia'' (Sophia Abrahão EP) * Sophia (Nerina Pallot song), "Sophia" (Nerina Pallot song) * Sophia (Laura Marling song), "Sophia" (Laura Marling song) * "Sophia", a song from ''Think Before You Speak (album), Think Before You Speak'' by Good Shoes * "Sophia", a song from ''Mother's Spiritual'' by Laura Nyro * "Sophia", a song from ''Dust and Chimes'' by Six Organs of Admittance Other uses in arts and entertainment * Sophia (TV series), ''Sophia'' (TV series), a Russian historical dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-nearest Neighbor Algorithm
In statistics, the ''k''-nearest neighbors algorithm (''k''-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method. It was first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. Most often, it is used for classification, as a ''k''-NN classifier, the output of which is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its ''k'' nearest neighbors (''k'' is a positive integer, typically small). If ''k'' = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor. The ''k''-NN algorithm can also be generalized for regression. In ''-NN regression'', also known as '' nearest neighbor smoothing'', the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of ''k'' nearest neighbors. If ''k'' = 1, then the output is simply assigned to the value of that single nearest neighbor, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Classifier
In machine learning, a linear classifier makes a classification decision for each object based on a linear combination of its features. Such classifiers work well for practical problems such as document classification, and more generally for problems with many variables ( features), reaching accuracy levels comparable to non-linear classifiers while taking less time to train and use. Definition If the input feature vector to the classifier is a real vector \vec x, then the output score is :y = f(\vec\cdot\vec) = f\left(\sum_j w_j x_j\right), where \vec w is a real vector of weights and ''f'' is a function that converts the dot product of the two vectors into the desired output. (In other words, \vec is a one-form or linear functional mapping \vec x onto R.) The weight vector \vec w is learned from a set of labeled training samples. Often ''f'' is a threshold function, which maps all values of \vec\cdot\vec above a certain threshold to the first class and all other value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space Model
Vector space model or term vector model is an algebraic model for representing text documents (or more generally, items) as vector space, vectors such that the distance between vectors represents the relevance between the documents. It is used in information filtering, information retrieval, index (search engine), indexing and relevancy rankings. Its first use was in the SMART Information Retrieval System. Definitions In this section we consider a particular vector space model based on the Bag-of-words model, bag-of-words representation. Documents and queries are represented as vectors. :d_j = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) :q = ( w_ ,w_ , \dotsc ,w_ ) Each Dimension (vector space), dimension corresponds to a separate term. If a term occurs in the document, its value in the vector is non-zero. Several different ways of computing these values, also known as (term) weights, have been developed. One of the best known schemes is tf-idf weighting (see the example below). The definition of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge Base
In computer science, a knowledge base (KB) is a set of sentences, each sentence given in a knowledge representation language, with interfaces to tell new sentences and to ask questions about what is known, where either of these interfaces might use inference. It is a technology used to store complex structured data used by a computer system. The initial use of the term was in connection with expert systems, which were the first knowledge-based systems. Original usage of the term The original use of the term knowledge base was to describe one of the two sub-systems of an expert system. A knowledge-based system consists of a knowledge-base representing facts about the world and ways of reasoning about those facts to deduce new facts or highlight inconsistencies. Properties The term "knowledge-base" was coined to distinguish this form of knowledge store from the more common and widely used term ''database''. During the 1970s, virtually all large management information sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
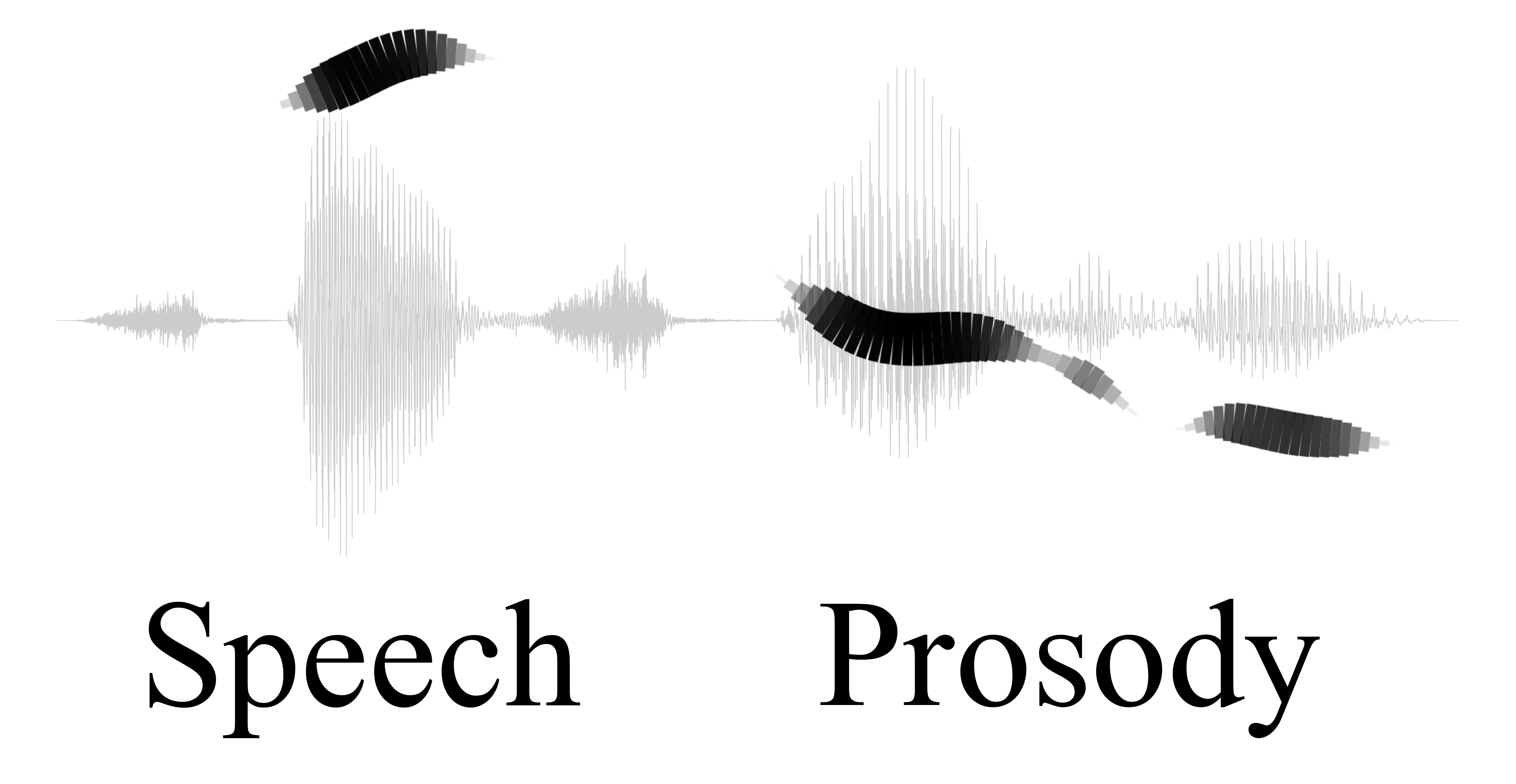
Prosody (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosody () is the study of elements of speech, including intonation, stress, rhythm and loudness, that occur simultaneously with individual phonetic segments: vowels and consonants. Often, prosody specifically refers to such elements, known as ''suprasegmentals'', when they extend across more than one phonetic segment. Prosody reflects the nuanced emotional features of the speaker or of their utterances: their obvious or underlying emotional state, the form of utterance (statement, question, or command), the presence of irony or sarcasm, certain emphasis on words or morphemes, contrast, focus, and so on. Prosody displays elements of language that are not encoded by grammar, punctuation or choice of vocabulary. Attributes of prosody In the study of prosodic aspects of speech, it is usual to distinguish between auditory measures ( subjective impressions produced in the mind of the listener) and objective measures (physical properties of the sound wave and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotion Recognition
Emotion recognition is the process of identifying human emotion. People vary widely in their accuracy at recognizing the emotions of others. Use of technology to help people with emotion recognition is a relatively nascent research area. Generally, the technology works best if it uses multiple modalities in context. To date, the most work has been conducted on automating the recognition of facial expressions from video, spoken expressions from audio, written expressions from text, and physiology as measured by wearables. Human Humans show a great deal of variability in their abilities to recognize emotion. A key point to keep in mind when learning about automated emotion recognition is that there are several sources of "ground truth", or truth about what the real emotion is. Suppose we are trying to recognize the emotions of Alex. One source is "what would most people say that Alex is feeling?" In this case, the 'truth' may not correspond to what Alex feels, but may corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Human
A virtual human (or also known as meta human or digital human) is a software fictional character or human being. Virtual humans have been created as tools and artificial companions in simulation, video games, film production, human factors and ergonomic and usability studies in various industries (aerospace, automobile, machinery, furniture etc.), clothing industry, telecommunications (avatars), medicine, etc. These applications require domain-dependent simulation fidelity. A medical application might require an exact simulation of specific internal organs; film industry requires highest aesthetic standards, natural movements, and facial expressions; ergonomic studies require faithful body proportions for a particular population segment and realistic locomotion with constraints, etc. Game engines such as Unreal Engine via metahuman and Unity by acquiring Wētā FX have enabled real-time interactions with digital humans using physically based rendering. Research Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Emotion Machine
''The Emotion Machine: Commonsense Thinking, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of the Human Mind'' is a 2006 book by cognitive scientist Marvin Minsky that elaborates and expands on Minsky's ideas as presented in his earlier book ''Society of Mind'' (1986). Minsky argues that emotions are different ways to think that our mind uses to increase our intelligence. He challenges the distinction between emotions and other kinds of thinking. His main argument is that emotions are "ways to think" for different "problem types" that exist in the world, and that the brain has rule-based mechanisms (selectors) that turn on emotions to deal with various problems. The book reviews the accomplishments of AI, why modelling an AI is difficult in terms of replicating the behaviors of humans, if and how AIs think, and in what manner they might experience struggles and pleasures. Reviews In a review for ''The Washington Post'', neurologist Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |