|
Slipped Strand Mispairing
Slipped strand mispairing (SSM), (also known as replication slippage), is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences. It is a form of mutation that leads to either a trinucleotide or dinucleotide expansion, or sometimes contraction, during DNA replication.Hartl L.D and Ruvolo M, 2012, Genetic Analysis of Genes and Genomes, Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington, pg. 529 A slippage event normally occurs when a sequence of repetitive nucleotides (tandem repeats) are found at the site of replication. Tandem repeats are unstable regions of the genome where frequent insertions and deletions of nucleotides can take place, resulting in genome rearrangements. DNA polymerase, the main enzyme to catalyze the polymerization of free deoxyribonucleotides into a newl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic Representation Of The Slippage Process At A Replication Fork
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal And Bulbar Muscular Atrophy
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder resulting in muscle cramps and progressive weakness due to degeneration of motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord and muscle wasting. The condition is associated with mutation of the androgen receptor (''AR'') gene and is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. As with many genetic disorders, no cure is known, although research continues. Because of its endocrine manifestations related to the impairment of the ''AR'' gene, patients with SBMA develop partial symptoms of androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) in addition to neuromuscular degeneration. SBMA is related to other neurodegenerative diseases caused by similar mutations, such as Huntington's disease. The prevalence of SBMA has been estimated at 2.6:100,000 males. Signs and symptoms Individuals with SBMA have muscle cramps and progressive weakness due to degeneration of motor neurons in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
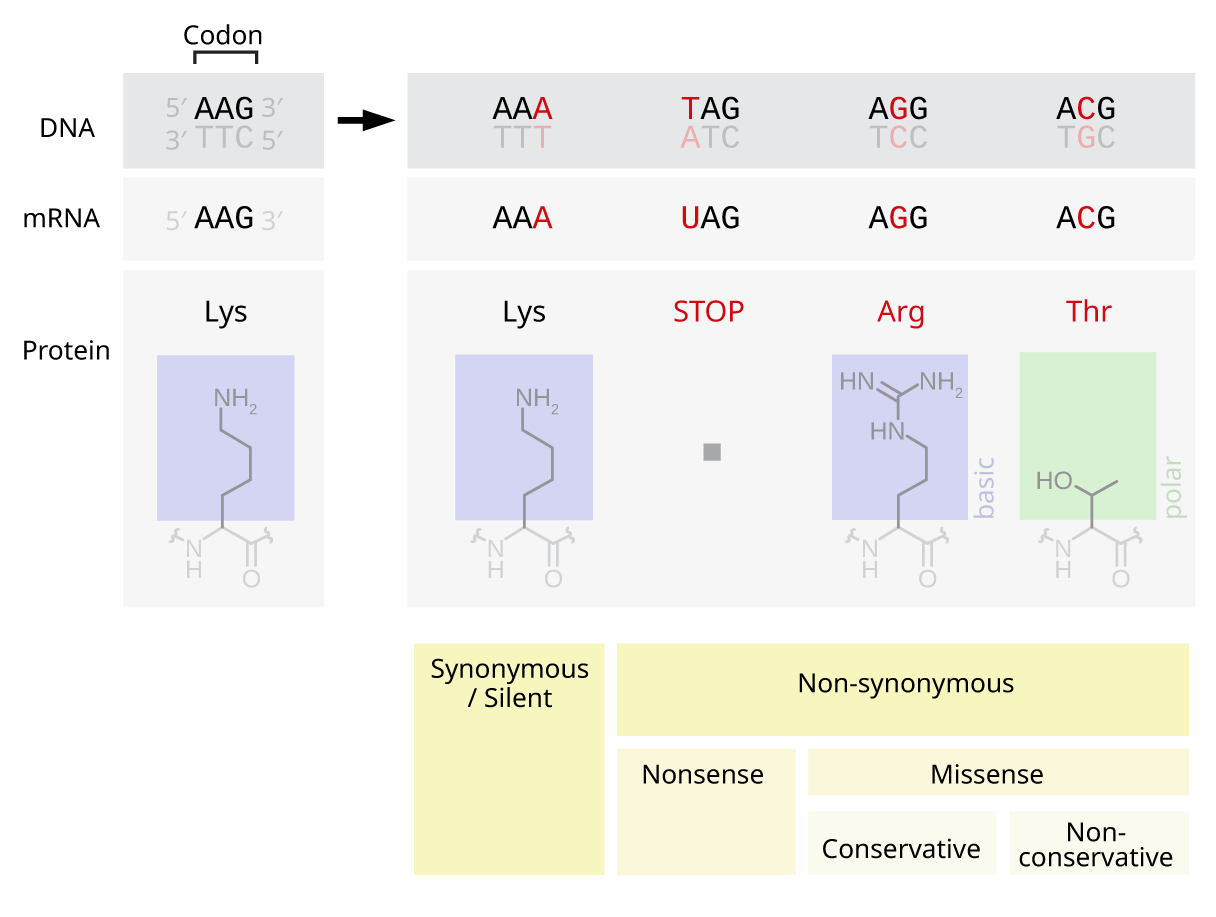
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Ataxia
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA or FA) is an autosomal-recessive genetic disease that causes difficulty walking, a loss of sensation in the arms and legs, and impaired speech that worsens over time. Symptoms generally start between 5 and 20 years of age. Many develop hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and require a mobility aid such as a cane, walker, or wheelchair in their teens. As the disease progresses, some affected people lose their sight and hearing. Other complications may include scoliosis and diabetes mellitus. The condition is caused by mutations in the ''FXN'' gene on chromosome 9, which makes a protein called frataxin. In FRDA, cells produce less frataxin. Degeneration of nerve tissue in the spinal cord causes the ataxia; particularly affected are the sensory neurons essential for directing muscle movement of the arms and legs through connections with the cerebellum. The spinal cord becomes thinner, and nerve cells lose some myelin sheath. No effective treatment is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder. Signs and symptoms Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is one of a group of genetic disorders characterized by slowly progressive incoordination of gait and is often associated with poor coordination of hands, speech, and eye movements. A review of different clinical features among SCA subtypes was recently published describing the frequency of non-cerebellar featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntington’s Disease
Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is a neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental abilities. A general lack of coordination and an unsteady gait often follow. It is also a basal ganglia disease causing a hyperkinetic movement disorder known as chorea. As the disease advances, uncoordinated, involuntary body movements of chorea become more apparent. Physical abilities gradually worsen until coordinated movement becomes difficult and the person is unable to talk. Mental abilities generally decline into dementia. The specific symptoms vary somewhat between people. Symptoms usually begin between 30 and 50 years of age but can start at any age. The disease may develop earlier in each successive generation. About eight percent of cases start before the age of 20 years, and are known as ''juvenile HD'', which typically present with the slow movement symptoms of Parkinson's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common, and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females. This disorder and finding of Fragile X syndrome has an X-linked dominant inheritance. It is typically caused by an expansion of the CGG triplet repeat within the ''FMR1'' (fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1) gene on the X chromosome. This results in silencing ( methylation) of this part of the gene and a deficiency of the resultant protein (FMRP), which is required for the normal development of connections between neurons. Diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion
A trinucleotide repeat expansion, also known as a triplet repeat expansion, is the DNA mutation responsible for causing any type of disorder categorized as a trinucleotide repeat disorder. These are labelled in dynamical genetics as dynamic mutations. Triplet expansion is caused by slippage during DNA replication, also known as "copy choice" DNA replication. Due to the repetitive nature of the DNA sequence in these regions, 'loop out' structures may form during DNA replication while maintaining complementary base pairing between the parent strand and daughter strand being synthesized. If the loop out structure is formed from the sequence on the daughter strand this will result in an increase in the number of repeats. However, if the loop out structure is formed on the parent strand, a decrease in the number of repeats occurs. It appears that expansion of these repeats is more common than reduction. Generally, the larger the expansion the more likely they are to cause disease or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem Repeat
Tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of one or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other. Several protein domains also form tandem repeats within their amino acid primary structure, such as armadillo repeats. However, in proteins, perfect tandem repeats are unlikely in most ''in vivo'' proteins, and most known repeats are in proteins which have been designed. An example would be: : ATTCG ATTCG ATTCG in which the sequence ATTCG is repeated three times. Terminology When between 10 and 60 nucleotides are repeated, it is called a minisatellite. Those with fewer are known as microsatellites or short tandem repeats. When exactly two nucleotides are repeated, it is called a ''dinucleotide repeat'' (for example: ACACACAC...). The microsatellite instability in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer most commonly affects such regions. When three nucleotides are repeated, it is called a ''trinucleotide repeat'' (for example: CAGCAGCAGCAG. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedreich's Ataxia
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA or FA) is an autosomal-recessive genetic disease that causes difficulty walking, a loss of sensation in the arms and legs, and impaired speech that worsens over time. Symptoms generally start between 5 and 20 years of age. Many develop hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and require a mobility aid such as a cane, walker, or wheelchair in their teens. As the disease progresses, some affected people lose their sight and hearing. Other complications may include scoliosis and diabetes mellitus. The condition is caused by mutations in the ''FXN'' gene on chromosome 9, which makes a protein called frataxin. In FRDA, cells produce less frataxin. Degeneration of nerve tissue in the spinal cord causes the ataxia; particularly affected are the sensory neurons essential for directing muscle movement of the arms and legs through connections with the cerebellum. The spinal cord becomes thinner, and nerve cells lose some myelin sheath. No effective treatment is kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotonic Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. In DM, muscles are often unable to relax after contraction. Other manifestations may include cataracts, intellectual disability and heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and an inability to have children. While myotonic dystrophy can occur at any age, onset is typically in the 20s and 30s. Myotonic dystrophy is caused by a genetic mutation in one of two genes. Mutation of the '' DMPK'' gene causes myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Mutation of '' CNBP'' gene causes type 2 (DM2). DM is typically inherited from a person's parents, following an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, and it generally worsens with each generation. A type of DM1 may be apparent at birth. DM2 is generally milder. Diagnosis is confirmed by genetic testing. There is no cure. Treatments may include braces or wheelchairs, pacemakers and non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


