|
Slavery In The District Of Columbia
The slave trade in the District of Columbia was legal from its creation until 1850, when the trade in enslaved people in the District was outlawed as part of the Compromise of 1850. That restrictions on slavery in the District were probably coming was a major factor in the retrocession of the Virginia part of the District back to Virginia in 1847. Thus the large slave-trading businesses in Alexandria, such as Franklin & Armfield, could continue their operations in Virginia, where slavery was more secure. Ownership of enslaved people remained legal in the District. It was not until the departure of the legislators from the seceding states that Congress could pass in 1862 the District of Columbia Compensated Emancipation Act. The Act provided partial compensation, up to $300 per slave, to slave owners. It was paid from general federal funds. Even though the compensation was small, as before the war a productive slave was worth much more than $300, it is the only place in the Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Market Of America
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is now outlawed in most countries of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Columbia
) , image_skyline = , image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, National Cathedral , image_flag = Flag of the District of Columbia.svg , image_seal = Seal of the District of Columbia.svg , nickname = D.C., The District , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive map of Washington, D.C. , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , established_title = Residence Act , established_date = 1790 , named_for = George Washington, Christopher Columbus , established_title1 = Organized , established_date1 = 1801 , established_title2 = Consolidated , established_date2 = 1871 , established_title3 = Home Rule Act , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Tenth Amendment (Amendment X) to the United States Constitution, a part of the Bill of Rights, was ratified on December 15, 1791. It expresses the principle of federalism, also known as states' rights, by stating that the federal government has only those powers delegated to it by the Constitution, and that all other powers not forbidden to the states by the Constitution are reserved to each state. The amendment was proposed by the 1st United States Congress in 1789 during its first term following the adoption of the Constitution. It was considered by many members as a prerequisite before they would ratify the Constitution, and particularly to satisfy demands of Anti-Federalists, who opposed the creation of a stronger federal government. The purpose of this amendment is to clarify how the federal government's powers should be interpreted and to reaffirm the nature of federalism. Justices and commentators have publicly wondered whether the Tenth Amendment retains any leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy. Lincoln was born into poverty in a log cabin in Kentucky and was raised on the frontier, primarily in Indiana. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Whig Party leader, Illinois state legislator, and U.S. Congressman from Illinois. In 1849, he returned to his successful law practice in central Illinois. In 1854, he was angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which opened the territories to slavery, and he re-entered politics. He soon became a leader of the new Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen A. Douglas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antebellum Period
In the history of the Southern United States, the Antebellum Period (from la, ante bellum, lit= before the war) spanned the end of the War of 1812 to the start of the American Civil War in 1861. The Antebellum South was characterized by the use of slavery and the culture it fostered. As the era proceeded, Southern intellectuals and leaders gradually shifted from portraying slavery as an embarrassing and temporary system, to a full-on defense of slavery as a positive good, and harshly criticized the budding abolitionist movement. The economy was largely plantation based, and dependent on exports. Society was stratified, inegalitarian, and perceived by immigrants as lacking in opportunities. Consequently the manufacturing base lagged behind the non-slave states. Wealth inequality grew as the larger landholders took the greater share of the profits generated by slaves, which also helped to entrench their power as a political class. As the country expanded westward, slaver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidency Of John Quincy Adams
The presidency of John Quincy Adams, began on March 4, 1825, when John Quincy Adams was inaugurated as President of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1829. Adams, the sixth United States president, took office following the 1824 presidential election, in which he and three other Democratic-Republicans—Henry Clay, William H. Crawford, and Andrew Jackson—sought the presidency. Adams was not a strong president, and he was under continuous attack from Jackson who easily defeated him in the 1828 presidential election. No candidate won a majority of Electoral College votes, and so the United States House of Representatives chose the president in a contingent election. With the help of Clay, Adams was elected by the House. Adams rewarded Clay with the prestigious role of Secretary of State. Upon taking office, Adams articulated an ambitious domestic agenda. He envisioned a national marketplace in which North and South, town and country, were tied together by trade and exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidency Of John Adams
The presidency of John Adams, began on March 4, 1797, when John Adams was inaugurated as the second president of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1801. Adams, who had served as vice president under George Washington, took office as president after winning the 1796 presidential election. The only member of the Federalist Party to ever serve as president, his presidency ended after a single term following his defeat in the 1800 presidential election. He was succeeded by Thomas Jefferson of the Democratic-Republican Party. When Adams entered office, the ongoing major European war between France and Great Britain was causing great difficulties for American merchants on the high seas and arousing intense partisanship among contending political parties nationwide. Attempts to negotiate with the French led to the XYZ Affair, in which French officials demanded bribes before they would assent to the beginning of negotiations. The XYZ Affair outraged the American public, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. The term "White House" is often used as a metonym for the president and his advisers. The residence was designed by Irish-born architect James Hoban in the neoclassical style. Hoban modelled the building on Leinster House in Dublin, a building which today houses the Oireachtas, the Irish legislature. Construction took place between 1792 and 1800, using Aquia Creek sandstone painted white. When Thomas Jefferson moved into the house in 1801, he (with architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe) added low colonnades on each wing that concealed stables and storage. In 1814, during the War of 1812, the mansion was set ablaze by British forces in the Burning of Washington, destroying the interior and charring much of the exterior. Reconstruction began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In Maryland
Slavery in Maryland lasted over 200 years, from its beginnings in 1642 when the first Africans were brought as slaves to St. Mary's City, to its end after the Civil War. While Maryland developed similarly to neighboring Virginia, slavery declined here as an institution earlier, and it had the largest free black population by 1860 of any state. The early settlements and population centers of the province tended to cluster around the rivers and other waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay. Maryland planters cultivated tobacco as the chief commodity crop, as the market was strong in Europe. Tobacco was labor-intensive in both cultivation and processing, and planters struggled to manage workers as tobacco prices declined in the late 17th century, even as farms became larger and more efficient. At first, indentured servants from England supplied much of the necessary labor but, as their economy improved at home, fewer made passage to the colonies. Maryland colonists turned to impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
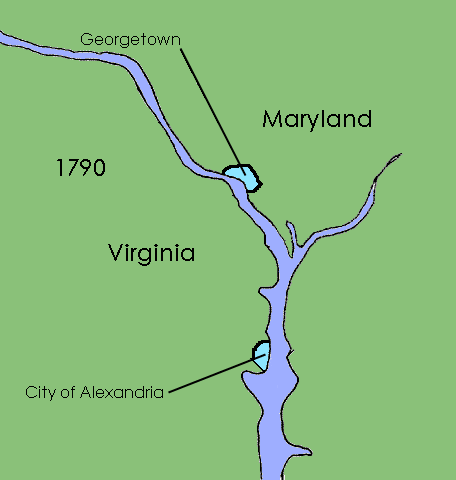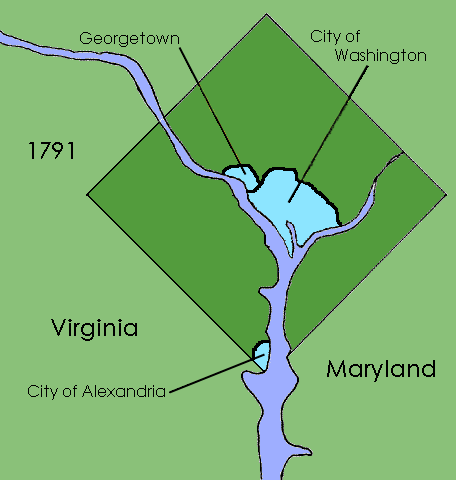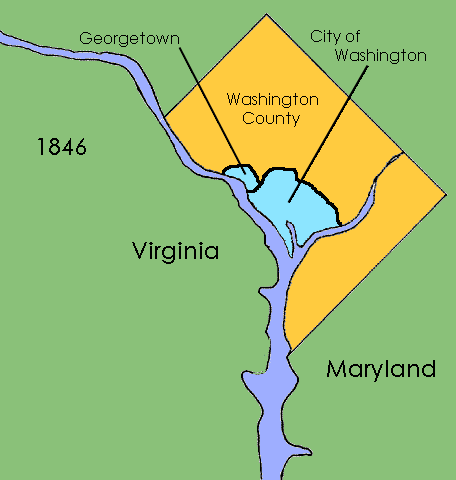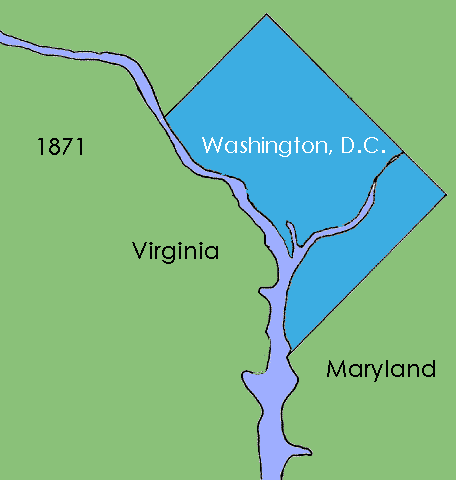
District Of Columbia (until 1871)
The District of Columbia was created in 1801 as the federal district of the United States, with territory previously held by the states of Maryland and Virginia ceded to the federal government of the United States for the purpose of creating its federal district, which would encompass the new national capital of the United States, the City of Washington. The district came into existence, with its own judges and marshals, through the District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801; previously it was the Territory of Columbia. According to specific language in the U.S. Constitution, it was 100 square miles (259 km2). The district encompassed three small cities: Alexandria, formerly in Virginia, Georgetown, formerly Maryland, and the deliberately planned central core, the City of Washington. Both the White House and the United States Capitol were already completed and in use by 1800 as called for by the 1791 L'Enfant Plan for the City of Washington, although the city was not formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table (parliamentary Procedure)
In parliamentary procedure, the verb to table has the opposite meaning in the United States from that of the rest of the world: *In the United States, to "table" usually means to postpone or suspend consideration of a pending motion. *In the rest of the English-speaking world, to "table" means to begin consideration (or reconsideration) of a proposal. Motions which use the word "table" have specific meanings and functions, depending on the parliamentary authority used. The meaning of "table" also depends on the context in which it is used. Difference between American and British usage Both the American and the British dialects have the expression "to table a topic" as a short way of saying "to lay a topic on the table" and "to make a topic lie on the table", but these have opposite meanings in the different varieties of the languages. The British meaning is based on the idea of parliamentarians gathering around a table with the bill laid upon so that all may point to sections for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gag Rule
A gag rule is a rule that limits or forbids the raising, consideration, or discussion of a particular topic, often but not always by members of a legislative or decision-making body. A famous example of gag rules is the series of rules concerning the discussion of slavery in effect in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1836 to 1844. By country England A gag rule may be formally neutral, that is, forbidding discussions or arguments either for or against a particular policy. For example, William Laud, the Archbishop of Canterbury during the reign of King Charles I of England:forbade ministers to discuss the sublime mysteries associated with Calvin's doctrine of predestination. They could not preach it, nor could they preach against it. They could not mention it at all ... For Laud, what was at stake was not so much the promotion of his own theological opinions as the suppression of the furor theologicus that had caused so much devastation in England and throughout Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |