|
Skookum
Skookum is a Chinook Jargon word that has historical use in the Pacific Northwest. It has a range of meanings, commonly associated with an English translation of "strong" or "monstrous". The word can mean "strong", "greatest", "powerful", "ultimate", or "brave". Something can be ''skookum'', meaning "strong" or "monstrously significant". When used in reference to another person, ''e.g.'', "he's skookum", it conveys connotations of reliability or a monstrous nature, as well as strength, size or hard-working. Derivative words ''Skookum house'' means 'jail' or 'prison' (cf. the English euphemism ''the big house'', but here meaning 'strong house'). ''Skookum tumtum'', lit. "strong heart", is generally translated as 'brave' or possibly 'good-hearted'. In the Chinook language, ''skookum'' is a verb auxiliary, used similarly to ''can'' or ''to be able''. Another compound, though fallen out of use in modern British Columbia English, is ''skookum lacasset'' or 'strongbox'. ''Skookumchuck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keish
Keish ( – July 11, 1916), also known as James Mason and by the nickname Skookum Jim Mason, was a member of the Tagish First Nation in what became the Yukon Territory of Canada. He was born near Bennett Lake on what is now the British Columbia and Yukon border. He lived in Caribou Crossing, now Carcross, Yukon, Canada. Childhood Keish was born around 1855 near Lake Bennett into the Daḵl'aweidi clan of Tagish. His mother, Gus'duteen, was from Tahltan country around Telegraph Creek while his father was Kaachgaawáa, chief of the Tagish Deisheetaan. His family was involved in trade between the coastal Tlingit and the inland Tagish. The family had two sons and six daughters who reached adulthood. The name ''Keish'' is a Tagish word meaning "wolf". Packing career In the mid-1880s, Keish worked the summers as a packer, carrying supplies from the Alaska Coast, over the passes to the Yukon River system. He earned his ''Skookum'' nickname because of his extraordinary stren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skookumchuck
Skookumchuck () is a Chinook Jargon term that is in common use in British Columbia English and occurs in Pacific Northwest English. ''Skookum'' means "strong" or "powerful", and "chuck" means water, so ''skookumchuck'' means "rapids" or "whitewater" (literally, "strong water"), or fresh, healthy water. It can mean any rapids, but in coastal usage refers to the powerful tidal rapids at the mouths of most of the major coastal inlets. Places named ''Skookumchuck'' include: *Skookumchuck, British Columbia, a town in British Columbia named for the large rapids in this area on the Kootenay River. *Skookumchuck Hot Springs, British Columbia, a town in British Columbia *Skookumchuck Narrows, a narrow entrance passage into Sechelt Inlet, a fjord in British Columbia's Sunshine Coast *Skookumchuck Narrows Provincial Park, a park located at the narrows *Skookumchuck Rapids Provincial Park, a park near Mabel Lake, British Columbia *Skookumchuck River, a river in southwestern Washington * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skookum Doll
A Skookum doll was a Native American themed doll, sold as a souvenir item in the early 20th century. Although considered collectible, they are not authentic Native American dolls, as they were designed and created by a white woman, and quickly mass-produced. History Mary Dwyer McAboy (1876-1961), who was from Missoula, Montana, learned to carve apple head dolls as a child from her mother. According to an account by McAboy, her mother had sold apple dolls at church socials and sewing circles. Mary Dwyer had worked as a schoolteacher before marrying Frank E. McAboy in 1909. Her husband died of tuberculosis four years later, in 1913. Later that year, Mary McAboy began to market apple head dolls dressed in Indian costumes, and achieved rapid commercial success. According to McAboy, her career as a doll maker began when she made an Indian village which she displayed in the window of a grocery store. Vaudeville actress Fritzi Scheff was performing in Missoula at the time, saw the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
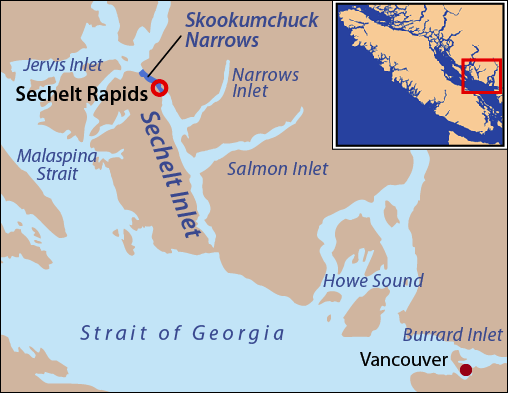
Skookumchuck Narrows
Skookumchuck Narrows is a strait forming the entrance of Sechelt Inlet on British Columbia's Sunshine Coast in Canada. Before broadening into Sechelt Inlet, all of its tidal flow together with that of Salmon Inlet and Narrows Inlet must pass through Sechelt Rapids. At peak flows, standing waves, whitecaps, and whirlpools form at the rapids even in calm weather. The narrows are also the site of Skookumchuck Narrows Provincial Park. Each day, tides force large amounts of seawater through the narrows— of water on a tide. The difference in water levels on either side of the rapids can exceed in height. Current speeds can exceed ,Skookumchuck Narrows Provincial Park BCParks up to . It is sometimes claimed to be the fastest tidal rapids in the world. The tidal patterns keep the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, and Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The variety of definitions can be attributed to partially overlapping commonalities of the region's history, culture, geography, society, ecosystems, and other factors. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Skook Davidson
Mount Skook Davidson, , is a mountain in the Kechika Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains in far northern British Columbia, Canada. It overlooks the "Diamond J Ranch", which was founded by John Ogilvie Davidson also known as "Skook" Davidson or "Skookum" Davidson because of his stature (big and strong, see skookum). Davidson was a notable local pioneer who worked as a land surveyor before taking up packing, guiding, and ranching in this area. He helped discover and select the route for the Alaska Highway.''The Newspapering Murrays'', Georgina Keddell'' See also * List of Chinook Jargon placenames Prominence Its topographic prominence In topography, prominence (also referred to as autonomous height, relative height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop or relative height in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contou ... is 1361m above its col at Denetiah Lake. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Skook Davidson Two-thousanders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Skook Jim
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England * Mounts, Indiana, a community in Gibson County, Indiana, United States People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kechika River
The Kechika River is a tributary of the Liard River, about long, in northern British Columbia, Canada. The Kechika flows generally northwest through the northernmost section of the Rocky Mountain Trench before turning east to join the Liard, a major branch of the Mackenzie River system. The river's drainage basin is characterized by high glaciated peaks, boreal forest, and open tundra. With no settlements, roads or dams along its course, the Kechika is considered "one of British Columbia's finest examples of wilderness and undisturbed wildlife habitat." Inhabited for thousands of years by the Kaska Dena, the Kechika was explored by fur traders in the 1800s and was one of the routes to gold strikes in the Yukon. The difficulty of accessing the remote Kechika country made it an unappealing location for European settlement. Today, the Kechika River basin includes a number of large parks and protected areas, most of which are administered under the umbrella of the Muskwa-Kechika ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gataga River
The Gataga River is a river in the Northern Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is a tributary of the Kechika River The Kechika River is a tributary of the Liard River, about long, in northern British Columbia, Canada. The Kechika flows generally northwest through the northernmost section of the Rocky Mountain Trench before turning east to join the Liard, a ..., which is a tributary of the Liard. References Rivers of British Columbia Northern Interior of British Columbia Rivers of the Canadian Rockies Cassiar Land District {{BritishColumbiaInterior-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stein River
The Stein River is a tributary of the Fraser River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The name is derived from the Nlaka'pamux word Stagyn, meaning "hidden place", referring to the fact that the size and extent of the Stein River valley is not very noticeable from the river's confluence with the Fraser. It is one of only 2 unlogged watersheds with an area greater than 50 km south of Prince George, BC Prince George is the largest city in northern British Columbia, Canada, with a population of 74,004 in the metropolitan area. It is often called the province's "northern capital" or sometimes the "spruce capital" because it is the hub city for .... Course The Stein River and its tributaries are contained in Stein Valley Nlaka'pamux Heritage Park. The river originates in remote Tundra Lake and flows generally east, joining the Fraser River north of Lytton. See also * List of British Columbia rivers References Tributaries of the Fraser River Fraser Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lillooet Ranges
The Lillooet Ranges are the southeasternmost subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of British Columbia. They are located between the drainage of the Lillooet River and Harrison Lake on the west and the canyon of the Fraser River on the east, and by the lowland coastal valley of that river on the south. The Lillooet Ranges are approximately 8100 square kilometres (3150 mi²) in area. The range is extremely rugged and varied in terrain, and includes some of the highest peaks in southwestern British Columbia. The highest is Skihist Mountain, , crowning the Cantilever Range in the heart of the area to the west of the community of Lytton at the confluence of the Thompson and Fraser Rivers. The northernmost subdivision of the Lillooet Ranges is the Cayoosh Range, which includes the second-highest summit in the Lillooet Ranges, an unnamed peak just south of Seton Lake and about WSW of the town of Lillooet. To the northeast of Harrison Lake, Mount Breakenri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |