|
Skills-based Routing
Skills-based routing (SBR), or skills-based call routing, is a call-assignment strategy used in call centres to assign incoming calls to the most suitable agent, instead of simply choosing the next available agent. It is an enhancement to the automatic call distributor (ACD) systems found in most call centres. The need for skills-based routing has arisen as call centres have become larger and dealt with a wider variety of call types. In the past, agents answering calls were generally able to be assigned to only one queue taking one type of call. This meant that agents who could deal with a range of call types had to be manually reassigned to different queue at different times of the day to make the best use of their skills, or face being exposed to a wide variety of calls for which they were not trained. With skills-based routing, the skills needed for a particular call are often assessed by the dialled telephone number and the calling number or caller's identity, as well as choices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
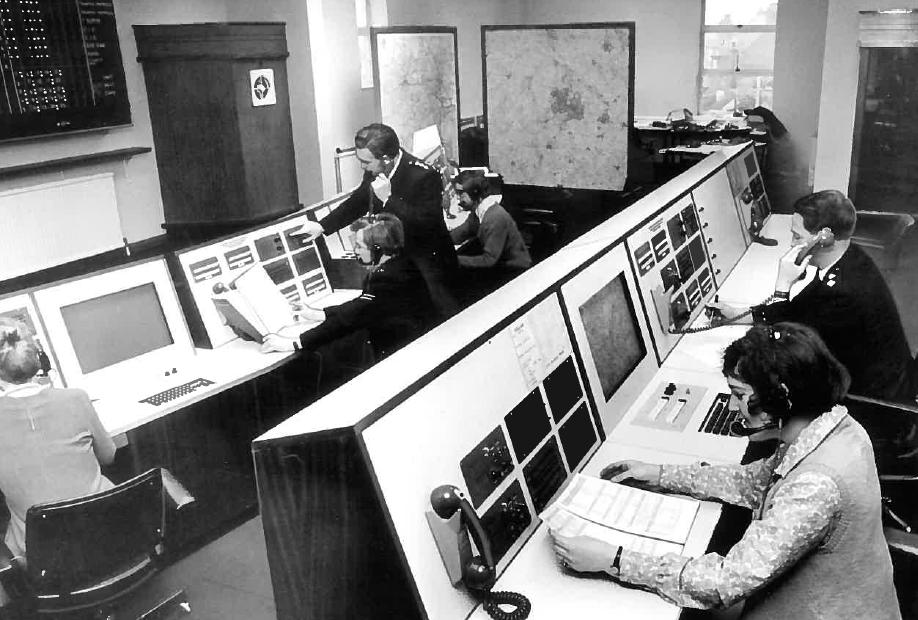
Call Center
A call centre ( Commonwealth spelling) or call center ( American spelling; see spelling differences) is a managed capability that can be centralised or remote that is used for receiving or transmitting a large volume of enquiries by telephone. An inbound call centre is operated by a company to administer incoming product or service support or information enquiries from consumers. Outbound call centres are usually operated for sales purposes such as telemarketing, for solicitation of charitable or political donations, debt collection, market research, emergency notifications, and urgent/critical needs blood banks. A contact centre is a further extension to call centres telephony based capabilities, administers centralised handling of individual communications, including letters, faxes, live support software, social media, instant message, and email. A call center was previously seen to be an open workspace for call center agents, with workstations that include a compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Call Distributor
An automated call distribution system, commonly known as automatic call distributor (ACD), is a telephony device that answers and distributes incoming calls to a specific group of terminals or agents within an organization. ACDs direct calls based on parameters that may include the caller's telephone number, the number they dialed, the time of day or a response to an automated voice prompt. Advanced ACD systems may use digital technologies such as Computer telephony integration (CTI), computer-supported telecommunications applications (CSTA) or IVR as input to determine the route to a person or voice announcement that will serve the caller. Experts claim that "the invention of ACD technology made the concept of a call centre possible." Background A Private Branch Exchange (PBX) is a telephone exchange device that acts as a switchboard to route phone calls within an organisation. This technology developed into Automated Call Distribution systems using computer technology to auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
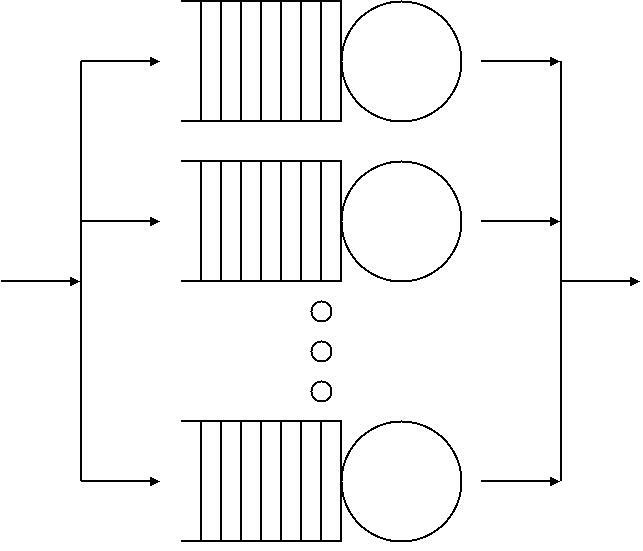
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang when he created models to describe the system of Copenhagen Telephone Exchange company, a Danish company. The ideas have since seen applications including telecommunication, traffic engineering, computing and, particularly in industrial engineering, in the design of factories, shops, offices and hospitals, as well as in project management. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is ''Queueing Systems''. Single queueing nodes A queue, or queueing no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operations Research
Operations research ( en-GB, operational research) (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a discipline that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve decision-making. It is considered to be a subfield of mathematical sciences. The term management science is occasionally used as a synonym. Employing techniques from other mathematical sciences, such as modeling, statistics, and optimization, operations research arrives at optimal or near-optimal solutions to decision-making problems. Because of its emphasis on practical applications, operations research has overlap with many other disciplines, notably industrial engineering. Operations research is often concerned with determining the extreme values of some real-world objective: the maximum (of profit, performance, or yield) or minimum (of loss, risk, or cost). Originating in military efforts before World War II, its techniques have gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlang-C
The Erlang distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support x \in exponential distribution">exponential variables with mean 1/\lambda each. Equivalently, it is the distribution of the time until the ''k''th event of a Poisson process with a rate of \lambda. The Erlang and Poisson distributions are complementary, in that while the Poisson distribution counts the number of events that occur in a fixed amount of time, the Erlang distribution counts the amount of time until the occurrence of a fixed number of events. When k=1, the distribution simplifies to the exponential distribution. The Erlang distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution wherein the shape of the distribution is discretised. The Erlang distribution was developed by Agner Krarup Erlang, A. K. Erlang to examine the number of telephone calls which might be made at the same time to the operators of the switching stations. This work on telephone Teletraffic en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |