|
Skid (automobile)
An automobile skid is an automobile handling condition where one or more tires are slipping relative to the road, and the overall handling of the vehicle has been affected. Subtypes of skid include: * fishtailing, where the vehicle yaws back and forth across the direction of motion. * ''spin'' or ''spinout'' where a vehicle rotates in one direction during the skid. * understeer and oversteer where front or rear wheels lose traction during cornering, causing a vehicle to follow a larger or smaller turning radius. * ''burnout'' where a vehicle slips or spins its tires during acceleration. * skidding during braking (with or without directional or yaw changes). __TOC__ Slip and skid Tire slip, and related slip angle (angle of motion relative to tire), describe the performance of an individual tire. Important concepts about slip and skid include circle of forces or circle of traction, and cornering force. To a first approximation, the tire can withstand approximately the same absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automobile Handling
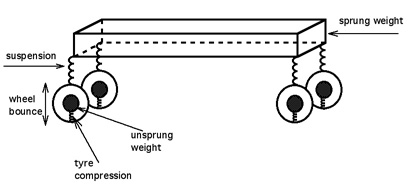
Automobile handling and vehicle handling are descriptions of the way a wheeled vehicle responds and reacts to the inputs of a driver, as well as how it moves along a track or road. It is commonly judged by how a vehicle performs particularly during cornering, acceleration, and braking as well as on the vehicle's directional stability when moving in steady state condition. In the automotive industry, handling and braking are the major components of a vehicle's "active" safety, as well as its ability to perform in auto racing. The maximum lateral acceleration is sometimes discussed separately as "road holding". (This discussion is directed at road vehicles with at least three wheels, but some of it may apply to other ground vehicles). Automobiles driven on public roads whose engineering requirements emphasize handling over comfort and passenger space are named sports cars. Factors that affect a car's handling Weight distribution Centre of mass height The centre of mass hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag Racing
Drag racing is a type of motor racing in which automobiles or motorcycles compete, usually two at a time, to be first to cross a set finish line. The race follows a short, straight course from a standing start over a measured distance, most commonly , with a shorter, distance becoming increasingly popular, as it has become the standard for Top Fuel dragsters and Funny Cars, where some major bracket races and other sanctioning bodies have adopted it as the standard. The is also popular in some circles. Electronic timing and speed sensing systems have been used to record race results since the 1960s. The history of automobiles and motorcycles being used for drag racing is nearly as long as the history of motorized vehicles themselves, and has taken the form of both illegal street racing and as a regulated motorsport. History Drag racing started in the 1940s. World War II veterans were prominently involved, and some early drag races were done at decommissioned aircraft b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Slipperiness
Road slipperiness is a condition of low skid resistance due to insufficient road friction. It is a result of snow, ice, water, loose material and the texture of the road surface on the traction produced by the wheels of a vehicle. Road slipperiness can be measured either in terms of the friction between a freely-spinning wheel and the ground, or the braking distance of a braking vehicle, and is related to the coefficient of friction between the tyre and the road surface. Public works agencies spend a sizeable portion of their budget measuring and reducing road slipperiness. Even a small increase in slipperiness of a section of road can increase the accident rate of the section of road tenfold. Maintenance activities affecting slipperiness include drainage repair, snow removal and street sweeping. More intensive measures may include grinding or milling a surface that has worn smooth, a surface treatment such as a chipseal, or overlaying a new layer of asphalt. A specific road s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directional Stability
Directional stability is stability of a moving body or vehicle about an axis which is perpendicular to its direction of motion. Stability of a vehicle concerns itself with the tendency of a vehicle to return to its original direction in relation to the oncoming medium (water, air, road surface, etc.) when disturbed (rotated) away from that original direction. If a vehicle is directionally stable, a restoring moment is produced which is in a direction ''opposite'' to the rotational disturbance. This "pushes" the vehicle (in rotation) so as to return it to the original orientation, thus tending to keep the vehicle oriented in the original direction. Directional stability is frequently called "weather vaning" because a directionally stable vehicle free to rotate about its center of mass is similar to a weather vane rotating about its (vertical) pivot. With the exception of spacecraft, vehicles generally have a recognisable front and rear and are designed so that the front points ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braking Distance
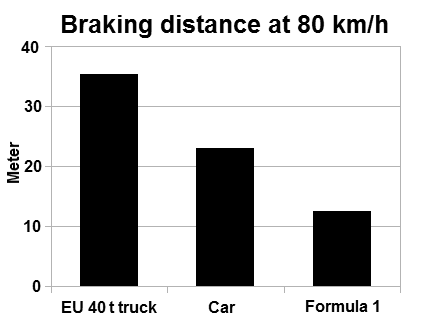
Braking distance refers to the distance a vehicle will travel from the point when its brakes are fully applied to when it comes to a complete stop. It is primarily affected by the original speed of the vehicle and the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road surface, and negligibly by the tires' rolling resistance and vehicle's air drag. The type of brake system in use only affects trucks and large mass vehicles, which cannot supply enough force to match the static frictional force. The braking distance is one of two principal components of the total stopping distance. The other component is the reaction distance, which is the product of the speed and the perception-reaction time of the driver/rider. A perception-reaction time of 1.5 seconds, and a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.7 are standard for the purpose of determining a bare baseline for accident reconstruction and judicial notice; most people can stop slightly sooner under ideal conditions. Braking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-lock Brake
An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a safety anti-skid braking system used on aircraft and on land vehicles, such as cars, motorcycles, trucks, and buses. ABS operates by preventing the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining tractive contact with the road surface and allowing the driver to maintain more control over the vehicle. ABS is an automated system that uses the principles of threshold braking and cadence braking, techniques which were once practiced by skillful drivers before ABS was widespread. ABS operates at a much faster rate and more effectively than most drivers could manage. Although ABS generally offers improved vehicle control and decreases stopping distances on dry and some slippery surfaces, on loose gravel or snow-covered surfaces ABS may significantly increase braking distance, while still improving steering control. Since ABS was introduced in production vehicles, such systems have become increasingly sophisticated and effective. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Stability Control
Electronic stability control (ESC), also referred to as electronic stability program (ESP) or dynamic stability control (DSC), is a computerized technology that improves a vehicle's stability by detecting and reducing loss of traction ( skidding). When ESC detects loss of steering control, it automatically applies the brakes to help steer the vehicle where the driver intends to go. Braking is automatically applied to wheels individually, such as the outer front wheel to counter oversteer, or the inner rear wheel to counter understeer. Some ESC systems also reduce engine power until control is regained. ESC does not improve a vehicle's cornering performance; instead, it helps reduce the chance of the driver losing control of the vehicle. According to the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety in 2004 and 2006 respectively, one-third of fatal accidents could be prevented by the use of the technology. In Europe the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slip (vehicle Dynamics)
In (automotive) vehicle dynamics, slip is the relative motion between a tire and the road surface it is moving on. This slip can be generated either by the tire's rotational speed being greater or less than the free-rolling speed (usually described as ''percent'' slip), or by the tire's plane of rotation being at an angle to its direction of motion (referred to as slip angle). In rail vehicle dynamics, this overall slip of the wheel relative to the rail is called ''creepage''. It is distinguished from the local sliding velocity of surface particles of wheel and rail, which is called ''micro-slip''. Longitudinal slip The longitudinal slip is generally given as a percentage of the difference between the surface speed of the wheel compared to the speed between axle and road surface, as: : \text=-\frac where \Omega is the longitudinal component of the rotational speed of the wheel, r is wheel radius at the point of contact and v_x is vehicle speed in the plane of the tire. A positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence Braking
Cadence braking or stutter braking is a driving technique that involves pumping the brake pedal and is used to allow a car to both steer and brake on a slippery surface. It is used to effect an emergency stop where traction is limited to reduce the effect of skidding from road wheels locking up under braking. This can be a particular problem when different tires have different traction, such as on patchy ice for example. Its use in an emergency requires a presence of mind that the situation itself might preclude. Cadence braking is supposed to maximize the time for the driver to steer around the obstacle ahead, as it allows the driver to steer while slowing. It needs to be learned and practiced. For most drivers of modern cars, it has been entirely superseded by ABS, however it is still a valuable skill for drivers of non-ABS equipped vehicles such as classic cars. Maximum braking force is obtained when there is approximately 10–20% slippage between the braked wheel's rotational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Braking
Threshold braking or limit braking is a driving technique most commonly used in motor racing, but also practiced in road vehicles to slow a vehicle at the maximum rate using the brakes. The technique involves the driver controlling the brake pedal (or lever) pressure to maximize the braking force developed by the tires. The optimal amount of braking force is developed at the point when the wheel just begins to slip. Kinetic and static friction Braking beyond the slipping point causes the tire to slide and the frictional adhesion between the tire and driving surface is reduced. The aim of threshold braking is to keep the amount of tire slip at the optimal amount, the value that produces the maximum frictional, and thus braking force. When wheels are slipping significantly (kinetic friction), the amount of friction available for braking is typically substantially less than when the wheels are not slipping (static friction), thereby reducing the braking force and eliminating steering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoon
A hoon is an Australian term describing a person who deliberately drives a vehicle in a reckless or dangerous manner, generally in order to provoke a reaction from onlookers. Hoon activities (or hooning) can include speeding, burnouts, doughnuts, or screeching tyres. Those commonly identified as being involved in hooning are young and predominantly male drivers in the age range of 17 to 25 years. Hoon control laws are beginning to be extended to dangerous hoon behaviour using boats and other vessels, particularly jet skis. The Australian state of Victoria passed legislation in late 2009 to control hoon activities using recreational vessels. Etymology At the turn of the 20th century in Australia, the term ''hoon'' (and its rhyming slang version "silver spoon") had a different meaning: one who lived off immoral earnings (i.e., the proceeds of prostitution, as a pimp or procurer of prostitutes). Linguist Sid Baker in his book ''The Australian Language'' suggested that ''hoon' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnout (vehicle)
A burnout (also known as a peel out, power brake, or brakestand) is the practice of keeping a vehicle stationary and spinning its wheels, the resultant friction causing the tires to heat up and smoke. History The origins of burnouts can be traced to drag racing, where they have a practical purpose: drag racing slicks perform better at higher temperatures, and a burnout is the quickest way to raise tire temperature immediately prior to a race. They also clean the tire of any debris and lay down a layer of rubber by the starting line for better traction. Drag race tracks sometimes use a specially-reserved wet-surface area known as the "water box", because water is poured onto a certain area to reduce the friction to initiate the burnout. This was once called a "bleach box", when bleach was used instead of water; this began in 1969, the year the first burnout was done in NHRA, at the Hot Rod Magazine Championship Drag Races in Riverside, California. Don Garlits was the first to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |