|
Ship Tracks
Ship tracks are clouds that form around the exhaust released by ships into the still ocean air. Water molecules collect around the tiny particles (aerosols) from exhaust to form a cloud seed. More and more water accumulates on the seed until a visible cloud is formed. In the case of ship tracks, the cloud seeds are stretched over a long narrow path where the wind has blown the ship's exhaust, so the resulting clouds resemble long strings over the ocean. Ship tracks are a type of homogenitus cloud. Ship tracks study In 1965, the first "anomalous cloud lines" were observed in images from the TIROS VII satellite. It was hypothesized that the most likely cause was from the exhaust from ships. Many studies since have confirmed the cause, and they are now referred to as ship tracks. Scientists soon realized that the climatic impacts from aerosols could have a large effect on climate through the Twomey effect, and that ship tracks provided an excellent laboratory for their studies. Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be transient (such as when a multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see Convection cell). The convection may be due to gravitational, electromagnetic or fictitious body forces. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics. Convection is often categorised or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
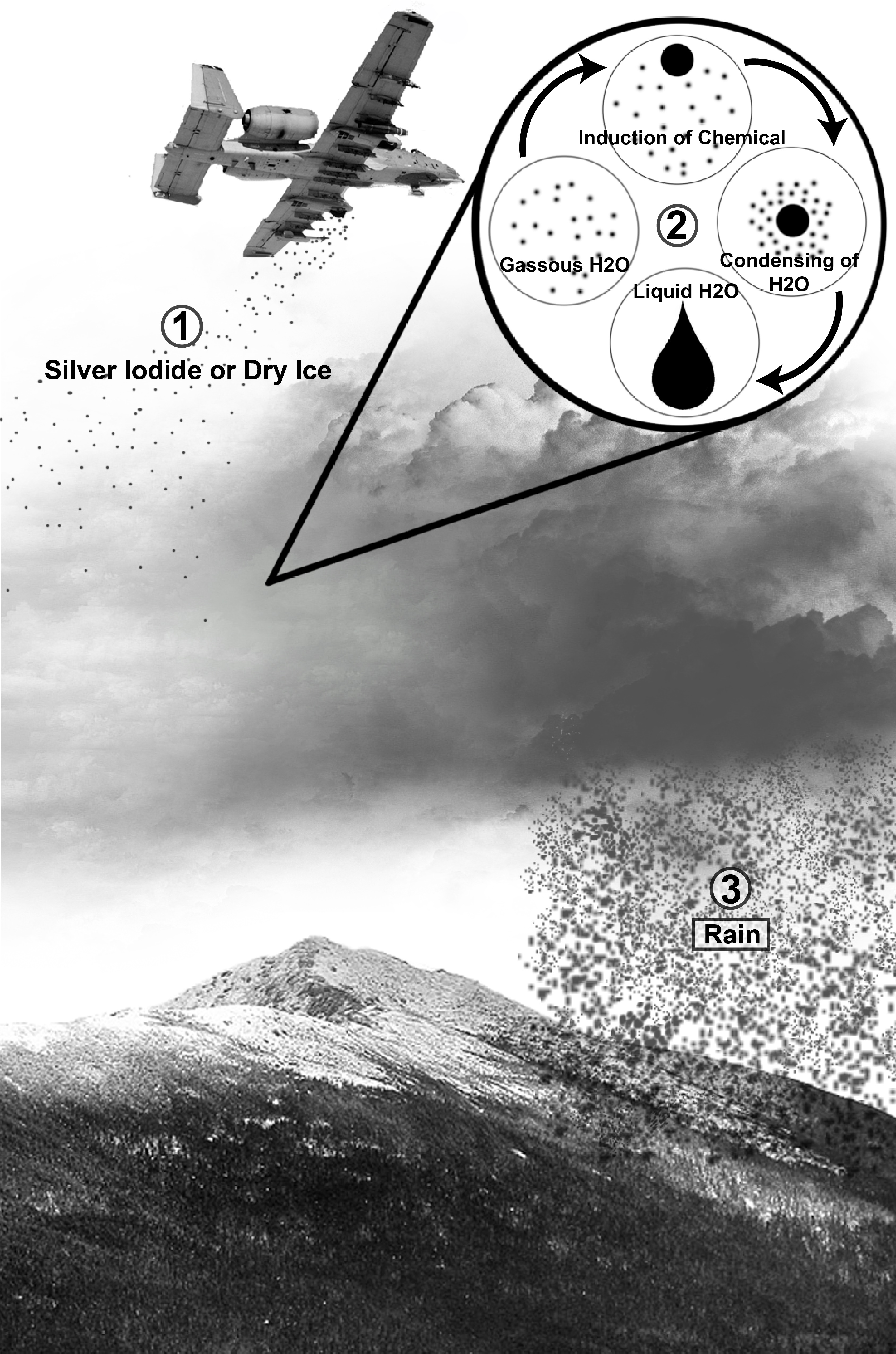
Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud. Its effectiveness is debated; some studies have suggested that it is "difficult to show clearly that cloud seeding has a very large effect." The usual objective is to increase precipitation (rain or snow), either for its own sake or to prevent precipitation from occurring in days afterward. Methodologies Salts The most common chemicals used for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide and dry ice (solid carbon dioxide). Liquid propane, which expands into a gas, has also been used. This can produce ice crystals at higher temperatures than silver iodide. After promising research, the use of hygroscopic materials, such as table salt, is becoming more popular. When cloud seeding, increased snowfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While the activation energy must be overcome to initiate combustion (e.g., using a lit match to light a fire), the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. Combustion is often a complicated sequence of elementary radical reactions. Solid fuels, such as wood and coal, first undergo endothermic pyrolysis to produce gaseous fuels whose combustion then supplies the heat required to produce more of them. Combustion is often hot enough that incandescent light in the form of either glowing or a flame is produced. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers. Moisture that is lifted or otherwise forced to rise over a layer of sub-freezing air at the surface may be condense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral molecular geometry of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smokestack
A chimney is an architectural ventilation structure made of masonry, clay or metal that isolates hot toxic exhaust gases or smoke produced by a boiler, stove, furnace, incinerator, or fireplace from human living areas. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the stack, or chimney effect. The space inside a chimney is called the ''flue''. Chimneys are adjacent to large industrial refineries, fossil fuel combustion facilities or part of buildings, steam locomotives and ships. In the United States, the term ''smokestack industry'' refers to the environmental impacts of burning fossil fuels by industrial society, including the electric industry during its earliest history. The term ''smokestack'' (colloquially, ''stack'') is also used when referring to locomotive chimneys or ship chimneys, and the term ''funnel'' can also be used. The height of a chim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other planets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |