|
Shahs Of Shirwan
''Shirvanshah'' ( fa, شروانشاه), also spelled as ''Shīrwān Shāh'' or ''Sharwān Shāh'', was the title of the rulers of Shirvan from the mid-9th century to the early 16th century. The title remained in a single family, the Yazidids, an originally Arab but speedily Persianized dynasty, although the later ''Shirvanshahs'' are also known as the Kasranids or Kaqanids.Barthold, W., C.E. Bosworth "Shirwan Shah, Sharwan Shah. "Encyclopaedia of Islam. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianquis, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2nd edition The Shirvanshah established a native state in Shirvan (located in modern Azerbaijan). The Shirvanshahs dynasty, existing as independent or a vassal state, from 861 until 1538; one of longest existing dynasties in the Islamic world, are known for their support of culture. There were two periods of an independent and strong Shirvan state: first in the 12th century, under kings Manuchehr and his son, Akhsitan I who built the stro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirvan Gerb
Shirvan (from fa, شروان, translit=Shirvān; az, Şirvan; Tat language (Caucasus), Tat: ''Şirvan''), also spelled as Sharvān, Shirwan, Shervan, Sherwan and Šervān, is a historical region, historical Iranian region in the eastern Caucasus, known by this name in both pre-Islamic Sasanian Empire, Sasanian and Islamic times. Today, the region is an industrially and agriculturally developed part of the Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan Republic that stretches between the western shores of the Caspian Sea and the Kura (river), Kura River, centered on the Shirvan Plain. History Etymology Vladimir Minorsky believes that names such as Sharvān (Shirwān), Lāyzān and Baylaqān are Iranian names from the Iranian languages of the coast of the Caspian Sea. There are several explanations about this name: * Shirvan or Sharvan are changed forms of the word "Shahrbān" ( fa, شهربان, links=no) which means "the governor". The word "Shahrban" has been used since Achaemenian Dynasty as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the Sasanian dynasty, House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived List of monarchs of Persia, Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
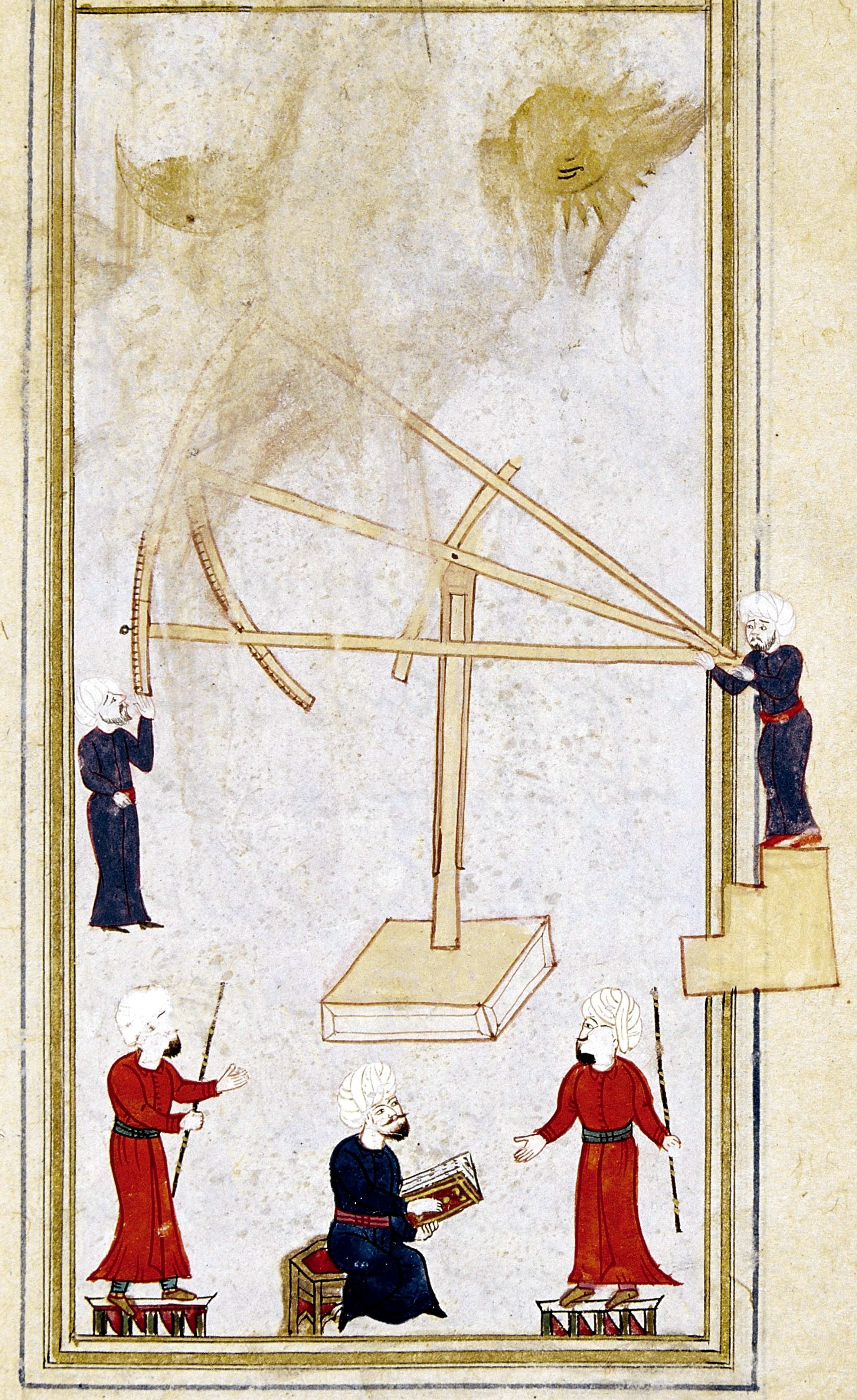
Munejjim-bashi Ahmed Dede
Ahmed Lütfullah (early 17th century – 27 February 1702), better known by his court title of Münejjim Bashi ( tr, Müneccimbaşı; "Chief Astrologer"), was an Ottoman courtier, scholar, Sufi poet and historian. His chief work is the ''Jamiʿ al-Duwal'', a world history particularly valuable for the history of the medieval Muslim dynasties of the regions around the southwestern shore of the Caspian Sea ( Adharbayjan, Shirvan, Arran, Derbent). In Turkish literature, he is referred to also as Ahmed Lütfullah. Biography His father Lütfullah was a native of Ereğli, Konya, but Ahmed was born in Salonica sometime in the first half of the 17th century (in 1631 according to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'').. He was educated at the Mevlevi dervish lodge in the quarter of Kasımpaşa, spending 15 years there under the supervision of Sheikh Halil Dede. After studies on astronomy and astrology, he advanced to the position of chief court astrologer ('' müneccimbaşi'') in 1667/8. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbent
Derbent (russian: Дербе́нт; lez, Кьвевар, Цал; az, Дәрбәнд, italic=no, Dərbənd; av, Дербенд; fa, دربند), formerly romanized as Derbend, is a city in Dagestan, Russia, located on the Caspian Sea. It is the southernmost city in Russia, and it is the second-most important city of Dagestan. Derbent occupies the narrow gateway between the Caspian Sea and the Caucasus Mountains connecting the Eurasian Steppe to the north and the Iranian Plateau to the south; covering an area of , with a population of roughly 120,000 residents. Derbent claims to be the oldest city in Russia, with historical documentation dating to the 8th century BC, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Due to its strategic location, over the course of history, the city changed ownership many times, particularly among the Persian, Arab, Mongol, Timurid, and Shirvan kingdoms. In the 19th century, the city passed from Persian into Russian ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haytham Ibn Khalid
Haytham ibn Khalid was the first Shirvanshah, or independent ruler of Shirvan, renouncing the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphate in 861 and beginning the Mazyadid dynasty. Biography He was the son of the Shayban (tribe), Shaybani Arabs, Arab Khalid ibn Yazid al-Shaybani and the grandson of Yazid ibn Mazyad al-Shaybani, both of whom had repeatedly served the Abbasid Caliphate as governors of Arminiya, a vast province encompassing most of the Transcaucasus, with Armenian Highland, Armenia, Caucasian Iberia, Iberia (Georgia (country), Georgia) Caucasian Albania, Albania (Azerbaijan). His brother Muhammad ibn Khalid al-Shaybani also served as governor of Arminiya. This succession of Shaybanid governors enabled them to become firmly entrenched in the region, especially in Shirvan, which came to be ruled directly by Haytham. Haytham soon adopted the Persian title "''Shirvanshah ''Shirvanshah'' ( fa, شروانشاه), also spelled as ''Shīrwān Shāh'' or ''Sharwān Shāh'', was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mutawakkil
Abū al-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad al-Muʿtaṣim bi-ʾllāh ( ar, جعفر بن محمد المعتصم بالله; March 822 – 11 December 861), better known by his regnal name Al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (, "He who relies on God") was the tenth Abbasid caliph. He succeeded his brother, al-Wathiq, and is known for expanding the empire to its maximum extent. He was deeply religious, and is remembered for discarding the Muʿtazila, ending the Mihna (a period of persecution of Islamic scholars), and releasing Ahmad ibn Hanbal. He is also known for his tough rule, especially with respect to non-Muslim subjects. He was assassinated on 11 December 861 by the Turkic guard with the support of his son, al-Muntasir, marking the beginning of the period of civil strife known as the "Anarchy at Samarra". Early life Al-Mutawakkil was born on February/March 822 to the Abbasid prince Abu Ishaq Muhammad (the future al-Mu'tasim) and a slave concubine from Khwarazm called Shuja. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchy At Samarra
The Anarchy at Samarra () was a period of extreme internal instability from 861 to 870 in the history of the Abbasid Caliphate, marked by the violent succession of four caliphs, who became puppets in the hands of powerful rival military groups. The term derives from the then capital and seat of the caliphal court, Samarra. The "anarchy" began in 861, with the murder of Caliph al-Mutawakkil by his Turkish guards. His successor, al-Muntasir, ruled for six months before his death, possibly poisoned by the Turkish military chiefs. He was succeeded by al-Musta'in. Divisions within the Turkish military leadership enabled Musta'in to flee to Baghdad in 865 with the support of some Turkish chiefs ( Bugha the Younger and Wasif) and the Police chief and governor of Baghdad Muhammad, but the rest of the Turkish army chose a new caliph in the person of al-Mu'tazz and besieged Baghdad, forcing the city's capitulation in 866. Musta'in was exiled and executed. Mu'tazz was able and energetic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Shayban
The Banu Shayban () is an Arab tribe, a branch of the Bakr ibn Wa'il group. Throughout the early Islamic era, the tribe was settled chiefly in the Jazira, and played an important role in its history. History In the pre-Islamic period, the Shayban with their flocks wandered according to the seasons, wintering in Jadiyya in the Najd and moving to the fertile lowlands around the Euphrates for the summer, ranging from the Jazira in the north to lower Iraq and the shores of the Persian Gulf.Bianquis (1997), pp. 391–392 Its chief opponents during this time were the Banu Taghlib and Banu Tamim tribes. Already from pre-Islamic times, the tribe was "celebrated ... for the remarkable quality of its poets, its use of a very pure form of Arabic language and its fighting ardour" (Th. Bianquis), a reputation its members retained into the Islamic period, when histories remark both on their own skills as, and on their patronage of, poets. During the time of Muhammad and his immediate successo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harun Al-Rashid
Abu Ja'far Harun ibn Muhammad al-Mahdi ( ar , أبو جعفر هارون ابن محمد المهدي) or Harun ibn al-Mahdi (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Harun al-Rashid ( ar, هَارُون الرَشِيد, translit=Hārūn al-Rashīd) was the fifth Abbasid caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, reigning from September 786 until his death. His reign is traditionally regarded to be the beginning of the Islamic Golden Age. His epithet "al-Rashid" translates to "the Orthodox", "the Just", "the Upright", or "the Rightly-Guided". Harun established the legendary library Bayt al-Hikma ("House of Wisdom") in Baghdad in present-day Iraq, and during his rule Baghdad began to flourish as a world center of knowledge, culture and trade. During his rule, the family of Barmakids, which played a deciding role in establishing the Abbasid Caliphate, declined gradually. In 796, he moved his court and government to Raqqa in present-day Syria. A Frankish mission came to offer H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazid Ibn Mazyad Al-Shaybani
Yazid ibn Mazyad al-Shaybani ( ar, يزيد بن مزيد الشيباني, Yazīd ibn Mazyad al-Shaybānī; died 801) was an Arab general and governor who served the Abbasid Caliphate. Biography Yazid was member of the Shayban tribe, dominant in the region of Diyar Bakr in the northern Jazira. The first member of his family to rise to prominence was his uncle, Ma'n ibn Za'ida al-Shaybani, under the Umayyads. Although Ma'n fought against the Abbasid Revolution, he reconciled himself with the Abbasid regime and both he and his sons, Za'ida and Sharahil held governorships and high military posts. Yazid first served under Ma'n during the latter's governorship in Sistan, where Ma'n fell in battle against the local Kharijites in 769. Under Caliph al-Mahdi (), he fought against Yusuf al-Barm in Khurasan, and in 782 took part in the great campaign against the Byzantine Empire under the future Caliph Harun al-Rashid's (). Yazid accompanied al-Mahdi's eldest son and successor al-Had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salman Ibn Rabiah
Salman ibn Rabiah al-Bahili () (died 650) was military governor of Armenia 633–644 CE, under Caliph Uthman ibn Affan. He may have been the brother of Abd ar-Rahman ibn Rabiah, who led the attempted conquest of the northern Caucasus Mountains and Khazaria. Under Uthman, the Muslim armies headed into Armenia for the first time, launching from Syria and led by Habib ibn Maslama al-Fihri Ḥabīb ibn Maslama al-Fihrī ( ar, حبيب بن مسلمة الفهري; –) was an Arab general during the Early Muslim conquests, under Mu'awiyah ibn Abi Sufyan. Life Origin and career under Umar Born in Mecca , Habib was a member of the M .... They conquered several Armenian territories but were challenged by large numbers of Byzantines joining the Armenian defense. Habib asked Uthman for help, and he sent 6,000 men led by Salman ibn Rabi'ah al-Bahili, marching from Kufa, Iraq. A dispute arose between Habib and Salman, and Uthman wrote to them and solved the issue with Salman taking over c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)