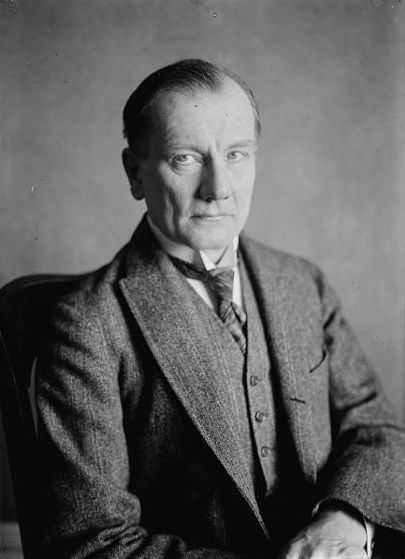|
Sextet
A sextet (or hexad) is a formation containing exactly six members. The former term is commonly associated with vocal ensembles (e.g. The King's Singers, Affabre Concinui) or musical instrument groups, but can be applied to any situation where six similar or related objects are considered a single unit. Musical compositions with six parts are sextets. Many musical compositions are named for the number of musicians for which they are written. If a piece is written for six performers, it may be called a "sextet". Steve Reich's "Sextet", for example, is written for six percussionists. However, much as many string quartets do not include "string quartet" in the title (though many do), many sextets do not include "sextet" in their title. See: string sextet and piano sextet. In jazz music a sextet is any group of six players, usually containing a drum set (bass drum, snare drum, hi-hat, ride cymbal), string bass or electric bass, piano, and various combinations of the following or other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Sextet
In classical music, a string sextet is a composition written for six string instruments, or a group of six musicians who perform such a composition. Most string sextets have been written for an ensemble consisting of two violins, two violas, and two cellos. Notable string sextets Among the earliest works in this form are the nine string sextets Op. 23 by Luigi Boccherini, written in 1776. Other notable string sextets include the String Sextets Op. 18 and 36 by Brahms, Dvořák's Op. 48, Tchaikovsky ''Souvenir de Florence'', Op. 70, Schoenberg's ''Verklärte Nacht'', Op. 4, Erich Wolfgang Korngold Op. 10, Erwin Schulhoff's String Sextet of 1924, and Charles Wuorinen's String Sextet of 1989. Less usual combinations More unusual combinations for a string sextet: * three violins, viola and two cellos: Ferdinand David (1810–1873), op. 38, Gaetano Brunetti (1744–1798), op. 1, Eugene Goossens (1893–1962), op. 37 * three violins, two violas and cello: Jan Brandts Buys (18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Sextet
A piano sextet is a composition for piano and five other musical instruments, or a group of six musicians who perform such works. There is no standard grouping of instruments with that name, and compared to the string quartet or piano quintet literature, relatively few such compositions exist. The best-known piano sextet is probably the ''Sextet'' by Poulenc, one of the pinnacles of the wind and piano repertoire. Chausson's ''Concert'' is widely regarded as one of the masterpieces of French strings and piano chamber music literature (for example, the critic Jean Gallois describes it as "superb"). The following is an incomplete list of piano sextet composers and their works in this genre: * Theodor Blumer (1881-1964), Sextet, Op. 45, composed 1921, for piano and wind quintet * Philippe Boesmans (1936–2022), Sextuor à clavier, composed 2005, for piano and string quintet * Ernest Chausson (1855–1899), ''Concert'' in D major, Op. 21, composed 1891, for piano, violin, and string ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextet (Poulenc)
Francis Poulenc's ''Sextuor'' (Sextet), FP 100, is a chamber music piece written for a standard wind quintet ( flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon, and French horn) and piano. Estimates about the time of its composition range from between 1931 and 1932 and 1932 alone. It received its debut in 1933 but was later revised in 1939. Performed in its entirety, the three-movement piece lasts approximately 18 minutes. Background Francis Poulenc, though rejected by the director of the Paris Conservatoire for the tendency of his compositional style to be overly progressive, was the most prolific member of the group of 20th-century French composers known as Les Six. In his Sextet there are obvious influences of the incidental music heard during the group's weekend visits to the circus as well as their general adherence to the melodic precedents set forth by Satie. Poulenc composed the piece around the same time as his cantata ''Le Bal Masqué'' and Concerto for Two Pianos. Structure and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steve Reich
Stephen Michael Reich ( ; born October 3, 1936) is an American composer known for his contribution to the development of minimal music in the mid to late 1960s. Reich's work is marked by its use of repetitive figures, slow harmonic rhythm, and canons. Reich describes this concept in his essay, "Music as a Gradual Process", by stating, "I am interested in perceptible processes. I want to be able to hear the process happening throughout the sounding music." To do so, his music employs the technique of phase shifting, in which a phrase is slightly altered over time, in a flow that is clearly perceptible to the listener. His innovations include using tape loops to create phasing patterns, as on the early compositions ''It's Gonna Rain'' (1965) and '' Come Out'' (1966), and the use of simple, audible processes, as on ''Pendulum Music'' (1968) and ''Four Organs'' (1970). The 1978 recording ''Music for 18 Musicians'' would help entrench minimalism as a movement. Reich's work took o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextet (Reich)
''Sextet'' is a composition by American composer Steve Reich. The piece was written and first performed in 1984, and slightly revised in 1985. Overview As the title indicates, it is written for an ensemble of six: four percussionists and two keyboardists. The percussionists play (at various times) three marimbas, two vibraphones, two bass drums, crotales, sticks, and tam-tam. Two percussionists double on piano during the opening "Pulse" section. The keyboardists play both pianos and synthesizers set to an electric organ sound. The piece is broken into five movements and, like many other Reich compositions, Sextet has an arch form: A-B-C-B-A. The paired movements share a tempo and a particular cycle of chords. These cycles use dominant chords with added tones to give it a darker, more chromatic sound, much like Reich's previous piece, ''The Desert Music''. A typical performance lasts about 26 minutes. Analysis ''Sextet'' plays with two aspects of music. First, it tries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextet (Penderecki)
The Sextet is a two-movement composition for clarinet, horn, violin, viola, cello, and piano by Polish composer Krzysztof Penderecki. The composition was written in 2000 and is, according to some critics, the composer's most substantial chamber work. Composition This composition takes approximately 30 minutes to perform. The movement list is as follows: # Allegro moderato # Larghetto Given its very unusual nature, for Penderecki's chamber music is rare, the melodic lines of this composition are very well defined, because Penderecki usually writes scores for large orchestras and ensembles. This work is remarkable for its chromatic scales, present all along the piece. This sextet was commissioned by Auftragswerk der Gesellschaft der Musikfreunde and was eventually premiered on June 7, 2000 in Vienna's Musikverein by Paul Meyer (clarinet), Radovan Vlatkovic (horn), Julian Rachlin (violin), Yuri Bashmet (viola), fellow musician Mstislav Rostropovich (cello), and Dmitri Alexeev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextet (Dohnányi)
The Sextet in C major for piano, violin, viola, cello, clarinet and horn, Op. 37, was composed by Ernst von Dohnányi in 1935. History The sextet was written in 1935 during a lengthy period of illness, during which Dohnányi was bedridden with a thrombosis for several months. It was premiered on 17 June 1935. Structure The sextet consists of four movements: Reception A reviewer for the ''Budapesti Hírlap The ''Budapesti Hírlap'' was a Hungarian daily newspaper published in Budapest from 16 June 1881 to 1938. Between 25 March and 28 September 1919 it was temporarily closed down. The paper had a conservative Conservatism is a cultural, s ...'', who attended the premiere on 17 June 1935, wrote favorably of the work: "One of the sextet's greatest values is that it is melodically original. Every tune is invented, not borrowed, and not based on a quotation." References External links * {{Authority control Compositions for piano sextet Compositions f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lennox Berkeley
Sir Lennox Randal Francis Berkeley (12 May 190326 December 1989) was an English composer. Biography Berkeley was born on 12 May 1903 in Oxford, England, the younger child and only son of Aline Carla (1863–1935), daughter of Sir James Charles Harris, former British consul in Monaco, and Royal Navy Captain Hastings George FitzHardinge Berkeley (1855–1934), the illegitimate and eldest son of George Lennox Rawdon Berkeley, the 7th Earl of Berkeley (1827–1888). He attended the Dragon School in Oxford, going on to Gresham's School, in Holt, Norfolk and St George's School in Harpenden, Hertfordshire. He studied French at Merton College, Oxford, graduating with a fourth class degree in 1926. While at university he coxed the college rowing eight. He became an honorary fellow of Merton College in 1974. In 1927, he went to Paris to study music with Nadia Boulanger, and there became acquainted with Francis Poulenc, Igor Stravinsky, Darius Milhaud, Arthur Honegger and Albert Rouss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Von Dohnányi
Ernst von Dohnányi (Hungarian: ''Dohnányi Ernő'', ; 27 July 1877 – 9 February 1960) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and conductor. He used a German form of his name on most published compositions. Biography Dohnányi was born in Pozsony, Kingdom of Hungary, Austria-Hungary (today Bratislava, capital of Slovakia). He was the son of Frigyes Dohnányi and his wife Ottilia Szlabey. He first studied music with his father, a professor of mathematics and an amateur cellist, and then when he was eight years old, with Carl Forstner, organist at the local cathedral. In 1894, in his 17th year, he moved to Budapest and enrolled in the '' Royal National Hungarian Academy of Music'', studying piano with István Thomán and composition with Hans von Koessler, a cousin of Max Reger. István Thomán had been a favorite student of Franz Liszt, while Hans von Koessler was a devotee of Johannes Brahms's music. These two influences played an important part in Dohnányi's life: Liszt on his p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Poulenc
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc (; 7 January 189930 January 1963) was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the best-known are the piano suite '' Trois mouvements perpétuels'' (1919), the ballet ''Les biches'' (1923), the ''Concert champêtre'' (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the Organ Concerto (1938), the opera ''Dialogues des Carmélites'' (1957), and the '' Gloria'' (1959) for soprano, choir, and orchestra. As the only son of a prosperous manufacturer, Poulenc was expected to follow his father into the family firm, and he was not allowed to enrol at a music college. Largely self-educated musically, he studied with the pianist Ricardo Viñes, who became his mentor after the composer's parents died. Poulenc also made the acquaintance of Erik Satie, under whose tutelage he became one of a group of young composers known collectively as ''Les Six''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ireland (composer)
John Nicholson Ireland (13 August 187912 June 1962) was an English composer and teacher of music. The majority of his output consists of piano miniatures and of songs with piano. His best-known works include the short instrumental or orchestral work " The Holy Boy", a setting of the poem " Sea-Fever" by John Masefield, a formerly much-played Piano Concerto, the hymn tune Love Unknown and the choral motet "Greater Love Hath No Man". Life John Ireland was born in Bowdon, near Altrincham, Cheshire, into a family of English and Scottish descent and some cultural distinction. His father, Alexander Ireland, a publisher and newspaper proprietor, was aged 69 at John's birth. John was the youngest of the five children from Alexander's second marriage (his first wife had died). His mother, Annie Elizabeth Nicholson Ireland, was a biographer and 30 years younger than Alexander. She died in October 1893, when John was 14, and Alexander died the following year, when John was 15. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Bass
The double bass (), also known simply as the bass () (or by other names), is the largest and lowest-pitched bowed (or plucked) string instrument in the modern symphony orchestra (excluding unorthodox additions such as the octobass). Similar in structure to the cello, it has four, although occasionally five, strings. The bass is a standard member of the orchestra's string section, along with violins, viola, and cello, ''The Orchestra: A User's Manual'' , Andrew Hugill with the Philharmonia Orchestra as well as the , and is featured in , solo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |