|
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is inflammation of the sesamoid bones. Humans Sesamoiditis occurs on the bottom of the foot, just behind the big toe. There are normally two sesamoid bones on each foot; sometimes sesamoids can be bipartite, which means they each comprise two separate pieces. The sesamoids are roughly the size of jelly beans. The sesamoid bones act as a fulcrum for the flexor tendons, the tendons which bend the big toe downward. Symptoms include inflammation and pain. Sometimes a sesamoid bone is fractured. This can be difficult to pick up on X-ray, so a bone scan or MRI is a better alternative. Among those who are susceptible to the malady are dancers, catchers and pitchers in baseball, soccer players, and football players. Horses In the horse it occurs at the horse's fetlock. The sesamoid bones lie behind the bones of the fetlock, at the back of the joint, and help to keep the tendons and ligaments that run between them correctly functioning. Usually periostitis (new bone gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josh Zeid
Joshua Alexander Zeid ( ; born March 24, 1987) is an American-Israeli former professional baseball pitcher. He plays for Team Israel. He formerly played for the Houston Astros of MLB. Zeid played for the gold-medal-winning Team USA Youth National Team in 2003. In his senior year in high school he was named Gatorade Connecticut High School Player of the Year, and ''Baseball America'' ranked him the nation's 27th-best prospect. He was drafted in the 10th round of the 2009 Major League Baseball Draft, and in 2010 he was named a South Atlantic League midseason All-Star, and won the MiLB Best Reliever (Class A–Full Season) Award. He debuted in the major leagues with the Houston Astros in 2013. He pitched for Team Israel at the 2017 World Baseball Classic, and was named to the 2017 All-World Baseball Classic team. His fastball reached 97 mph. After retiring from major league baseball, Zeid joined the Chicago Cubs front office as a pitching analyst. In November 2019, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
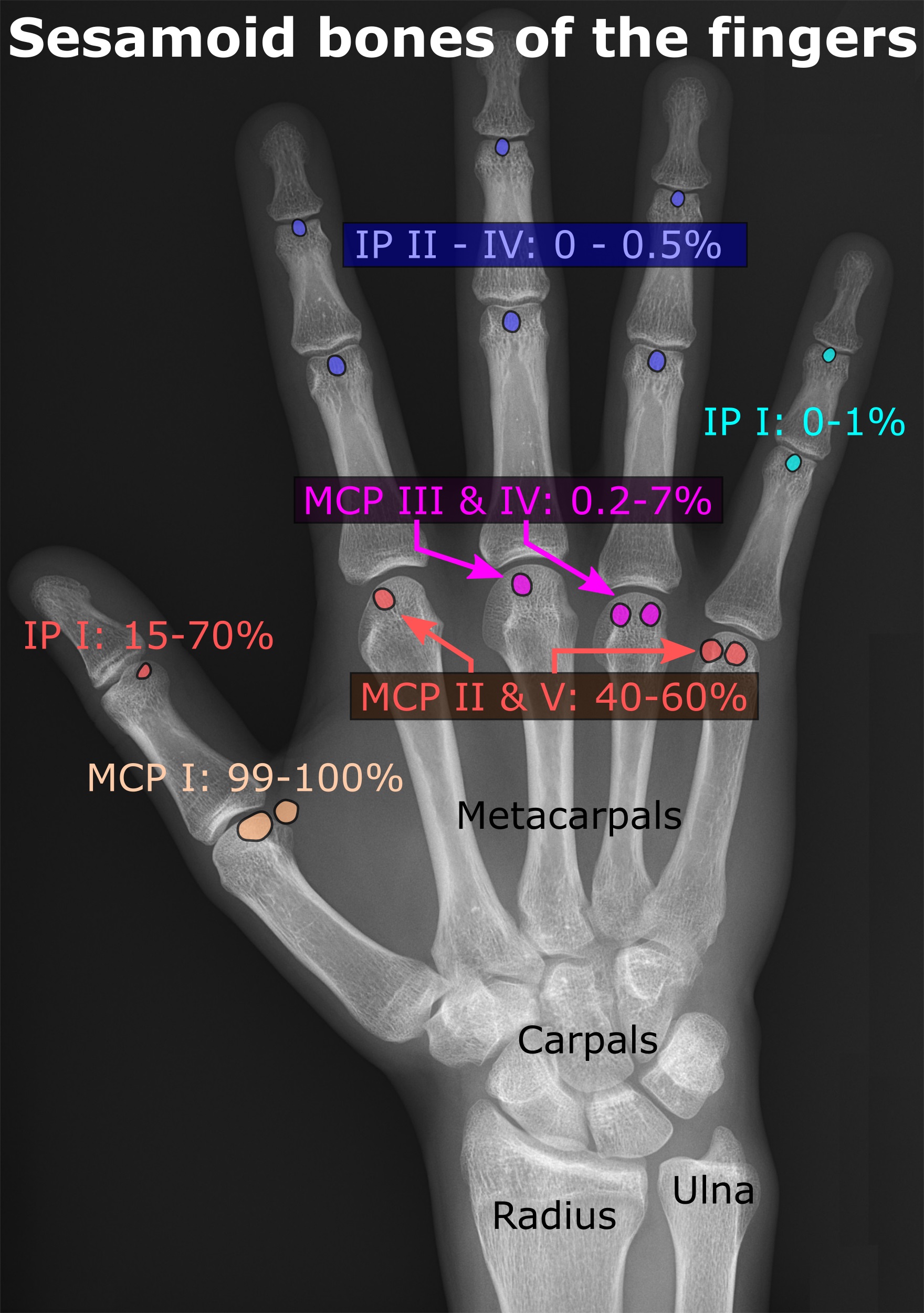
Sesamoid Bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for ' sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a sesamoid bone (within the tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedics
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternatively spelt orthopaedics), is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ὀρθός ''orthos'' ("correct", "straight") and παιδίον ''paidion'' ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Heels
High-heeled shoes, also known as high heels, are a type of shoe with an angled sole. The heel in such shoes is raised above the ball of the foot. High heels cause the legs to appear longer, make the wearer appear taller, and accentuate the calf muscle. There are many types of heels in varying colors, materials, styles, and heights. High heels have been used in various ways to communicate nationality, professional affiliation, gender, and social status. High heels have been important in the West. In early 17th century Europe, for example, high heels were a sign of masculinity and high social status. It wasn't until the end of the century that this trend spread to women's fashion. By the 18th century, high-heeled shoes had split along gender lines. By this time, heels for men's shoes were chunky squares attached to riding boots or tall formal dress boots while women's high heels were narrow and pointy and often attached to slipper-like dress shoes (similar to modern heels). B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disorders Of Fascia
Disorder may refer to randomness, non-order, or no intelligible pattern. Disorder may also refer to: Healthcare * Disorder (medicine), a functional abnormality or disturbance * Mental disorder or psychological disorder, a psychological pattern associated with distress or disability that occurs in an individual and is not a part of normal development or culture: :* Anxiety disorder, different forms of abnormal and pathological fear and anxiety :* Conversion disorder, neurological symptoms such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits, where no neurological explanation is possible :* Obsessive–compulsive disorder, an anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing anxiety :* Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder, obsession with perfection, rules, and organization :* Personality disorder, an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the culture of the individual who exhibits it Law enforceme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Injury And Lameness
Equinae is a subfamily of the family Equidae, which have lived worldwide (except Indonesia and Australia) from the Hemingfordian stage of the Early Miocene (16 million years ago) onwards. They are thought to be a monophyletic grouping.B. J. MacFadden. 1998. Equidae. In C. M. Janis, K. M. Scott, and L. L. Jacobs (eds.), Evolution of Tertiary Mammals of North America Members of the subfamily are referred to as equines; the only extant equines are the horses, asses, and zebras of the genus ''Equus''. The subfamily contains two tribes, the Equini and the Hipparionini, as well as two unplaced genera, ''Merychippus'' and ''Scaphohippus''. Sister taxa * Anchitheriinae * Hyracotheriinae ''Hyracotherium'' ( ; "hyrax-like beast") is an extinct genus of very small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal was once considered to be the earliest kno ... References Miocene horses Pliocene odd- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateshead FC
Gateshead Football Club is a professional football club based in Gateshead, England. The team compete in and play at the Gateshead International Stadium. Established in 1977 after Gateshead United folded, the club are known as the "Tynesiders" or the "Heed". There had been a Gateshead A.F.C. in the English Football League from 1930 to 1960, which had itself folded before Gateshead United had been established. The current incarnation of the club began life in the Northern Premier League, winning Premier Division titles in the 1982–83 and 1985–86 seasons. However they were relegated out of the Conference in 1984 and 1987. They secured promotion back into the Conference at the end of the 1989–90 season, though would remain there only until another relegation in 1998. The club were further relegated out of the Northern Premier League Premier Division in 2003. They won the First Division play-offs in 2004 and the Premier Division play-offs in 2008, before winning promotion ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melvin Upton
Melvin Emanuel Upton Jr. (born August 21, 1984), known as B. J. Upton, is an American former professional baseball outfielder. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the Tampa Bay Devil Rays / Rays, Atlanta Braves, San Diego Padres, and Toronto Blue Jays. Upton has played with his brother, Justin Upton, as members of the Atlanta Braves and San Diego Padres. They are the only two brothers in MLB history to be selected in the No. 1 and 2 slots of the draft (in separate years). The Upton brothers are also the first brothers to both hit 20 home runs and steal 20 bases in a season. Early life and amateur career Upton was born to Melvin and Yvonne (née Gordon) Upton. Yvonne worked as a teacher and Melvin worked variously as a scout for the Kansas City Royals, a mortgage broker and a college basketball referee in the Mid-Eastern Athletic Conference after playing both college football and basketball at Norfolk State. Before high school, Upton played on the same travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastern
The is a part of the leg of a horse between the fetlock and the top of the hoof. It incorporates the long pastern bone (proximal phalanx) and the short pastern bone (middle phalanx), which are held together by two sets of paired ligaments to form the pastern joint (proximal interphalangeal joint). Anatomically homologous to the two largest bones found in the human finger, the pastern was famously mis-defined by Samuel Johnson in his dictionary as "the knee of a horse". When a lady asked Johnson how this had happened, he gave the much-quoted reply: "Ignorance, madam, pure ignorance." Anatomy and importance The pastern consists of two bones, the uppermost called the "large pastern bone" or proximal phalanx, which begins just under the fetlock joint, and the lower called the "small pastern bone" or middle phalanx, located between the large pastern bone and the coffin bone, outwardly located at approximately the coronary band. The joint between these two phalangeal bones is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotics
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the Neuromuscular junction, neuromuscular and Skeletal muscle, skeletal system". Orthotists are professionals who specialize in the provision of orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the Human leg, lower extremities, orthotics of the Upper limb, upper extremities, orthotics for the Torso, trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses, relief orthoses, and soft braces. Under the International standard, International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, a knee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug; it is not synthesized in the adrenal glands. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzyme corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 into the inactive metabolite cortisone, particularly in the kidneys. Cortisone is converted back to the active steroid cortisol by the action of the enzyme 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, particularly in the liver. The term "cortisone" is frequently misused to mean either any corticosteroid or hydrocortisone, which is actually another name for cortisol. Many who speak of receiving a "cortisone shot" or taking "cortisone" are actually receiving hydrocortisone or one of many other, much more potent synthetic corticosteroids; it is unlikely that the drug administered is actually cortisone. Cortisone can be administered as a prodrug, meaning it has to be converted by the body (speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |