|
Series Circuit
Terminal (electronics), Two-terminal components and electrical networks can be connected in series or parallel. The resulting electrical network will have two terminals, and itself can participate in a series or parallel Topology (electrical circuits), topology. Whether a two-terminal "object" is an electrical component (e.g. a resistor) or an electrical network (e.g. resistors in series) is a matter of perspective. This article will use "component" to refer to a two-terminal "object" that participates in the series/parallel networks. Components connected in series are connected along a single "electrical path", and each component has the same electric current through it, equal to the current through the network. The voltage across the network is equal to the sum of the voltages across each component. Components connected in parallel are connected along multiple paths, and each component has the same voltage across it, equal to the voltage across the network. The current throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: ''self capacitance'' and ''mutual capacitance''. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit. The capacitance between two conductors depends only on the geometry; the opposing surface area of the conductors and the distance between them; and the permittivity of any dielectric material between them. For many dielectric materials, the permittivity, and thus the capacitance, is independent of the potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistors In Parallel
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law states that the electric current through a Electrical conductor, conductor between two Node (circuits), points is directly Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the Electrical resistance, resistance, one arrives at the three mathematical equations used to describe this relationship: V = IR \quad \text\quad I = \frac \quad \text\quad R = \frac where is the current through the conductor, ''V'' is the voltage measured across the conductor and ''R'' is the electrical resistance, resistance of the conductor. More specifically, Ohm's law states that the ''R'' in this relation is constant, independent of the current. If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called ''Ohm's law'', but it can still be used as a definition of Electrical resistance and conductance#Static and differential resistance, static/DC resistance. Ohm's law is an empirical law, empirical rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirchhoff's Circuit Laws
Kirchhoff's circuit laws are two equalities that deal with the current and potential difference (commonly known as voltage) in the lumped element model of electrical circuits. They were first described in 1845 by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. This generalized the work of Georg Ohm and preceded the work of James Clerk Maxwell. Widely used in electrical engineering, they are also called Kirchhoff's rules or simply Kirchhoff's laws. These laws can be applied in time and frequency domains and form the basis for network analysis. Both of Kirchhoff's laws can be understood as corollaries of Maxwell's equations in the low-frequency limit. They are accurate for DC circuits, and for AC circuits at frequencies where the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation are very large compared to the circuits. Kirchhoff's current law This law, also called Kirchhoff's first law, or Kirchhoff's junction rule, states that, for any node (junction) in an electrical circuit, the sum of cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Battery
An automotive battery, or car battery, is a usually 12 Volt lead-acid rechargeable battery that is used to start a motor vehicle, and to power lights, screen wiper etc. while the engine is off. Its main purpose is to provide an electric current to the Starter (engine), electric-powered starting motor, which in turn starts the chemically-powered internal combustion engine that actually propels the vehicle. Once the engine is running, power for the car's electrical systems is still supplied by the battery, with the alternator (automotive), alternator charging the battery as demands increase or decrease. Battery in modern cars Gasoline and diesel engine Typically, starting uses less than three percent of the battery capacity. For this reason, automotive batteries are designed to deliver maximum current for a short period of time. They are sometimes referred to as "SLI batteries" for this reason, for starting, lighting and ignition. SLI batteries are not designed for deep dischargi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Cell
An electrochemical cell is a device that either generates electrical energy from chemical reactions in a so called galvanic cell, galvanic or voltaic cell, or induces chemical reactions (electrolysis) by applying external electrical energy in an electrolytic cell. Both galvanic and electrolytic cells can be thought of as having two half-cells: consisting of separate Redox, oxidation and reduction reactions. When one or more electrochemical cells are connected in parallel or series they make a Battery (electricity), battery. Primary battery consists of single-use galvanic cells. Rechargeable batteries are built from #Secondary cells, secondary cells that use reversible reactions and can operate as galvanic cells (while providing energy) or electrolytic cells (while charging). Types of electrochemical cells Galvanic cell A galvanic cell (voltaic cell), named after Luigi Galvani (Alessandro Volta), is an electrochemical cell that generates electrical energy from spontaneous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery (electricity)
An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, those negatively charged electrons flow through the circuit and reach the positive terminal, thus causing a redox reaction by attracting positively charged ions, or cations. Thus, higher energy reactants are converted to lower energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell. Primary (single-use or "disposable") batteries are used once and discarded, as the electrode mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AND Gate
The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements the logical conjunction (∧) from mathematical logic AND gates behave according to their truth table. A HIGH output (1) results only if all the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH (1). If any of the inputs to the AND gate are not HIGH, a LOW (0) is outputted. The function can be extended to any number of inputs by multiple gates up in a chain. Symbols There are three symbols for AND gates: the American (ANSI or 'military') symbol and the IEC ('European' or 'rectangular') symbol, as well as the deprecated DIN symbol. Additional inputs can be added as needed. For more information see the Logic gate symbols article. It can also be denoted as symbol "^" or "&". The AND gate with inputs ''A'' and ''B'' and output ''C'' implements the logical expression C = A \cdot B. This expression also may be denoted as C=A \wedge B or C=A \And B. As of Unicode 16.0.0, the AND gate is also encoded in the Symbols for Legacy Computing Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Conjunction
In logic, mathematics and linguistics, ''and'' (\wedge) is the Truth function, truth-functional operator of conjunction or logical conjunction. The logical connective of this operator is typically represented as \wedge or \& or K (prefix) or \times or \cdot in which \wedge is the most modern and widely used. The ''and'' of a set of operands is true if and only if ''all'' of its operands are true, i.e., A \land B is true if and only if A is true and B is true. An operand of a conjunction is a conjunct. Beyond logic, the term "conjunction" also refers to similar concepts in other fields: * In natural language, the denotation of expressions such as English language, English "Conjunction (grammar), and"; * In programming languages, the Short-circuit evaluation, short-circuit and Control flow, control structure; * In set theory, Intersection (set theory), intersection. * In Lattice (order), lattice theory, logical conjunction (Infimum and supremum, greatest lower bound). Notati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
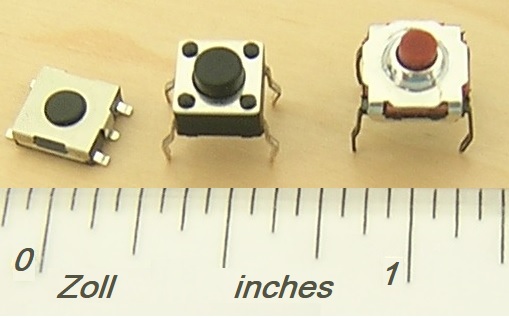
Switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |