|
Separate System
The separate system is a form of prison management based on the principle of keeping prisoners in solitary confinement. When first introduced in the early 19th century, the objective of such a prison or "penitentiary" was that of penance by the prisoners through silent reflection upon their crimes and behavior, as much as that of prison security. More commonly however, the term "separate system" is used to refer to a specific type of prison architecture built to support such a system. Early British prisons Millbank Prison was a prison in Millbank, Westminster, London. It was originally constructed as the National Penitentiary and for part of its history served as a holding facility for convicted prisoners before they were transported to Australia. It was opened in 1816 and closed in 1890. Pentonville Prison in the Barnsbury area of North London had a central hall with five radiating wings, all visible to staff at the center. It opened in 1842 and had separate cells for 520 pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which inmates (or prisoners) are confined against their will and usually denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Prisons are most commonly used within a criminal justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those pleading or being found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment. In simplest terms, a prison can also be described as a building in which people are legally held as a punishment for a crime they have committed. Prisons can also be used as a tool of political repression by authoritarian regimes. Their perceived opponents may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentonville (HM Prison)
HM Prison Pentonville (informally "The Ville") is an English Category B men's prison, operated by His Majesty's Prison Service. Pentonville Prison is not in Pentonville, but is located further north, on the Caledonian Road in the Barnsbury area of the London Borough of Islington, north London. In 2015 the justice secretary, Michael Gove, described Pentonville as "the most dramatic example of failure" within the prisons estate. The prison today Pentonville is a local prison, holding Category B/C adult males remanded by local magistrates' courts and the Crown Court, and those serving short sentences or beginning longer sentences. The prison is divided into these main wings: * A wing: Remand and convicted * J wing: Induction wing * C wing: Remands and convicted prisoners * D wing: Remands and convicted * E wing: Remands and convicted * F wing: Detoxification Unit (F4 F5 Vulnerable Prisoners) * G wing: remands and convicted (G5 enhanced only) G wing has an education department, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solitary Confinement
Solitary confinement is a form of imprisonment in which the inmate lives in a single cell with little or no meaningful contact with other people. A prison may enforce stricter measures to control contraband on a solitary prisoner and use additional security equipment in comparison to the general population. Solitary confinement is a punitive tool within the prison system to discipline or separate disruptive prison inmates who are security risks to other inmates, the prison staff, or the prison itself. However, solitary confinement is also used to protect inmates whose safety is threatened by other inmates by separating them from the general population. In a 2017 review, "a robust scientific literature has established the negative psychological effects of solitary confinement", leading to "an emerging consensus among correctional as well as professional, mental health, legal, and human rights organizations to drastically limit the use of solitary confinement." The United Nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhouse (lock-up)
A village lock-up is a historic building once used for the temporary detention of people in England and Wales, mostly where official prisons or criminal courts were beyond easy walking distance. Lockups were often used for the confinement of drunks, who were usually released the next day, or to hold people being brought before the local magistrate. The archetypal form comprises a small room with a single door and a narrow slit window, grating or holes. Most lock-ups feature a tiled or stone-built dome or spire as a roof and are built from brick, stone and/or timber. Such a room was built in many shapes; many are round, which gives rise to a sub-description: the punishment or village round-house. Village lock-ups, though usually freestanding, were often attached to walls, tall pillar/tower village crosses or incorporated into other buildings. Varying in architectural strength and ornamentation, they were all built to perform the same function. Nicknames and forms They have acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panopticon
The panopticon is a type of institutional building and a system of control designed by the English philosopher and social theorist Jeremy Bentham in the 18th century. The concept of the design is to allow all prisoners of an institution to be observed by a single security guard, without the inmates being able to tell whether they are being watched. Although it is physically impossible for the single guard to observe all the inmates' cells at once, the fact that the inmates cannot know when they are being watched means that they are motivated to act as though they are being watched at all times. Thus, the inmates are effectively compelled to regulate their own behaviour. The architecture consists of a rotunda with an inspection house at its centre. From the centre, the manager or staff of the institution are able to watch the inmates. Bentham conceived the basic plan as being equally applicable to hospitals, schools, sanatoriums, and asylums, but he devoted most of his effort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Imprisonment
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment for a crime under which convicted people are to remain in prison for the rest of their natural lives or indefinitely until pardoned, paroled, or otherwise commuted to a fixed term. Crimes for which, in some countries, a person could receive this sentence include murder, torture, terrorism, child abuse resulting in death, rape, espionage, treason, drug trafficking, drug possession, human trafficking, severe fraud and financial crimes, aggravated criminal damage, arson, kidnapping, burglary, and robbery, piracy, aircraft hijacking, and genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or any three felonies in case of three-strikes law. Life imprisonment (as a maximum term) can also be imposed, in certain countries, for traffic offences causing death. Life imprisonment is not used in all countries; Portugal was the first country to abolish life imprisonment, in 1884. Where life imprisonment is a possible sentence, there may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Row
Death row, also known as condemned row, is a place in a prison that houses inmates awaiting Capital punishment, execution after being convicted of a capital crime and sentenced to death. The term is also used figuratively to describe the state of awaiting execution ("being on death row"), even in places where no special facility or separate unit for condemned inmates exists. In the United States, after an individual is found guilty of a Capital punishment in the United States#Capital crimes, capital offense in U.S. state, states where execution is a legal penalty, the judge will give the jury the option of imposing a death sentence or life imprisonment without the possibility of parole. It is then up to the jury to decide whether to give the death sentence; this usually has to be a unanimous decision. If the jury agrees on death, the defendant will remain on death row during appeal and ''habeas corpus'' procedures, which may continue for several decades. Opponents of capital punis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borstal
A Borstal was a type of youth detention centre in the United Kingdom, several member states of the Commonwealth and the Republic of Ireland. In India, such a detention centre is known as a Borstal school. Borstals were run by HM Prison Service and were intended to reform young offenders. The word is sometimes used loosely to apply to other kinds of youth institutions and reformatories, such as approved schools and youth detention centres. The court sentence was officially called "Borstal training". Borstals were originally for offenders under 21, but in the 1930s the maximum age was increased to 23. The Criminal Justice Act 1982 abolished the Borstal system in the UK, replacing Borstals with youth custody centres. In India, Borstal schools are used for the imprisonment of minors. As of 31 December 2014, there were twenty functioning Borstal schools in India, with a combined total capacity of 2,108 inmates. History United Kingdom The Gladstone Committee (1895) first propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boot Camp (correctional)
Boot camps are part of the correctional and penal system of some countries. Modeled after military recruit training camps, these programs are based on shock incarceration grounded on military techniques. The aggressive training used has resulted in deaths in a variety of circumstances. Boot camps are also criticized around the world for their lack of behavioral change and for the way extreme force can traumatize children and teenagers. Background The term "boot" originates from US Navy and Marine recruits in the Spanish–American War (1898) who wore leggings called boots. These recruits were trained in "boot" camps. Military-style training was used in the eighteenth century to rehabilitate civilian prisoners in the United States and for military prisoners during World War 2. Use around the world Australia In Australia the Premier of the state of Queensland Campbell Newman announced that bootcamps for convicted young people will open in Townsville and Rockhampton by Septemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
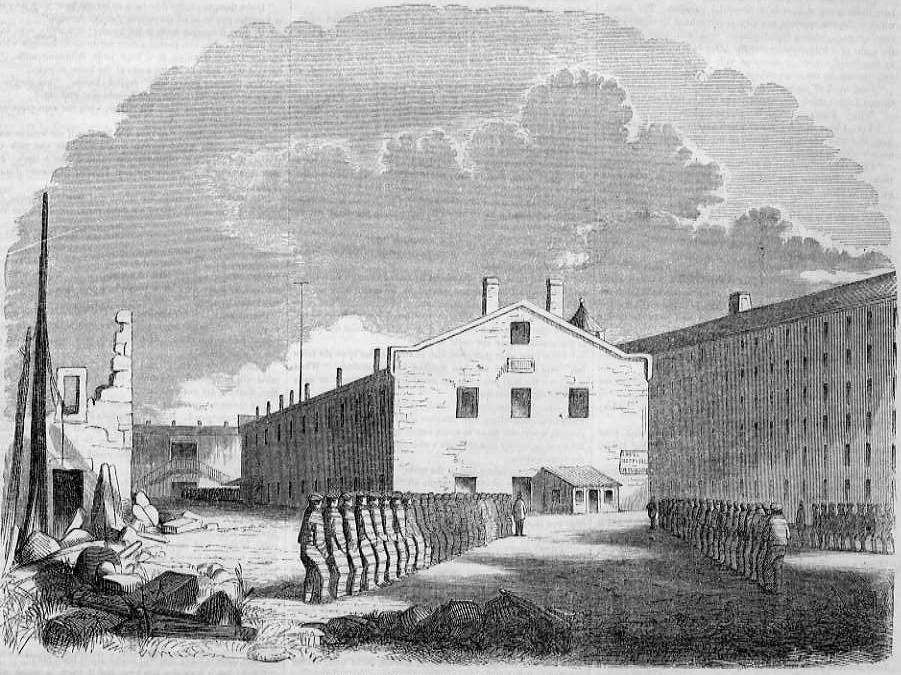
Auburn System
The Auburn system (also known as the New York system and Congregate system) is a penal method of the 19th century in which persons worked during the day in groups and were kept in solitary confinement at night, with enforced silence at all times. The silent system evolved during the 1820s at Auburn Prison in Auburn, New York, as an alternative to and modification of the Pennsylvania system of solitary confinement, which it gradually replaced in the United States. Whigs favored this system because it promised to rehabilitate criminals by teaching them personal discipline and respect for work, property, and other people. Among notable elements of the Auburn system were striped uniforms, lockstep, and silence. Prison life During the 19th century, prisoners had no rights nor any opportunity to live semi-comfortably. The Auburn system established several characteristics that were unique to the world of disciplinary conditions. Silence was the biggest factor among rules for the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of United States Prison Systems
Imprisonment began to replace other forms of criminal punishment in the United States just before the American Revolution, though penal incarceration efforts had been ongoing in England since as early as the 1500s, and prisons in the form of dungeons and various detention facilities had existed as early as the first sovereign states. In colonial times, courts and magistrates would impose punishments including fines, forced labor, public restraint, flogging, maiming, and death, with sheriffs detaining some defendants awaiting trial. The use of confinement as a punishment in itself was originally seen as a more humane alternative to capital and corporal punishment, especially among Quakers in Pennsylvania. Prison building efforts in the United States came in three major waves. The first began during the Jacksonian Era and led to the widespread use of imprisonment and rehabilitative labor as the primary penalty for most crimes in nearly all states by the time of the American Civil Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auburn Lockstep
Auburn may refer to: Places Australia * Auburn, New South Wales * City of Auburn, the local government area *Electoral district of Auburn *Auburn, Queensland, a locality in the Western Downs Region *Auburn, South Australia *Auburn, Tasmania *Auburn, Victoria United States * Auburn, Alabama * Auburn, California * Auburn, Colorado * Auburn, Georgia * Auburn, Illinois * Auburn, Indiana * Auburn, Iowa * Auburn, Kansas * Auburn, Kentucky * Auburn, Maine * Auburn House (Towson, Maryland), a historic home located on the grounds of Towson University * Auburn, Massachusetts * Auburn, Michigan * Auburn, Mississippi * Auburn (Natchez, Mississippi), a mansion in Duncan Park and a U.S. National Historic Landmark * Auburn, Missouri * Auburn, Nebraska * Auburn, New Hampshire * Auburn, New Jersey * Auburn, New York * Auburn, North Carolina * Auburn, North Dakota * Auburn, Oregon * Auburn, Pennsylvania * Auburn, Rhode Island * Auburn, Texas * Auburn (Bowling Green, Virginia), listed on the Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |