 |
Sectional Density
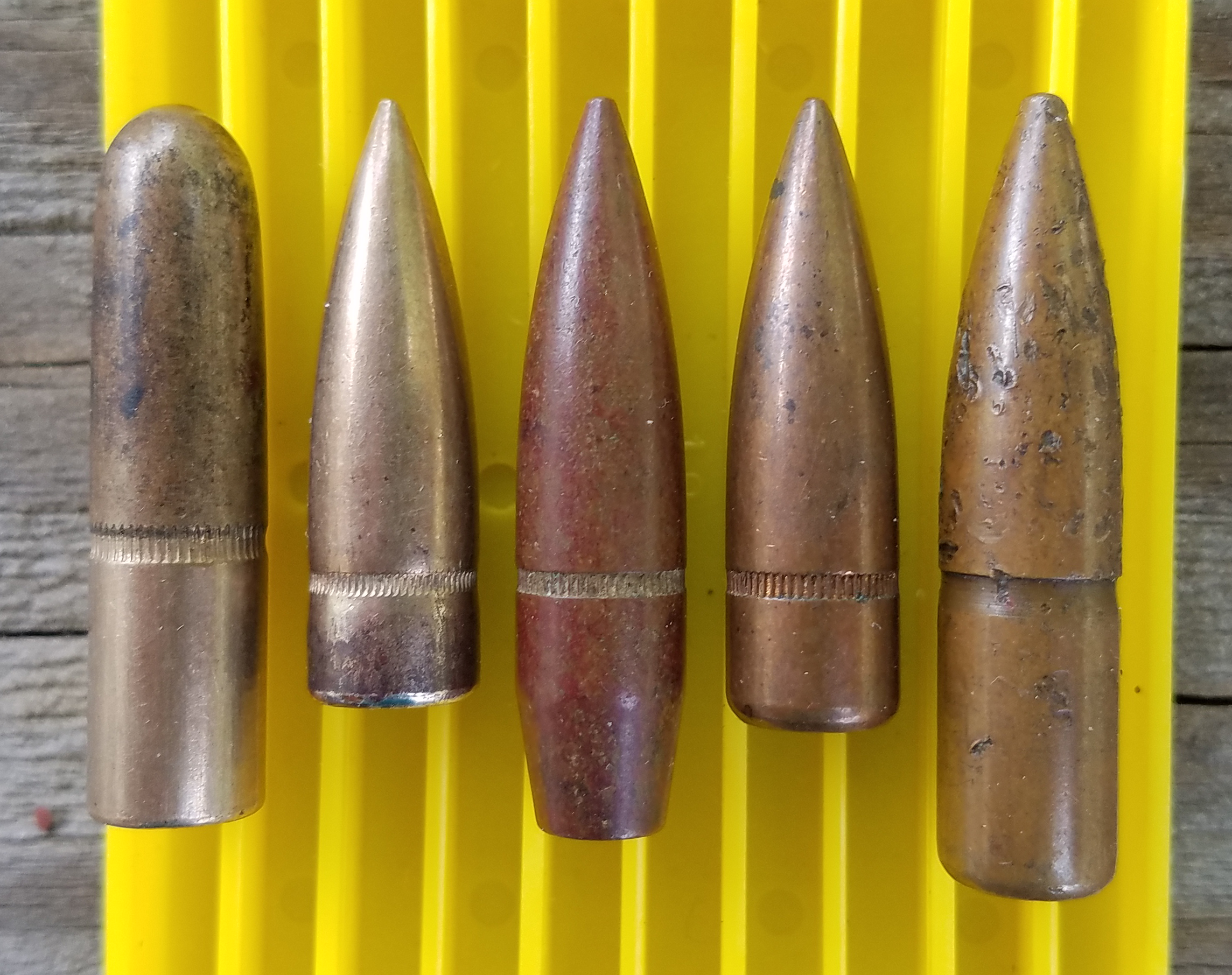
Sectional density (often abbreviated SD) is the ratio of an object's mass to its cross sectional area with respect to a given axis. It conveys how well an object's mass is distributed (by its shape) to overcome resistance along that axis. Sectional density is used in gun ballistics. In this context, it is the ratio of a projectile's weight (often in either kilograms, grams, pounds or grains) to its transverse section (often in either square centimeters, square millimeters or square inches), with respect to the axis of motion. It conveys how well an object's mass is distributed (by its shape) to overcome resistance along that axis. For illustration, a nail can penetrate a target medium with its pointed end first with less force than a coin of the same mass lying flat on the target medium. During World War II, bunker-busting Röchling shells were developed by German engineer August Cönders, based on the theory of increasing sectional density to improve penetration. R� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Nail
Nail or Nails may refer to: In biology * Nail (anatomy), toughened protective protein-keratin (known as alpha-keratin, also found in hair) at the end of an animal digit, such as fingernail * Nail (beak), a plate of hard horny tissue at the tip of some bird beaks Objects * Nail (fastener), the pin-shaped fastener used in engineering, woodworking and construction ** Nail (relic), used in the crucifixion of Christ * The Exchange nails, bronze tables outside of The Exchange, Bristol Arts and entertainment * '' JLA: The Nail series'', a 1998 three-issue comic book miniseries * '' Nail'', a 1985 album by Scraping Foetus Off The Wheel * '' Nails'', a 1992 American TV movie * Nails (band), an American powerviolence band founded 2009 * Nine Inch Nails, an American industrial rock band founded 1988 * The Nails, an American new wave band founded 1976 as The Ravers (name change 1977) People * Nail (given name), a list of people with the given name Nail * Nail (surname), a list of people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
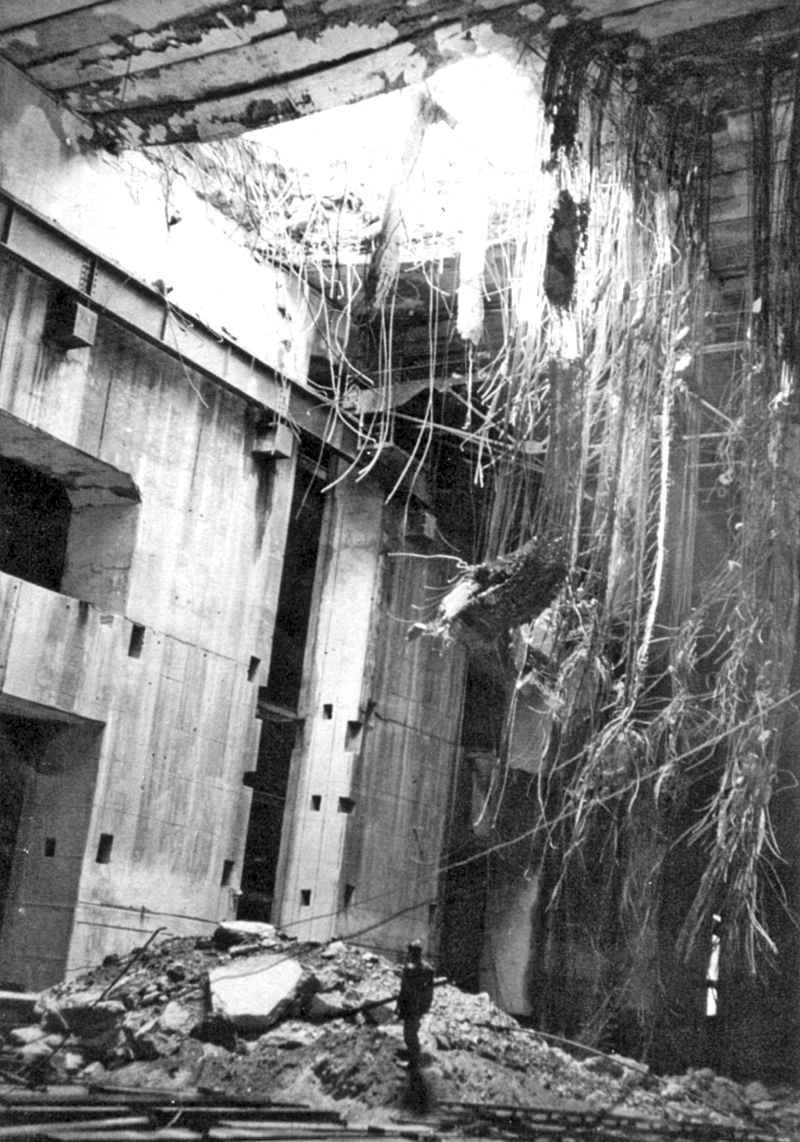 |
Bunker Buster
A bunker buster is a type of munition that is designed to penetrate hardened targets or targets buried deep underground, such as military bunkers. Armor piercing shells Germany Röchling shells were bunker-busting artillery shells, developed by the German engineer August Cönders, based on the theory of increasing sectional density to improve penetration. They were tested in 1942 and 1943 against the Belgian Fort d'Aubin-Neufchâteau. Aircraft delivered bombs World War II Germany In World War II the Luftwaffe developed a series of unguided rocket-propelled armor-piercing bombs for use against shipping and fortifications. United Kingdom In World War II, the British designer Barnes Wallis, already famous for inventing the bouncing bomb, designed two bombs that would become the conceptual predecessors of modern bunker busters: the five tonne Tallboy and the ten tonne Grand Slam. These were "Earthquake" bombs—a concept he had first proposed in 1939. The designs were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ballistic Coefficient
In ballistics, the ballistic coefficient (BC, ''C'') of a body is a measure of its ability to overcome air resistance in flight. It is inversely proportional to the negative acceleration: a high number indicates a low negative acceleration—the drag on the body is small in proportion to its mass. BC can be expressed with the units kilograms per square meter (kg/m2) or pounds per square inch (lb/in2) (where 1 lb/in2 corresponds to ). Formulas General :C_\text = \frac = \frac where: *''C''b,Physics, ballistic coefficient as used in physics and engineering *''m'', mass *''A'', cross-sectional area *''C''d, drag coefficient *\rho, density *\ell, characteristic body length Ballistics The formula for calculating the ballistic coefficient for small and large arms projectiles ''only'' is as follows: :C_\text = \frac where: *''C''b,Projectile, ballistic coefficient as used in point mass trajectory from the Siacci method (less than 20 degrees). *''m'', mass of bullet *''d'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Small Arms
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions). The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes containing gunpowder and pellet projectiles were mounted on spears to make the portable fire lance, operable by a single person, which was later used effectively as a shock weapon in the Siege of De'an in 1132. In the 13th century, fire lance barrels were replaced with metal tubes and transformed into the metal-barreled hand cannon. The technology gradually spread throughout Eurasia during the 14th century. Older firearms typically used black powder as a propellant, but modern firearms use smokeless powder or other propellants. Most modern firearms (with the notable exception of smoothbore shotguns) have rifled barrels to impart spin to the projectile for improved flight stability. Modern firearms can be described by their caliber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch ( psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Pounds Per Square Inch
The pound per square inch or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch (symbol: lbf/in2; abbreviation: psi) is a unit of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units. It is the pressure resulting from a force of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch. In SI units, 1 psi is approximately equal to 6895 Pa. Pounds per square inch absolute (psia) is used to make it clear that the pressure is relative to a vacuum rather than the ambient atmospheric pressure. Since atmospheric pressure at sea level is around , this will be added to any pressure reading made in air at sea level. The converse is pounds per square inch gauge (psig), indicating that the pressure is relative to atmospheric pressure. For example, a bicycle tire pumped up to 65 psig in a local atmospheric pressure at sea level (14.7 psi) will have a pressure of 79.7 psia (14.7 psi + 65 psi). When gauge pressure is referenced to something other than ambient atmospheric pressure, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
M107 Projectile
The M107 155 mm projectile was the standard 155 mm high explosive (HE) projectile for howitzers of the US Army and US Marine Corps. A bursting round with fragmentation and blast effects, the M107 is being superseded in the US military by the M795. Development The M107 is a development of the M102 155 mm shell that was developed in the 1930s from the French Schneider 155 mm projectile for the Model 1917 Howitzer. The M107 differs from the M102 mainly in having a wider rotating or driving band. Description The body consists of a hollow steel shell containing high explosive (either TNT or Composition B) painted olive drab with yellow markings. A fuze adapter is screwed into the body and brazed in place. An eyebolt lifting plug is screwed into the fuze well to assist in transportation. The plug is removed and replaced with a fuze for firing. The complete projectile weighs 43.2 kg, is 800 mm long and contains 15.8% explosive by weight. It is a separate- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Terminal Ballistics
Terminal ballistics (also known as wound ballistics) is a sub-field of ballistics concerned with the behavior and effects of a projectile when it hits and transfers its energy to a target. Bullet design (as well as the velocity of impact) largely determine the effectiveness of penetration. General The concept of terminal ballistics can be applied to any projectile striking a target. Much of the topic specifically regards the effects of small arms fire striking live targets, and a projectile's ability to incapacitate or eliminate a target. Common factors include bullet weight, composition, velocity, and shape. Firearm projectiles Classes of bullets There are three basic classes of bullets: * Those designed to maximize accuracy at varying ranges, * Those designed to maximize damage to a target (by penetrating as deeply as possible), * Those designed to avoid over-penetration of a target. This is done by deformation (to control the depth to which the bullet penetrates) which, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ballistic Coefficient
In ballistics, the ballistic coefficient (BC, ''C'') of a body is a measure of its ability to overcome air resistance in flight. It is inversely proportional to the negative acceleration: a high number indicates a low negative acceleration—the drag on the body is small in proportion to its mass. BC can be expressed with the units kilograms per square meter (kg/m2) or pounds per square inch (lb/in2) (where 1 lb/in2 corresponds to ). Formulas General :C_\text = \frac = \frac where: *''C''b,Physics, ballistic coefficient as used in physics and engineering *''m'', mass *''A'', cross-sectional area *''C''d, drag coefficient *\rho, density *\ell, characteristic body length Ballistics The formula for calculating the ballistic coefficient for small and large arms projectiles ''only'' is as follows: :C_\text = \frac where: *''C''b,Projectile, ballistic coefficient as used in point mass trajectory from the Siacci method (less than 20 degrees). *''m'', mass of bullet *''d'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
External Ballistics
External ballistics or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or in the vacuum of space, but most certainly flying under the influence of a gravitational field. Gun-launched projectiles may be unpowered, deriving all their velocity from the propellant's ignition until the projectile exits the gun barrel. However, exterior ballistics analysis also deals with the trajectories of rocket-assisted gun-launched projectiles and gun-launched rockets; and rockets that acquire all their trajectory velocity from the interior ballistics of their on-board propulsion system, either a rocket motor or air-breathing engine, both during their boost phase and after motor burnout. External ballistics is also concerned with the free-flight of other projectiles, such as balls, arrows etc. Forces acting on the projectile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ballistics
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance. A ballistic body is a free-moving body with momentum which can be subject to forces such as the forces exerted by pressurized gases from a gun barrel or a propelling nozzle, normal force by rifling, and gravity and air drag during flight. A ballistic missile is a missile that is guided only during the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight and the trajectory is subsequently governed by the laws of classical mechanics; in contrast to (for example) a cruise missile which is aerodynamically guided in powered flight like a fixed-wing aircraft. History and prehistory The earliest known ballistic projectiles were stones and spears, and the throwing stic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
SI Derived Unit
SI derived units are units of measurement derived from the seven base units specified by the International System of Units (SI). They can be expressed as a product (or ratio) of one or more of the base units, possibly scaled by an appropriate power of exponentiation (see: Buckingham π theorem). Some are dimensionless, as when the units cancel out in ratios of like quantities. The SI has special names for 22 of these derived units (for example, hertz, the SI unit of measurement of frequency), but the rest merely reflect their derivation: for example, the square metre (m2), the SI derived unit of area; and the kilogram per cubic metre (kg/m3 or kg⋅m−3), the SI derived unit of density. The names of SI derived units, when written in full, are always in lowercase. However, the symbols for units named after persons are written with an uppercase initial letter. For example, the symbol for hertz is "Hz", while the symbol for metre is "m". Special names The International Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |