|
Rovalpituzumab Tesirine
Rovalpituzumab tesirine (Rova-T) is an experimental antibody-drug conjugate targeting the protein DLL3 on tumor cells. It was originally developed by Stemcentrx and was purchased by AbbVie. It was tested for use in small-cell lung cancer, but development was terminated after unsuccessful phase III trial. Development In 2018, an Independent Data Monitoring Committee found that in the TAHOE phase III trial, Rova-T shortened survival of lung cancer patients compared to SOC chemotherapy topotecan, prompting termination of trial enrollment. Another phase III trial (MERU) demonstrated no survival benefit over placebo. A phase II trial using the drug as a third-line treatment for relapsed or refractory lung cancer showed objective response rate at just 16%. Chemical structure Chemical structure of "tesirine" (drawn in black). It consists of a pyrrolobenzodiazepine type dimer (top), which is the actual anti-cancer agent, a Val– Ala structure that can be cleaved by an enzyme to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DLL3
Delta-like 3 (Drosophila), also known as DLL3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DLL3'' gene. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the delta protein ligand family. This family functions as Notch ligands that are characterized by a DSL domain, EGF repeats, and a transmembrane domain. Expression of DLL3 is highest in fetal brain. It plays a key role in somitogenesis within the Paraxial mesoderm. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal recessive genetic disorder Jarcho-Levin syndrome. Expression of the gene occurs in Neuroendocrine tumor Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lun ...s, which has been targeted as a potential pathway for treatment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
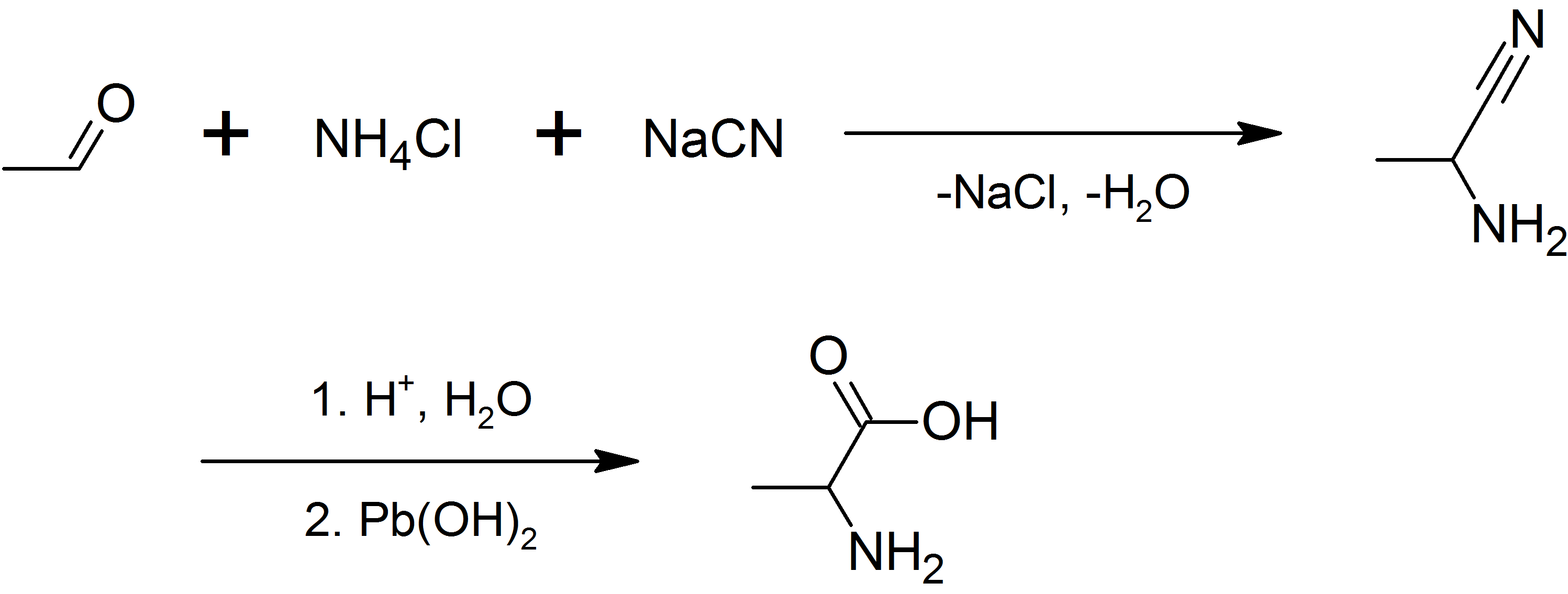
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody-drug Conjugates
Antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs are a class of biopharmaceutical drugs designed as a targeted therapy for treating cancer. Unlike chemotherapy, ADCs are intended to target and kill tumor cells while sparing healthy cells. As of 2019, some 56 pharmaceutical companies were developing ADCs. ADCs are complex molecules composed of an antibody linked to a biologically active cytotoxic (anticancer) payload or drug. Antibody-drug conjugates are an example of bioconjugates and immunoconjugates. ADCs combine the targeting properties of monoclonal antibodies with the cancer-killing capabilities of cytotoxic drugs, designed to discriminate between healthy and diseased tissue. Mechanism of action An anticancer drug is coupled to an antibody that targets a specific tumor antigen (or protein) that, ideally, is only found in or on tumor cells. Antibodies attach themselves to the antigens on the surface of cancerous cells. The biochemical reaction that occurs upon attaching triggers a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Cancer Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons (e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadastuximab Talirine
Vadastuximab talirine is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) directed to CD33 (siglec-3) which is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. The experimental drug, being developed by Seattle Genetics, was in clinical trials for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Development of vadastuximab talirine was discontinued in 2017 after a pivotal phase III clinical trial. Target, mAb, linker, and cytotoxin The drug target, CD33, is expressed on most AML cells. The CD33 antibody is attached to a highly potent DNA binding agent, a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer (SGD-1882), via a proprietary site-specific conjugation chemistry via a cleavable (valine-alanine dipeptide as cathepsin B cleavage site) maleimidocaproyl type linker, to a monoclonal antibody with engineered cysteines (EC-mAb). Vadastuximab talirine contains two site-specific drug attachment engineered cysteines. This use of engineered cysteine residues at the sites of drug linker attachment resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |