|
Robotics Middleware
Robotics middleware is middleware to be used in complex robot control software systems. :"''...robotic middleware is designed to manage the complexity and heterogeneity of the hardware and applications, promote the integration of new technologies, simplify software design, hide the complexity of low-level communication and the sensor heterogeneity of the sensors, improve software quality, reuse robotic software infrastructure across multiple research efforts, and to reduce production costs.''" It can be described as "software glue" to make it easier for robot builders focus on their specific problem area. Robotics middleware projects A wide variety of projects for robotics middleware exist, but no one of these dominates - and in fact many robotic systems do not use any middleware. Middleware products rely on a wide range of different standards, technologies, and approaches that make their use and interoperation difficult, and some developers may prefer to integrate their system th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middleware
Middleware is a type of computer software program that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue". Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement communication and input/output, so they can focus on the specific purpose of their application. It gained popularity in the 1980s as a solution to the problem of how to link newer applications to older legacy systems, although the term had been in use since 1968. In distributed applications The term is most commonly used for software that enables communication and management of data in distributed applications. An IETF workshop in 2000 defined middleware as "those services found above the transport (i.e. over TCP/IP) layer set of services but below the application environment" (i.e. below application-level APIs). In this more specific sense ''middleware'' can be described as the hyphen ("-") in '' client-server'', or the ''-to-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inter-process Communication
In computer science, interprocess communication (IPC) is the sharing of data between running Process (computing), processes in a computer system. Mechanisms for IPC may be provided by an operating system. Applications which use IPC are often categorized as client–server model, clients and servers, where the client requests data and the server responds to client requests. Many applications are both clients and servers, as commonly seen in distributed computing. IPC is very important to the design process for microkernels and nanokernels, which reduce the number of functionalities provided by the kernel. Those functionalities are then obtained by communicating with servers via IPC, leading to a large increase in communication when compared to a regular monolithic kernel. IPC interfaces generally encompass variable analytic framework structures. These processes ensure compatibility between the multi-vector protocols upon which IPC models rely. An IPC mechanism is either Synchroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robotics Software
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots. Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer science, robotics focuses on robotic automation algorithms. Other disciplines contributing to robotics include electrical engineering, electrical, control engineering, control, software engineering, software, Information engineering (field), information, electronics, electronic, telecommunications engineering, telecommunication, computer engineering, computer, mechatronic, and materials engineering, materials engineering. The goal of most robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people, such as finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring space, mines and shipwrecks. Others replace people in jobs that are boring, repetitive, or unpleasant, such as cleaning, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Seventh Framework Programme
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middleware For Robotic Applications
Middleware for Robotic Applications (MIRA) is a cross-platform, open-source software framework written in C++ that provides a middleware, several base functionalities and numerous tools for developing and testing distributed software modules. It also focuses on easy creation of complex, dynamic applications, while reusing these modules as plugins. The main purpose of MIRA is the development of robotic applications, but as it is designed to allow type safe data exchange between software modules using intra- and interprocess communication it is not limited to these kinds of applications. MIRA is developed in a cooperation of the MetraLabs GmbH and the Ilmenau University of Technologybr>Neuroinformatics and Cognitive Robotics Lab Therefore, MIRA was designed to fulfill the requirements of both commercial and educational purposes. Features General: * adds introspection/reflection and serialization to C++ with the usage of C++ language-constructs only (a meta-language or metaco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
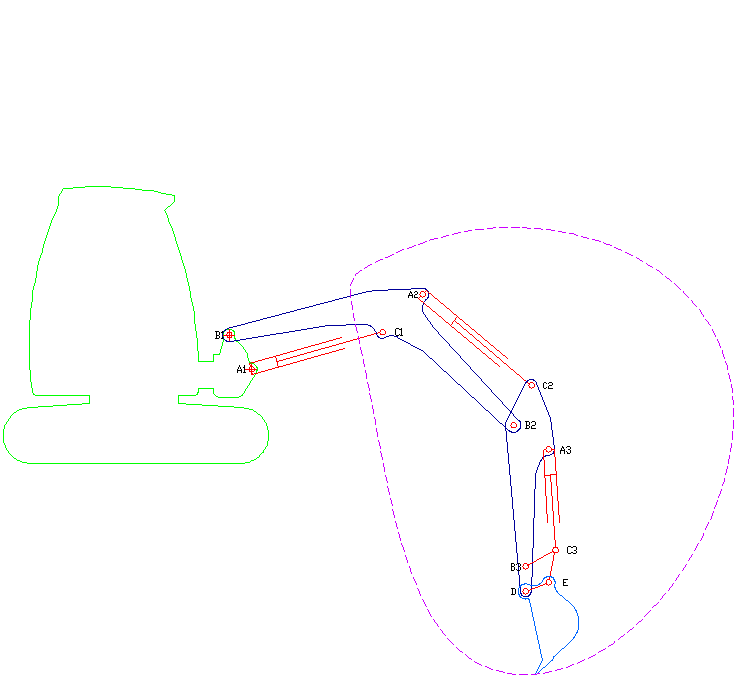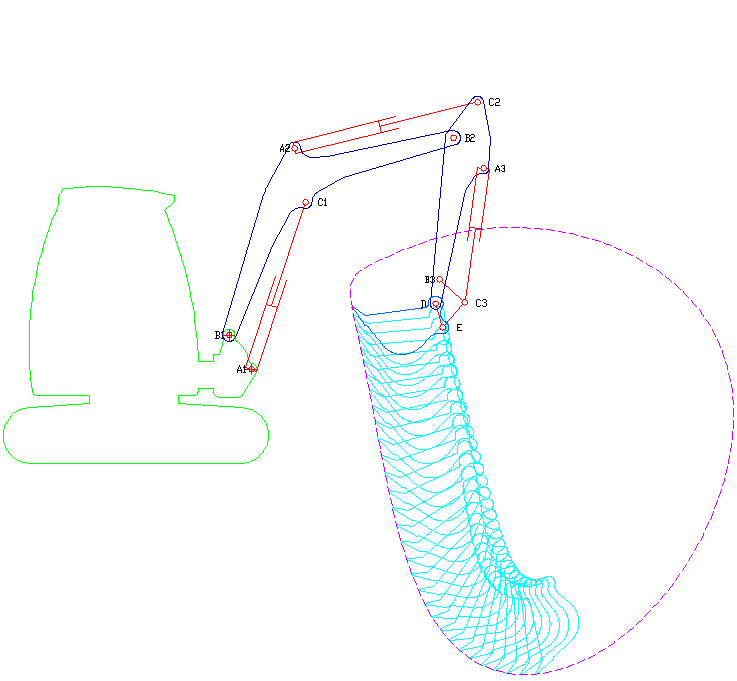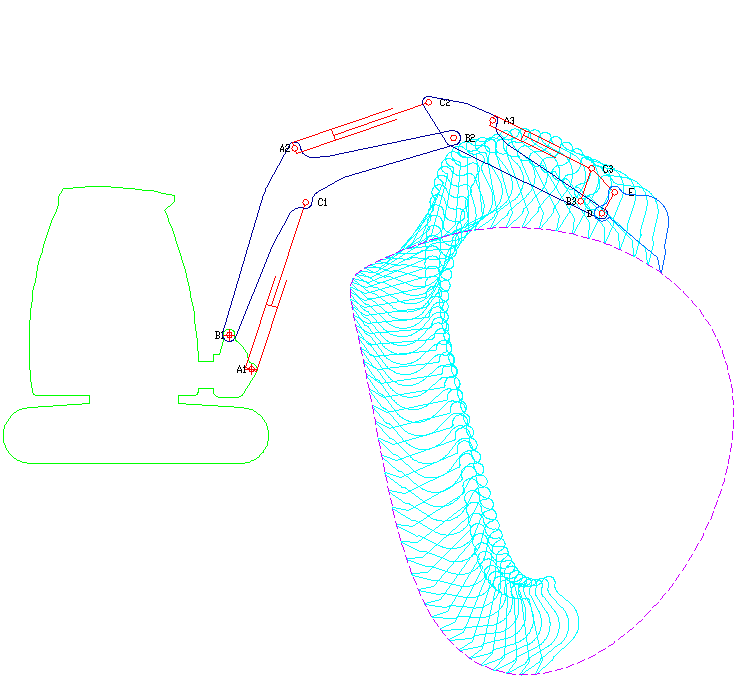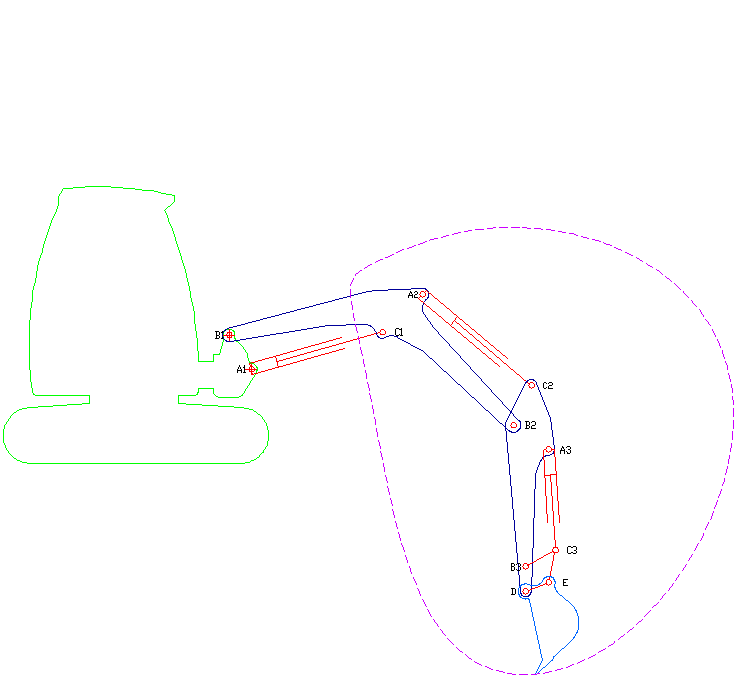
Excavator
Excavators are heavy equipment (construction), heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a backhoe, boom, dipper (or stick), Bucket (machine part), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with Caterpillar track, tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LHD (load, Haul, Dump Machine)
LHD (load, haul, dump) loaders are similar to conventional front end loaders but developed for the toughest of hard rock mining applications, keeping overall production economy, safety, and reliability in consideration. They are extremely rugged, highly maneuverable, and exceptionally productive. More than 75% of the world's underground metal mines use LHD for handling the muck of their excavations. Surface and Underground Excavations, 2nd Edition: Methods, Techniques and ..., By Ratan Raj Tatiya, p. 181 Constructional details LHDs have powerful Prim ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
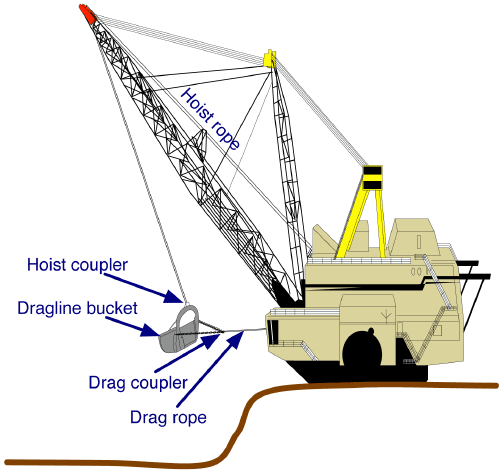
Dragline Excavator
A dragline excavator is a heavy-duty excavator used in civil engineering and surface mining. It was invented in 1904, and presented an immediate challenge to the steam shovel and its diesel and electric powered descendant, the power shovel. Much more efficient than even the largest of the latter, it enjoyed a heyday in extreme size for most of the 20th century, first becoming challenged by more efficient rotary excavators in the 1950s, then superseded by them on the upper end from the 1970s on. The largest ever walking dragline was Big Muskie, a Bucyrus-Erie 4250-W put online in 1969 that swung a , 325 ton capacity bucket, had a boom, and weighed 13,500 tons. The largest walking dragline produced as of 2014 was Joy Global’s digital AC drive control P&H 9020XPC, which has a bucket capacity of and boom lengths ranging from ; working weights vary between 7,539 and 8,002 tons. Types Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting crane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multicast Address
A multicast address is a logical identifier for a group of hosts in a computer network that are available to process datagrams or frames intended to be multicast for a designated network service. Multicast addressing can be used in the link layer (layer 2 in the OSI model), such as Ethernet multicast, and at the internet layer (layer 3 for OSI) for Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) or Version 6 (IPv6) multicast. IPv4 IPv4 multicast addresses are defined by the most-significant bit pattern of ''1110''. This originates from the classful network design of the early Internet when this group of addresses was designated as ''Class D''. The CIDR notation for this group is . The group includes the addresses from to . The address range is divided into blocks each assigned a specific purpose or behavior. ;Local subnetwork :Addresses in the range of to are individually assigned by IANA and designated for multicasting on the local subnetwork only. For example, the Routing Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Publish–subscribe Pattern
In software architecture, the publish–subscribe pattern (pub/sub) is a messaging pattern in which message senders, called publishers, categorize messages into classes (or ''topics''), and send them without needing to know which components will receive them. Message recipients, called subscribers, express interest in one or more classes and only receive messages in those classes, without needing to know the identity of the publishers. This pattern decouples the components that produce messages from those that consume them, and supports asynchronous, many-to-many communication. The publish–subscribe model is commonly contrasted with message queue-based and point-to-point messaging models, where producers send messages directly to consumers. Publish–subscribe is a sibling of the message queue paradigm, and is typically a component of larger message-oriented middleware systems. Many modern messaging frameworks and protocols, such as the Java Message Service (JMS), Apac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CSIRO
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency that is responsible for scientific research and its commercial and industrial applications. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia as well as in France and the United States, employing over 6,500 people. Federally funded scientific research in Australia began in 1916 with the creation of the Advisory Council of Science and Industry. However, the council struggled due to insufficient funding. In 1926, research efforts were revitalised with the establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly, achieving significant early successes. In 1949, legislative changes led to the renaming of the organisation as Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |