|
Rivet Nut
A rivet nut, also known as a blind rivet nut, or rivnut, is a one-piece internally threaded and counterbored tubular rivet that can be anchored entirely from one side. It is a kind of threaded insert. There are two types: one is designed to form a bulge on the back side of the panel as a screw is tightened in its threads. The other is similarly drawn in using a screw, but is drawn into the sleeve instead of creating a bulge. History The first rivet nut was created by BF Goodrich in the 1930s, and sold under the trademark RIVNUT®. It was first used to mount rubber de-icing boots to aircraft wings. Usage In the field of aviation, rivet nuts are often used to attach various items, such as static dischargers and inspection access covers, to the surface of an aircraft. Rivet nuts are an ideal replacement for weld nuts because they will not distort base materials, eliminate weld splatter, toxic fumes, and other by-products of the welding process, and can be installed in many di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
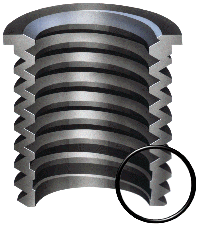
Screw Thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and the latter called a ''tapered'' thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener. The mechanical advantage of a screw thread depends on its ''lead'', which is the linear distance the screw travels in one revolution. In most applications, the lead of a screw thread is chosen so that friction is sufficient to prevent linear motion being converted to rotary, that is so the screw does not slip even when linear force is applied, as long as no external rotational force is present. This characteristic is essential to the vast majority of its uses. The tightening of a fastener's screw thread is comparable to driving a wedge into a gap until it sticks fast thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterbore
A counterbore (symbol: ⌴) is a cylindrical flat-bottomed hole that enlarges another coaxial hole, or the tool used to create that feature. A counterbore hole is typically used when a fastener, such as a socket head cap screw or fillister head screw, is required to sit flush with or below the level of a workpiece's surface. Whereas a counterbore is a ''flat-bottomed'' enlargement of a smaller coaxial hole, a countersink is a '' conical'' enlargement of such. A spotface often takes the form of a very shallow counterbore. As mentioned above, the cutters that produce counterbores are often also called counterbores; sometimes, to avoid ambiguity, the term counterbore cutter is used instead. The symbol is Unicode character . Description A counterbore hole is usually used when the head of a fastener, such as a hex head or socket head capscrew, is required to be flush with or below the level of a workpiece's surface. For a spotface, material is removed from a surface to mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivet
A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite to the head is called the ''tail''. On installation, the rivet is placed in a punched or drilled hole, and the tail is ''upset'', or ''bucked'' (i.e., deformed), so that it expands to about 1.5 times the original shaft diameter, holding the rivet in place. In other words, the pounding or pulling creates a new "head" on the tail end by smashing the "tail" material flatter, resulting in a rivet that is roughly a dumbbell shape. To distinguish between the two ends of the rivet, the original head is called the ''factory head'' and the deformed end is called the ''shop head'' or buck-tail. Because there is effectively a head on each end of an installed rivet, it can support tension loads. However, it is much more capable of supporting shear loads (loads perpendicular to the axis of the shaft). Fastenings used in traditional w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threaded Insert
A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thread on a material too thin to accept it, mold or cast threads into a work piece thereby eliminating a machining operation, or simplify changeover from unified to metric threads or vice versa. Types Thread inserts come in many varieties, depending on the application. Threaded inserts for plastics are used in plastic materials and applied with thermal insertion or ultrasonic welding machines. Manufacturers of ready-to-assemble furniture often ship the parts with threaded inserts and other kinds of knock-down fasteners pre-installed. People who use sheet metal or sandwich panel or honeycomb sandwich-structured composite often install threaded inserts to spread shear, tension, and torque loads over a larger area of the material. Captive n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De-icing Boot
A deicing boot is a type of ice protection system installed on aircraft surfaces to permit a mechanical deicing in flight. Such boots are generally installed on the leading edges of wings and control surfaces (e.g. horizontal and vertical stabilizer) as these areas are most likely to accumulate ice and any contamination could severely affect the aircraft's performance. Design A deicing boot consists of a thick rubber membrane that is installed over the surface to be deiced. As atmospheric icing occurs and ice builds up, a pneumatic system inflates the boot with compressed air. This expansion in size cracks any ice that has accumulated, and this ice is blown away into the airflow. The boots are then deflated to return the wing or surface to its optimal shape. Boots require proper care. Holes in the boot may create air leaks that will decrease the effectiveness of the boots. As such, boots must be carefully inspected before each flight and any holes or cuts must be patched. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Discharger
Static dischargers, also called static wicks or static discharge wicks, are devices used to remove static electricity from aircraft in flight. They take the form of small sticks pointing backwards from the wings, and are fitted on almost all civilian aircraft. Function Precipitation static is an electrical charge on an airplane caused by flying through rain, snow, ice, or dust particles. Charge also accumulates through friction between the aircraft hull and the air. When the aircraft charge is great enough, it discharges into the surrounding air. Without static dischargers, the charge discharges in large batches through pointed aircraft extremities, such as antennas, wing tips, vertical and horizontal stabilizers, and other protrusions. The discharge creates a broad-band radio frequency noise from DC to 1000 MHz, which can affect aircraft communication. To control this discharge, so as to allow the continuous operation of navigation and radio communication systems, stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weld Nut
A weld nut is a special type of nut specifically designed to be welded to another object (spot welding). There are various types for different applications. Types ;Round base nuts These nuts have a long threaded cylinder with a large circular base to make welding easy. They also sometimes have projections (known as weld nibs or bosses) to keep the nut from warping while welding with a high current.McMaster-Carr, p3151 ;Slab base nuts These are very similar to the round base nuts, but with an obround, or slab shaped, base. These are used in channels, tubes, or other tight quarters. ;Tab base nuts Tab base nuts are designed for spot welding on flat workpieces. They have a locating boss around the threads to locate it in a pilot hole. ;Hex & square nuts These nuts are very similar to standard square or hex nuts, but have a locating boss and welding projections. The bosses also keep weld spatter out of the threads.McMaster-Carr, p3152 ;Retainer weld nuts Retainer weld nuts, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swage Nut
A swage nut or self-clinching nut is a type of nut or threaded insert that is used on sheet metal. It permanently anchors itself to the sheet metal by swaging the surrounding material. Generally, the swage nut is made of a hard metal such as stainless steel, which is inserted into a pre-drilled hole in a softer ductile material such as aluminum. The inserted shank has three diameters: a main shaft which fits the hole closely, a thin smaller-diameter undercut, and a larger-diameter serrated clinching ring. Forcing the clinching ring into softer material, with an arbor press or by tightening a screw through the hole, causes it to plastically deform (swage) into the annular recess in the shank. This locks the nut into the hole. The knurling on the clinching ring is not necessary for this step, but prevents the nut from rotating after installation. This is a popular method for adding strong, load-bearing threads to a relatively thin piece of soft sheet metal. Self-clinching n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction Drilling
Friction drilling is a method of making holes in metal in which the material is pushed out of the way with the aid of heat from friction. The process is also called thermal drilling, flow drilling, form drilling, or friction stir drilling. Friction drilling is commonly used on bicycle frames, heat exchangers, and to create holes for mounting bearings. History In 1923, the Frenchman Jean Claude de Valière tried making a tool that could make holes in metal by friction heat, instead of by machining. It was only a moderate success, because at that time the right materials were not yet available. Moreover, he hadn't yet discovered the right shape for this kind of tool. It was not until the 1980s that a useful tool could be produced. Principle Friction drilling uses a conical bit made of very heat-resistant material such as cemented carbide. This device is pressed against a target material with both high rotational speed and high pressure. That way, there is a high local production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |