|
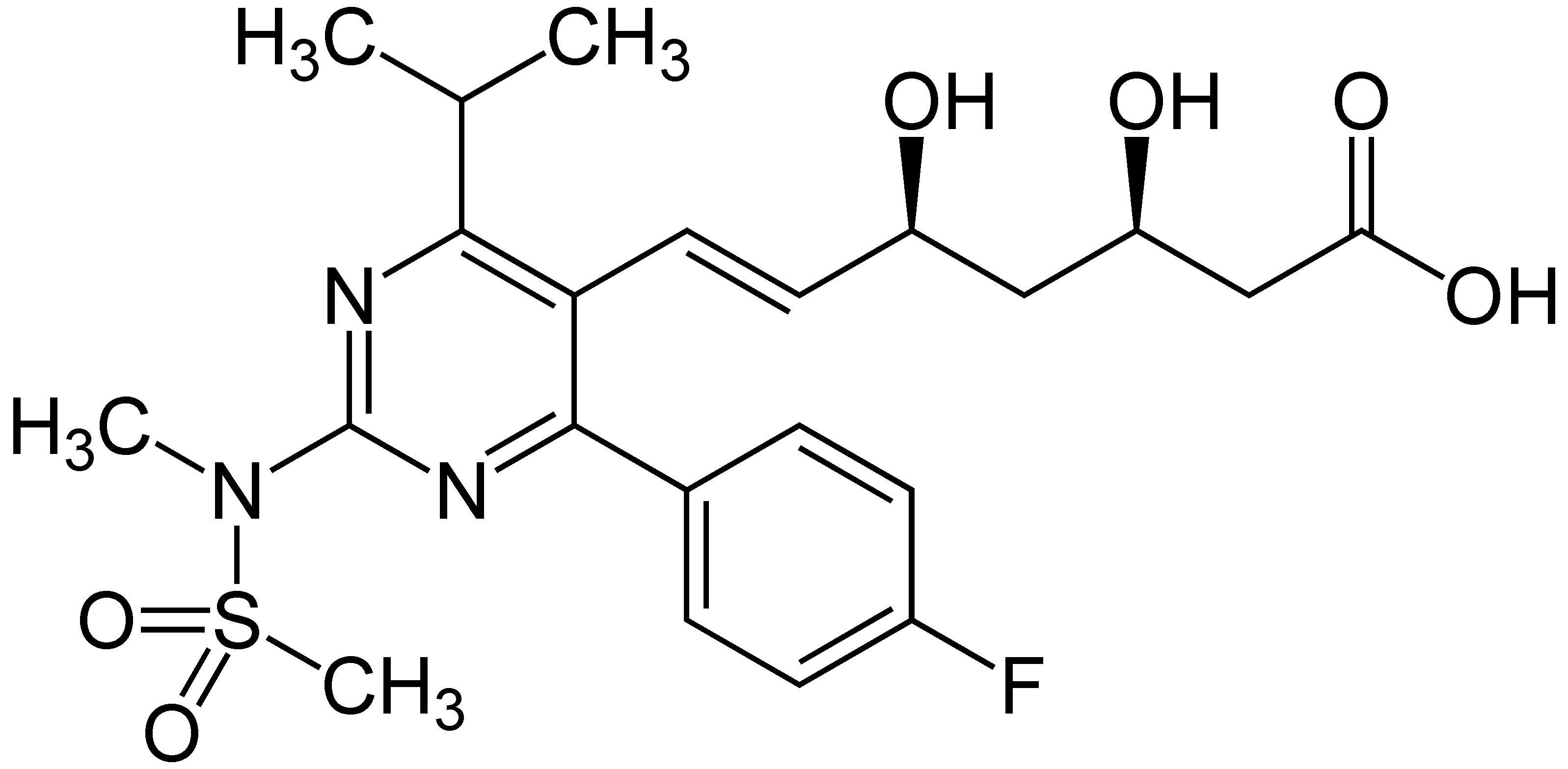
Ripretinib
Ripretinib, sold under the brand name Qinlock, is a medication for the treatment of adults with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), a type of tumor that originates in the gastrointestinal tract. It is taken by mouth. Ripretinib inhibits the activity of the kinases KIT and PDGFRA, which helps keep cancer cells from growing. The most common side effects include alopecia (hair loss), fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, myalgia (muscle pain), diarrhea, decreased appetite, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (a skin reaction in the palms and soles) and vomiting. Ripretinib was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2020, in Australia in July 2020, and in the European Union in November 2021. Ripretinib is the first new drug specifically approved in the United States as a fourth-line treatment for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Medical uses Ripretinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced gastrointestina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
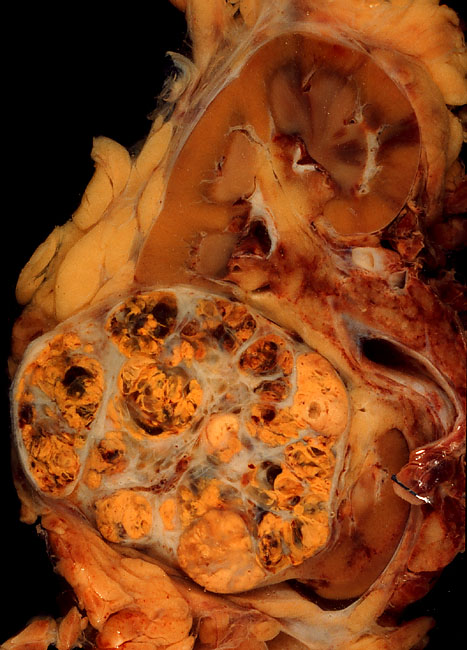
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. GISTs arise in the smooth muscle pacemaker interstitial cell of Cajal, or similar cells. They are defined as tumors whose behavior is driven by mutations in the KIT gene (85%), PDGFRA gene (10%), or BRAF kinase (rare). 95% of GISTs stain positively for KIT (CD117). Most (66%) occur in the stomach and gastric GISTs have a lower malignant potential than tumors found elsewhere in the GI tract. Classification GIST was introduced as a diagnostic term in 1983. Until the late 1990s, many non-epithelial tumors of the gastrointestinal tract were called "gastrointestinal stromal tumors". Histopathologists were unable to specifically distinguish among types we now know to be dissimilar molecularly. Subsequently, CD34, and later CD117 were identified as markers that could distinguish the various types. Additionally, in the absence of specific therapy, the diagnostic categori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Track (FDA)
Fast track is a designation by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) of an investigational drug for expedited review to facilitate development of drugs that treat a serious or life-threatening condition and fill an unmet medical need. Fast Track designation must be requested by the drug company. The request can be initiated at any time during the drug development process. FDA will review the request and attempt to make a decision within sixty days. Purpose Fast Track is one of five Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approaches to make new drugs available as rapidly as possible: the others are priority review, breakthrough therapy, accelerated approval and Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy. Fast Track was introduced by the FDA Modernization Act of 1997. Requirements Fast track designation is designed to aid in the development and expedite the review of drugs which show promise in treating a serious or life-threatening disease and address an unmet medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Treatments
Cancer can be treated by surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy (including immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibody therapy) and synthetic lethality, most commonly as a series of separate treatments (e.g. chemotherapy before surgery). The choice of therapy depends upon the location and grade of the tumor and the stage of the disease, as well as the general state of the patient (performance status). Cancer genome sequencing helps in determining which cancer the patient exactly has for determining the best therapy for the cancer. A number of experimental cancer treatments are also under development. Under current estimates, two in five people will have cancer at some point in their lifetime. Complete removal of the cancer without damage to the rest of the body (that is, achieving cure with near-zero adverse effects) is the ideal, if rarely achieved, goal of treatment and is often the goal in practice. Sometimes this can be accomplished by sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineoplastic Drugs
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals ( signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Adopted Name
A United States Adopted Name (USAN) is a unique nonproprietary name assigned to a medication marketed in the United States. Each name is assigned by the USAN Council, which is co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA). The USAN Program states that its goal is to select simple, informative, and unique nonproprietary names (also called generic names) for drugs by establishing logical nomenclature classifications based on pharmacological or chemical relationships. In addition to drugs, the USAN Council names agents for gene therapy and cell therapy, List of soft contact lens materials, contact lens polymers, surgical materials, diagnostics, carriers, and substances used as an excipient. The USAN Council works in conjunction with the World Health Organization (WHO) international nonproprietary name (INN) Expert Committee and national nomenclature groups to standardize drug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combination with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regorafenib
Regorafenib, sold under the brand name Stivarga among others, is an oral multi-kinase inhibitor developed by Bayer which targets angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). Regorafenib shows anti-angiogenic activity due to its dual targeted VEGFR2-TIE2 tyrosine kinase inhibition. Since 2009 it was studied as a potential treatment option in multiple tumor types. By 2015 it had two US approvals for advanced cancers. Approvals and indications Metastatic colorectal cancer Regorafenib demonstrated to increase the overall survival of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and has been approved by the US FDA on September 27, 2012. After a manufacturer's appeal Regorafenib was restored to the list of treatments funded by the English Cancer Drugs Fund. Advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours On February 25, 2013 the US FDA expanded the approved use to treat patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors that cannot be surgically removed and no long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priority Review
Priority review is a program of the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to expedite the review process for drugs that are expected to have a particularly great impact on the treatment of a disease. The priority review voucher program is a program that grants a voucher for priority review to a drug developer as an incentive to develop treatments for disease indications with limited profitability. Priority review vouchers are currently earned by pharmaceutical companies for the development and approval of drugs treating neglected tropical diseases, rare pediatric diseases, and "medical countermeasures" for terrorism. The voucher can be used for future drugs that could have wider indications for use, but the company is required to pay a fee (approximately $2.8 million) to use the voucher. When seeking approval for a drug, manufacturers can apply to the FDA for priority review. This is granted when a drug is intended to treat a serious condition and would "provide a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |