|
Ripon Barbel
The Ripon barbel (''Labeobarbus altianalis'') is an East African ray-finned fish species in the family Cyprinidae. A notably large barb, its maximum recorded total length is . Taxonomy Like other African "barbs", placement of this species in ''Barbus'' – the genus of the typical barbels and relatives – was provisional. Though called "barbel", it is probably not closely enough related to the typical barbels – the core group of ''Barbus'' – to be considered congeneric. Several supposedly distinct species have been merged into ''B. altianalis'', and numerous subspecies have been proposed. None of these are deemed valid. Some authorities place this species in the genus Labeobarbus. On the other hand, '' B. longifilis'', '' B. paucisquamatus'' and '' B. somereni'' were once considered subspecies of ''L: altianalis'', the second as sspp. ''lobogenysoides'' and ''paucisquamata'' and the third as ssp. ''urundensis''. Significant junior synonyms of ''L. altianal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labeobarbus Intermedius
''Labeobarbus intermedius'' is an East African ray-finned fish species in the family Cyprinidae. Like the closely related yellowfish, it is hexaploid. A large species, the maximum recorded standard length is nearly . This species has a subspecies named '' Labeobarbus intermedius intermedius''. Systematics and taxonomy The year of its first description – as ''Barbus intermedius'' – was for some time erroneously reported as 1837. ''L. intermedius'' was still placed by most modern authors in the "wastebin genus" ''Barbus'' by default, and the IUCN still does so until a thorough taxonomic revision of the African "barbs" is published. However, the species is increasingly being restored to the related yellowfish genus ''Labeobarbus'', which seems a much more appropriate placement. It is a close relative of ''Labeobarbus bynni'', another African "barb". No subspecies are recognized at present. The population from the Barino River basin invalidly described as ''L. i. austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbus Paucisquamatus
''Labeobarbus lobogenysoides'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus ''Labeobarbus'' is endemic to the Loama River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in .... References lobogenysoides Taxa named by Jacques Pellegrin Fish described in 1935 {{Labeobarbus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake George (Uganda)
Lake George or Lake Katunguru is a lake in Uganda. It covers a total surface area of and is a part of the African Great Lakes system, although it is not considered one of the Great Lakes. Like the other lakes in the region, it was renamed after a member of the British royal family, in this case Prince George, later to become King George V. Lake George drains to the southwest into Lake Edward through the Kazinga Channel. The area surrounding the lake is populated by the Batooro, Basongora, Banyampaka and Banyankore peoples, among others. All these nations speak closely-related dialects which are generally referred as Runyakitara language. ''Akatunguru'' is a word which means ‘onion’ and is used by all these different peoples. Thus, the lake came to be known as Katunguru because of its onion-like shape. The explorer Henry Morton Stanley was the first European to see the lake in 1875, after following the course of the Katonga River from Lake Victoria during his trans-Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Edward
Lake Edward (locally Rwitanzigye or Rweru) is one of the smaller African Great Lakes. It is located in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift, on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Uganda, with its northern shore a few kilometres south of the equator. History Henry Morton Stanley first saw the lake in 1888, during the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition. The lake was named in honour of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales, son of then British monarch Queen Victoria, and later to become King Edward VII. In 1973, Uganda and Zaire (DRC) renamed it Lake Idi Amin after Ugandan dictator Idi Amin. After his overthrow in 1979, it recovered its former name. In 2014, the lake was the center of an oil dispute. SOCO international entered the premises of the Virunga National Park where the lake is situated to prospect for oil. However, villagers and workers who attempted to stop the oil company from entering the area were beaten up and even kidnapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
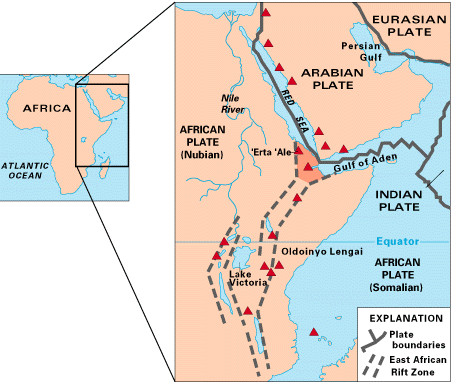
East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor. A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate, at a rate of 6-7 mm per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria Microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria Microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS. Extent A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after Lake Superior in North America. In terms of volume, Lake Victoria is the world's ninth-largest continental lake, containing about of water. Lake Victoria occupies a shallow depression in Africa. The lake has an average depth of and a maximum depth of .United Nations, ''Development and Harmonisation of Environmental Laws Volume 1: Report on the Legal and Institutional Issues in the Lake Victoria Basin'', United Nations, 1999, page 17 Its catchment area covers . The lake has a shoreline of when digitized at the 1:25,000 level, with islands constituting 3.7% of this length. The lake's area is divided among three countries: Kenya occupies 6% (), Uganda 45% (), and Tanzania 49% (). Though having multiple local language names ( luo, Nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mara River
The Mara River is a river in that begins in Narok County (Kenya) and in ends in Mara Region (Tanzania), and lies across the migration path of ungulates in the Maasai Mara/Serengeti ecosystem. The River's Flow The Mara River basin covers a surface of 13,504 km2, of which approximately 65% is located in Kenya and 35% in Tanzania.Jim K. Kairu, "Biodiversity Action Plan for Sustainable Management: Mara River Basin" (WWF, 2008) From its sources in the Kenyan highlands, the river flows for about 395 km and originates from the Mau Escarpment and drains into Lake Victoria. The basin can be roughly divided into four land use and/or administrative units. The Mara's Regions The Mau Escarpment: The Mara River originates from the Napuiyapi swamp (2932 m), with the main perennial tributaries being the Amala and the Nyangores, which drain from the western Mau Escarpment. This part of the basin supports besides forests, both small-scale agriculture (less than 10 acres) and med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean. The Irtysh is a chief tributary of the Ob river and is also the longest tributary river in the world with a length of . The Madeira River is the largest tributary river by volume in the world with an average discharge of . A confluence, where two or more bodies of water meet, usually refers to the joining of tributaries. The opposite to a tributary is a distributary, a river or stream that branches off from and flows away from the main stream. PhysicalGeography.net, Michael Pidwirny & S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's Linnaean taxonomy, system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard de Jussieu, Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Baringo
Lake Baringo is, after Lake Turkana, the most northern of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes, with a surface area of and an elevation of . The lake is fed by several rivers: the Molo, Perkerra and Ol Arabel. It has no obvious outlet; the waters are assumed to seep through lake sediments into the faulted volcanic bedrock. It is one of the two freshwater lakes in the Rift Valley in Kenya, the other being Lake Naivasha. See "Kenya designates freshwater lake in Great Rift Valley," aRamsar 2009 - 2002 The lake is in a remote hot and dusty area with over 470 species of birds, occasionally including migrating flamingos. A Goliath heronry is located on a rocky islet in the lake known as Gibraltar. Description The lake is part of the East African Rift system. The Tugen Hills, an uplifted fault block of volcanic and metamorphic rocks, lies west of the lake. The Laikipia Escarpment lies to the east. Water flows into the lake from the Mau Hills and Tugen Hills. It is a critical habitat a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amala River
Amala may refer to: People * Amala Akkineni, South Indian actress * Amala Chebolu, playback singer in the Telugu film industry, also known as Tollywood * Amala Paul (born 1991), South Indian actress * Amala Shankar (1919–2020), Indian dancer * Amala and Kamala, two girls discovered in 1920 who were allegedly raised by wolves in India *Amala Ratna Zandile Dlamini, known professionally as Doja Cat, American rapper, singer, songwriter, and record producer Places * Amala, Iran, a village in Kermanshah Province, Iran * Amala Nagar, a village in Kerala, India Other * Amala (food), a food in western Africa * Amala (mythology), a Native American mythological giant * ''Amala'' (TV series), an Indian television series * Amala Institute of Medical Sciences in Thrissur, India * Seeds of the ''Nectandra ''Nectandra'' is a genus of plant in the family Lauraceae. They are primarily Neotropical, with ''Nectandra coriacea'' being the only species reaching the southernmost United States. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |