|
Rings Of Chariklo
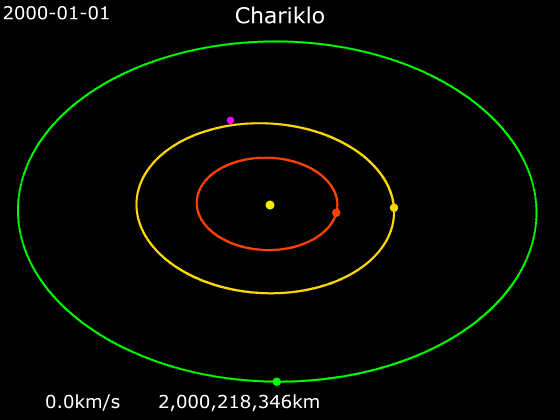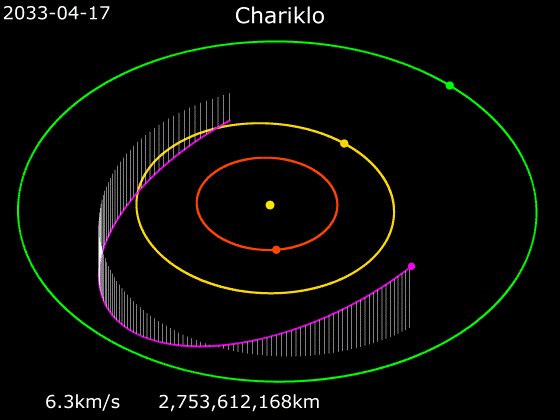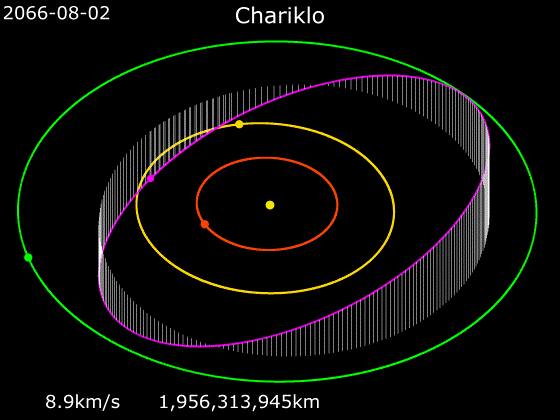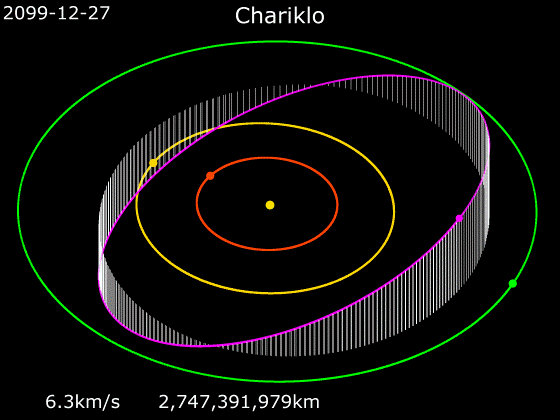
The minor planet and Centaur (astronomy), centaur 10199 Chariklo, with a diameter of about , is the smallest celestial object with confirmed rings and the fifth ringed celestial object discovered in the Solar System, after the Gas giant, gas giants and Ice giant, ice giants. Orbiting Chariklo is a bright Planetary ring, ring system consisting of two narrow and dense bands, 6–7 km (4 mi) and 2–4 km (2 mi) wide, separated by a gap of . The rings orbit at distances of about from the centre of Chariklo, a thousandth the distance between Earth and the Moon. The discovery was made by a team of astronomers using ten telescopes at various locations in Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Uruguay in South America during observation of a stellar occultation on 3 June 2013, and was announced on 26 March 2014. The existence of a ring system around a minor planet was unexpected because it had been thought that rings could only be stable around much more massive bodies. Ring sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariklo With Rings Eso1410b
10199 Chariklo is the largest confirmed Centaur (minor planet), centaur (small body of the outer Solar System). It orbits the Sun between Saturn and Uranus, list of Uranus-crossing minor planets, grazing the orbit of Uranus. On 26 March 2014, astronomers announced the discovery of two planetary ring, rings (nicknamed as the rivers Oyapock, Oiapoque and Chuí Stream, Chuí) around Chariklo by observing a stellar occultation, making it the first minor planet known to have rings. A photometric study in 2001 was unable to find a definite period of rotation. Infrared observations of Chariklo indicate the presence of water ice, which may in fact be located in its rings. Michael E. Brown, Michael Brown's website lists it as List of possible dwarf planets, possibly a dwarf planet with a measured diameter of 232 km. Discovery and naming Chariklo was discovered by James V. Scotti of the Spacewatch program on February 15, 1997. Chariklo is named after the nymph Chariclo ('), the wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation that pre-dates the Greeks; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Its old astronomical symbol is (♏︎). Notable features Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco (Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco (Sargas, of unknown origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale). Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco (Shaula) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes. The constellation' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontifical Catholic University Of Chile
The Pontifical Catholic University of Chile (''PUC or UC Chile'') ( es, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile) is one of the six Catholic Universities existing in the Chilean university system and one of the two pontifical universities in the country, along with the Pontifical Catholic University of Valparaíso. Founded in 1888, it is also one of Chile's oldest universities and one of the most recognized educational institutions in Latin America. Pontifical Catholic University of Chile has a strong and long-standing rivalry with Universidad de Chile, as they are both widely recognized as the most traditional and prestigious in the country, and one is catholic and the other, secular. This rivalry also translates to sports, especially football. Campuses UC Chile has four campuses in Santiago and one campus in Villarrica. The campuses in Santiago are: * Casa Central (in downtown Santiago) * San Joaquín (in Macul Commune of Greater Santiago) * Oriente (in Ñuñoa Commune o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leoncito Astronomical Complex
The El Leoncito Astronomical Complex (Spanish: Complejo Astronómico El Leoncito - CASLEO) is an astronomical observatory in the San Juan Province of Argentina. CASLEO is one of two observatories located within El Leoncito National Park, which is in a part of the country which rarely sees cloud cover. The other facility in the park is the Carlos U. Cesco Astronomical Station of the Félix Aguilar Observatory. CASLEO was established in 1983 by an agreement between National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) of Argentina, the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MINCYT) of Argentina, the National University of San Juan (UNSJ), the National University of La Plata (UNLP), and the National University of Córdoba (UNC). The facility was dedicated in 1986 and regular observations began in 1987. CASLEO's telescopes are located in two separate areas within the El Leoncito Park. The Jorge Sahade and Submillimeter telescopes are at the main site on the edge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Pachón
Cerro Pachón (Spanish for "Pachón hill") is a mountain located close to the Chilean city of Vicuña and 10 km southeast of the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory, at an altitude of 2,715 m above sea level in the foothills of the Andes. The location is exceedingly dry, making it suitable for infrared observations. The air overhead is very stable, yielding excellent visualization/seeing. During the summer months, Cerro Pachón is often above the haze layer that can envelop lower altitudes. There are currently two telescopes commissioned on Cerro Pachón, Gemini South and the Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope. A third, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, is under construction. Gallery File:Cerro Las Tortolas indistance incenter.jpg, Wide view observatories from the air, including Cerro Pachón. In the distance are the Andes File:Telescope Silhouettes at Cerro Pachón.jpg, A night view of the Gemini South, the southern half of the international Gemini Observatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Astrophysical Research Telescope
The Southern Astrophysical Research (SOAR) telescope is a modern aperture optical and near-infrared telescope located on Cerro Pachón, Chile at elevation. It was commissioned in 2003, and is operated by a consortium including the countries of Brazil and Chile, Michigan State University, the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) (part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, NOAO), and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Partners have guaranteed shares varying from 10 to 30 percent of the observing time. The telescope uses active optics on its primary and secondary mirrors to attain median image quality 0.7 arcsec at a wavelength of 500 nm. Multiple instruments are available on standby, mounted at unusually high weight-capacity Nasmyth foci and two lower capacity bent- Cassegrain foci. Switching is accomplished within a few minutes by rotating the 45° tertiary mirror. The pointing of this mirror is adjusted at high speed to prevent image blur f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory
The Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) is an astronomical observatory located on Cerro Tololo in the Coquimbo Region of northern Chile, with additional facilities located on Cerro Pachón about to the southeast. It is approximately east of La Serena, where support facilities are located. The site was identified by a team of scientists from Chile and the United States in 1959, and it was selected in 1962. Construction began in 1963 and regular astronomical observations commenced in 1965. Construction of large buildings on Cerro Tololo ended with the completion of the Víctor Blanco Telescope in 1974, but smaller facilities have been built since then. Cerro Pachón is still under development, with two large telescopes (Gemini South and SOAR) inaugurated since 2000, and one in the early stages of construction (the Vera C. Rubin Observatory) The principal telescopes at CTIO are the 4 m Víctor M. Blanco Telescope, named after Puerto Rican astronomer Víctor Manuel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PROMPT Telescopes
PROMPT, an acronym for Panchromatic Robotic Optical Monitoring and Polarimetry Telescopes, is being built by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) in Chile. PROMPT's primary objective is rapid and simultaneous multiwavelength observations of gamma-ray burst afterglows, some when they are only tens of seconds old. In addition to measuring redshifts by dropout, and early-time SFDs and extinction curves of sufficiently bright afterglows in unprecedented detail, PROMPT will facilitate quick response observations at larger observatories such as the UNC-led 4.1-m SOAR Telescope. PROMPT will also serve as a platform for undergraduate and high school education throughout the State of North Carolina. PROMPT consists of six 0.41-m Ritchey-Chrétien telescopes by RC Optical Systems on rapidly slewing (9°/sec) Paramount ME mounts by Software Bisque, each under a clamshell dome by Astro Haven. Five of these telescopes use rapid-rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRAPPIST
The Trappists, officially known as the Order of Cistercians of the Strict Observance ( la, Ordo Cisterciensis Strictioris Observantiae, abbreviated as OCSO) and originally named the Order of Reformed Cistercians of Our Lady of La Trappe, are a Catholic religious order of cloistered monastics that branched off from the Cistercians. They follow the Rule of Saint Benedict and have communities of both monks and nuns that are known as Trappists and Trappistines, respectively. They are named after La Trappe Abbey, the monastery from which the movement and religious order originated. The movement first began with the reforms that Abbot Armand Jean le Bouthillier de Rancé introduced in 1664, later leading to the creation of Trappist congregations, and eventually the formal constitution as a separate religious order in 1892. History The order takes its name from La Trappe Abbey or ''La Grande Trappe'', located in the French province of Normandy, where the reform movement began. Arma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets, or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, a cataclysmic variable star, a supernova or a microlensing event or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of the light curve, together with other observations, can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces it or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly done from their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucky Imaging
Lucky imaging (also called lucky exposures) is one form of speckle imaging used for astrophotography. Speckle imaging techniques use a high-speed camera with exposure times short enough (100 ms or less) so that the changes in the Earth's atmosphere during the exposure are minimal. With lucky imaging, those optimum exposures least affected by the atmosphere (typically around 10%) are chosen and combined into a single image by shifting and adding the short exposures, yielding much higher angular resolution than would be possible with a single, longer exposure, which includes all the frames. Explanation Images taken with ground-based telescopes are subject to the blurring effect of atmospheric turbulence (seen to the eye as the stars twinkling). Many astronomical imaging programs require higher resolution than is possible without some correction of the images. Lucky imaging is one of several methods used to remove atmospheric blurring. Used at a 1% selection or less, lucky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Silla Observatory
La Silla Observatory is an astronomy, astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is one of the largest in the Southern Hemisphere and was the first in Chile to be used by ESO. The La Silla telescopes and instruments are located 150 km northeast of La Serena, Chile, La Serena at the outskirts of the Chilean Atacama Desert, one of the driest and most remote areas of the world. Like other observatories in this geographical area, La Silla is located far from sources of light pollution and, like the Paranal Observatory, home to the Very Large Telescope, it has one of the darkest night skies on the Earth. History Following the decision in 1963 to approve Chile as the site for the ESO observatory, scouting parties were sent to various locations to assess their suitability. The site that was decided upon was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



