|
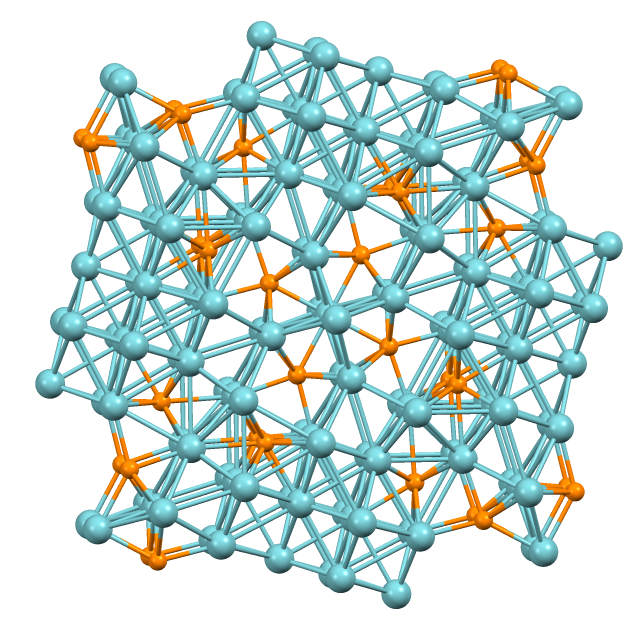
Rhenium Disulfide
Rhenium disulfide is an inorganic compound of rhenium and sulfur with the formula ReS2. It has a layered structure where atoms are strongly bonded within each layer. The layers are held together by weak Van der Waals bonds, and can be easily peeled off from the bulk material. Production ReS2 is found in nature as the mineral rheniite. It can be synthesized from the reaction between rhenium and sulfur at 1000 °C, or the decomposition of rhenium(VII) sulfide at 1100 °C: :Re + 2 S → ReS2 :Re2S7 → 2 ReS2 + 3 S Nanostructured ReS2 can usually be achieved through mechanical exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and chemical and liquid exfoliations. Larger crystals can be grown with the assistance of liquid carbonate flux at high pressure. It is widely used in electronic and optoelectronic device, energy storage, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic reactions. Properties It is a two-dimensional (2D) group VII transition metal dichalcogenide : 220px, Cadmium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triclinic
180px, Triclinic (a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ γ ) In crystallography, the triclinic (or anorthic) crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three basis vectors. In the triclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal length, as in the orthorhombic system. In addition, the angles between these vectors must all be different and may not include 90°. The triclinic lattice is the least symmetric of the 14 three-dimensional Bravais lattices. It has (itself) the minimum symmetry all lattices have: points of inversion at each lattice point and at 7 more points for each lattice point: at the midpoints of the edges and the faces, and at the center points. It is the only lattice type that itself has no mirror planes. Crystal classes The triclinic crystal system class names, examples, Schönflies notation, Hermann-Mauguin notation, point groups, International Tables for Crystallography space group number, orbifold, type, and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der Waals contact distance; this phenomenon resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfides
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion, S2−, does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + 8&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenium Compounds
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except +2, although the oxidation states +7, +6, +4, and +2 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. Tetrathioperrhenate anion eS4sup>− is possible. Chalcogenides Oxides Rhenium(IV) oxide (or rhenium dioxide) is an oxide of rhenium, with the formula ReO2. This gray to black crystalline solid is a laboratory reagent that can be used as a catalyst. It adopts the rutile structure. It forms via comproportionation: :2 Re2O7 + 3 Re → 7 ReO2 Single crystals are obtained by chemical transport, using iodine as the transporting agent. At high temperatures it undergoes disproportionation. It forms perrhenates with alkaline hydrogen peroxide and oxidizing acids. In m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Dichalcogenide
: 220px, Cadmium sulfide, a prototypical metal chalcogenide, is used as a yellow pigment. A chalcogenide is a chemical compound consisting of at least one chalcogen anion and at least one more electropositive element. Although all group 16 elements of the periodic table are defined as chalcogens, the term chalcogenide is more commonly reserved for sulfides, selenides, tellurides, and polonides, rather than oxides. Many metal ores exist as chalcogenides. Photoconductive chalcogenide glasses are used in xerography. Some pigments and catalysts are also based on chalcogenides. The metal dichalcogenide MoS2 is a common solid lubricant. Alkali metal and alkaline earth chalcogenides Alkali metal and alkaline earth monochalcogenides are salt-like, being colourless and often water-soluble. The sulfides tend to undergo hydrolysis to form derivatives containing bisulfide (SH−) anions. The alkali metal chalcogenides often crystallize with the antifluorite structure and the alkaline eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In typical CVD, the wafer (substrate) is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Frequently, volatile by-products are also produced, which are removed by gas flow through the reaction chamber. Microfabrication processes widely use CVD to deposit materials in various forms, including: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, and epitaxial. These materials include: silicon ( dioxide, carbide, nitride, oxynitride), carbon (fiber, nanofibers, nanotubes, diamond and graphene), fluorocarbons, filaments, tungsten, titanium nitride and various high-κ dielectrics. The term ''chemical vapour deposition'' was coined 1960 by ''John M. Blocher, Jr.'' who intended to differentiate ''chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenium(VII) Sulfide
Rhenium(VII) sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Re2S7. It has a complex structure, but can be synthesized from direct combination of the elements: 2Re + 7S -> atop\DeltaRe2S7Alternatively, rhenium(VII) oxide reacts with hydrogen sulfide in 4N HCl to the same end: Re2O7 + 7H2S -> atop\DeltaRe2S7 + 7H2O The compound catalyses the reduction of nitric oxide to nitrous oxide and hydrogenation of double bonds. In this regard, it unusually tolerates sulfur compounds, which poison noble metal catalysts. Rhenium(VII) sulfide decomposes when heated. In vacuum, it generates rhenium(IV) sulfide: :\mathrm In air, the sulfur oxidizes to sulfur dioxide: :\mathrm References * Kunyants, I. L. ''et al'', eds. (1995). ''Химическая энциклопедия'' 'Chemical encyclopedia''. Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedias. * Nikolsky, B. P. ''et al'', eds. (1971). ''Справочник химика'' 'Handbook of Chemistry''. 3rd (revised) ed. Leningrad: Khimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheniite
Rheniite is a very rare rhenium sulfide mineral with the chemical formula ( ). It forms metallic, silver grey platey crystals in the triclinic - pinacoidal class. It has a specific gravity of 7.5. It was discovered at the Kudriavy Volcano, Iturup Island in the Kurile Islands, Russia and approved in 2004. It is found in active hot fumaroles on the volcano. Rheniite is one of the first minerals of the element rhenium to be found. The other known approved rhenium mineral is the sulfide mineral tarkianite. Almost all commercially mined rhenium is retrieved as a by-product of molybdenum mining as rhenium occurs in amounts up to 0.2% in the mineral molybdenite. A discredited rhenium sulfide known as ''zappinite'' does not appear to be valid. Rheniite has also been reported in the Pagoni Rachi Mo–Cu–Te–Ag–Au deposit in northeastern Greece where it occurs with molybdenite in quartz veins associated with an epithermal system in a dacite Dacite () is a volcanic rock formed by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W. B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example: * Diamond structure, ''cF''8 * Rutile structure, ''tP''6 The two (italicised) letters specify the Bravais lattice. The lower-case letter specifies the crystal family, and the upper-case letter the centering type. The number at the end of the Pearson symbol gives the number of the atoms in the conventional unit cell.Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 IR-3.4.4, pp. 49–51; IR-11.5, pp. 241–242. |
Rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. Rhenium has the third-highest melting point and highest boiling point of any stable element at 5869 K. Rhenium resembles manganese and technetium chemically and is mainly obtained as a by-product of the extraction and refinement of molybdenum and copper ores. Rhenium shows in its compounds a wide variety of oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7. Discovered by Walter Noddack, Ida Tacke and Otto Berg in 1925, rhenium was the last stable element to be discovered. It was named after the river Rhine in Europe, from which the earliest samples had been obtained and worked commercially. Nickel-based superalloys of rhenium are used in combustion chambers, turbine blades, and exhaust nozzles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |