|
Reunification Clause
The Reunification clause was part of the preamble of the German Constitution. As a whole, it is known as the German Basic Law. The preamble was in force from 1949 until 1990. The preamble ended with the sentence: :''Das gesamte Deutsche Volk bleibt aufgefordert, in freier Selbstbestimmung die Einheit und Freiheit Deutschlands zu vollenden.'' :''The whole German People remains compelled to fulfill the Unity and Freedom of Germany by virtue of its right to free self-determination.'' The jurisprudence of the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany therefrom resulted in a constitutional prerogative, which was binding to all governmental entities, to regain German Unity and work toward achieving this objective. At the time, an attempt was made by opposition parties to the social-liberal administrative coalition headed by German Chancellor Willy Brandt to block the ratification of the Basic Treaty of 1972. The treaty was negotiated by Brandt's administration to establish good ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preamble
A preamble is an introductory and expressionary statement in a document that explains the document's purpose and underlying philosophy. When applied to the opening paragraphs of a statute, it may recite historical facts pertinent to the subject of the statute. It is distinct from the long title or enacting formula of a law. In parliamentary procedure using Robert's Rules of Order, a preamble consists of "Whereas" clauses that are placed before the resolving clauses in a resolution (formal written motion). However, preambles are not required to be placed in resolutions. According to Robert's Rules of Order, including such background information may not be helpful in passing the resolution. Legal effect While preambles may be regarded as unimportant introductory matter, their words may have effects that may not have been foreseen by their drafters. France In France, the preamble to the constitution of the Fifth Republic of 1958 was considered ancillary and therefore non-bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of a supreme court are not subject to further review by any other court. Supreme courts typically function primarily as appellate courts, hearing appeals from decisions of lower trial courts, or from intermediate-level appellate courts. However, not all highest courts are named as such. Civil law states tend not to have a single highest court. Additionally, the highest court in some jurisdictions is not named the "Supreme Court", for example, the High Court of Australia. On the other hand, in some places the court named the "Supreme Court" is not in fact the highest court; examples include the New York Supreme Court, the supreme courts of several Canadian provinces/territories, and the former Supreme Court of Judicature of England and Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine States of Austria, states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the March of Pannonia, Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the 1st millennium, first millennium. Originally Margraviate of Austria, a margraviate of Duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria, it developed into Duchy of Austria, a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made Archduchy of Austria, an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian State Treaty
The Austrian State Treaty (german: Österreichischer Staatsvertrag ) or Austrian Independence Treaty re-established Austria as a sovereign state. It was signed on 15 May 1955 in Vienna, at the Schloss Belvedere among the Allied occupying powers (France, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union) and the Austrian government. The neighbouring Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia acceded to the treaty subsequently. It officially came into force on 27 July 1955. Its full title is "Treaty for the re-establishment of an independent and democratic Austria, signed in Vienna on 15 May 1955" (german: Staatsvertrag betreffend die Wiederherstellung eines unabhängigen und demokratischen Österreich, unterzeichnet in Wien am 15. Mai, links=no). Generalities and structure The treaty re-established a free, sovereign and democratic Austria. The basis for the treaty was the Moscow Declaration of 30 October 1943. The agreement and its annexes provided for Soviet oilfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
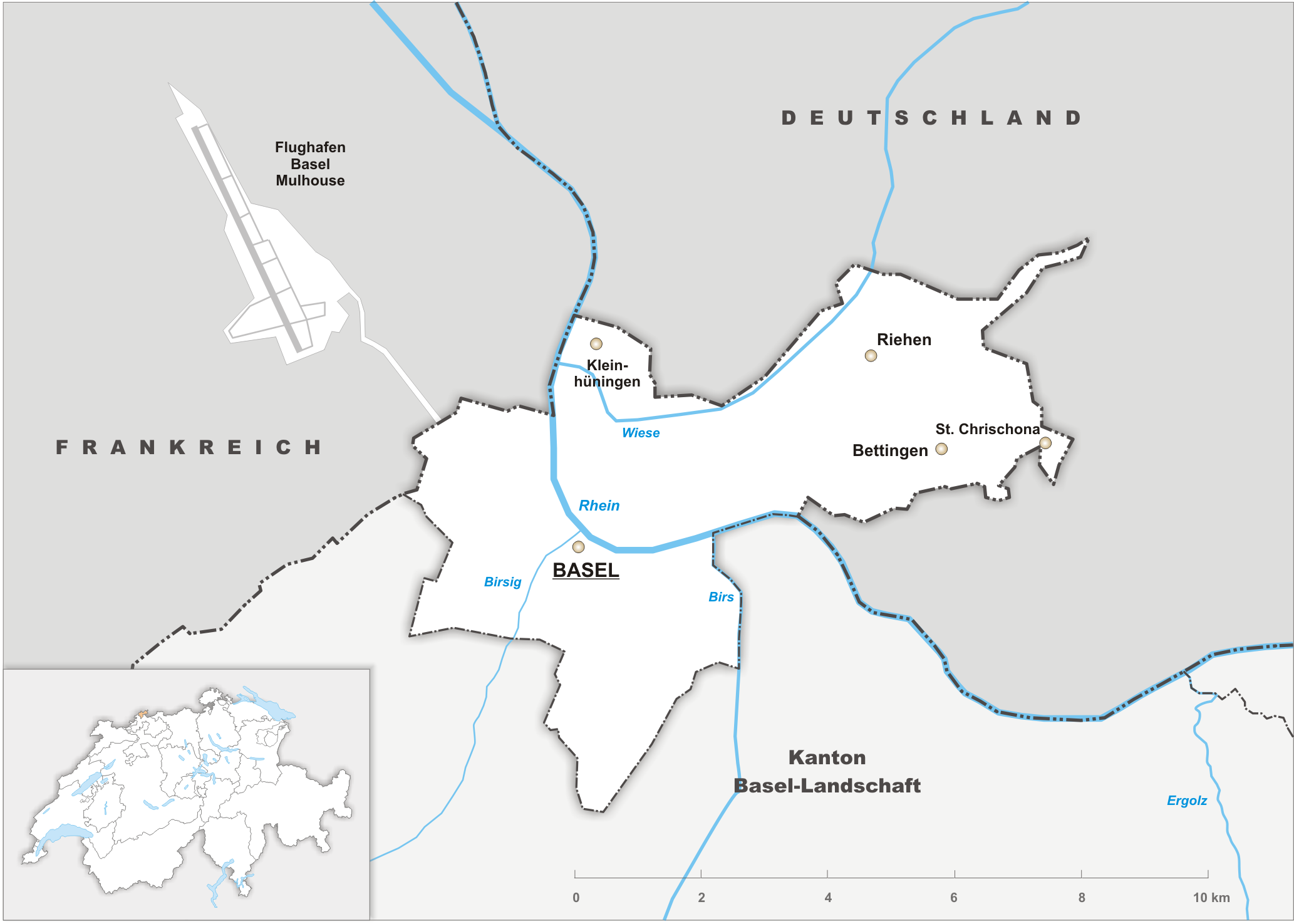
Basel-Land
Basel-Landschaft or Basel-Country informally known as Baselland or Baselbiet (; german: Kanton Basel-Landschaft ; rm, Chantun Basilea-Champagna; french: Canton de Bâle-Campagne; it, Canton Basilea Campagna), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts and its capital city is Liestal. It is traditionally considered a " half-canton", the other half being Basel-Stadt, its urban counterpart. Basel-Landschaft is one of the northernmost cantons of Switzerland. It lies essentially south of the Rhine and north of the Jura Mountains. The canton shares borders with the canton of Basel-Stadt to the north, the canton of Aargau to the east, the canton of Solothurn to the south and the canton of Jura to the west. It shares international borders as well with France and Germany to the north. Together with Basel-Stadt, Basel-Landschaft was part of the canton of Basel, who joined the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1501. Political quarrels and armed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body, or institution that has the ultimate authority over other people in order to establish a law or change an existing law. In political theory, sovereignty is a substantive term designating supreme legitimate authority over some polity. In international law, sovereignty is the exercise of power by a state. ''De jure'' sovereignty refers to the legal right to do so; ''de facto'' sovereignty refers to the factual ability to do so. This can become an issue of special concern upon the failure of the usual expectation that ''de jure'' and ''de facto'' sovereignty exist at the place and time of concern, and reside within the same organization. Etymology The term arises from the unattested Vulgar Latin's ''*superanus'', (itself derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel-Stadt
Basel-Stadt or Basel-City (german: Kanton ; rm, Chantun Basilea-Citad; french: Canton de Bâle-Ville; it, Canton Basilea Città) is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of three municipalities with Basel as the capital. It is traditionally considered a " half-canton", the other half being Basel-Landschaft, its rural counterpart. Basel-Stadt is one of the northernmost and lowest cantons of Switzerland, and the smallest by area. The canton lies on both sides of the Rhine and is very densely populated. The largest municipality is Basel, followed by Riehen and Bettingen. The only canton sharing borders with Basel-Stadt is Basel-Landschaft to the south. To the north of Basel-Stadt are France and Germany, with the tripoint being in the middle of the Rhine. Together with Basel-Landschaft, Basel-Stadt was part of the canton of Basel, who joined the Old Swiss Confederacy in 1501. Political quarrels and armed conflict led to the partition of the can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the . Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms ('Eight Cantons'; from 1353–1481) and ('Thirteen Cantons', from 1513–1798).rendered "the 'confederacy of eight'" and "the 'Thirteen-Canton Confederation'", respectively, in: Each canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy, formerly also ('lieu/locality', from before 1450), or ('estate', from ), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848, with a brief period of centralised government during the Helvetic Republic ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * German (song), "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Law For The Federal Republic Of Germany
The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Grundgesetz für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland) is the constitution of the Federal Republic of Germany. The West German Constitution was approved in Bonn on 8 May 1949 and came into effect on 23 May after having been approved by the occupying western Allies of World War II on 12 May. It was termed "Basic Law" (german: Grundgesetz) to indicate that it was a provisional piece of legislation pending the reunification of Germany. However, when reunification took place in 1990, the Basic Law was retained as the definitive constitution of reunified Germany. Its original field of application (german: Geltungsbereich)—that is, the states that were initially included in the Federal Republic of Germany—consisted of the three Western Allies' zones of occupation, but at the insistence of the Western Allies, formally excluded West Berlin. In 1990, the Two Plus Four Agreement between the two parts of Germany and all four All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |