|
Retrocausality
Retrocausality, or backwards causation, is a concept of cause and effect in which an effect precedes its cause in time and so a later event affects an earlier one. In quantum physics, the distinction between cause and effect is not made at the most fundamental level and so T-symmetry, time-symmetric systems can be viewed as causal or retrocausal. Philosophical considerations of time travel often address the same issues as retrocausality, as do treatments of the subject in fiction, but the two phenomena are distinct. Philosophy Philosophical efforts to understand causality extend back at least to Aristotle's discussions of the four causes. It was long considered that an effect preceding its cause is an inherent self-contradiction because, as 18th century philosopher David Hume discussed, when examining two related events, the cause, by definition, is the one that precedes the effect. In the 1950s, Michael Dummett wrote in opposition to such definitions, stating that there was no ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cause And Effect
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the cause is partly responsible for the effect, and the effect is partly dependent on the cause. In general, a process has many causes, which are also said to be ''causal factors'' for it, and all lie in its past. An effect can in turn be a cause of, or causal factor for, many other effects, which all lie in its future. Some writers have held that causality is metaphysically prior to notions of time and space. Causality is an abstraction that indicates how the world progresses. As such a basic concept, it is more apt as an explanation of other concepts of progression than as something to be explained by others more basic. The concept is like those of agency and efficacy. For this reason, a leap of intuition may be needed to grasp it. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachyon
A tachyon () or tachyonic particle is a hypothetical particle that always travels faster than light. Physicists believe that faster-than-light particles cannot exist because they are not consistent with the known laws of physics. If such particles did exist they could be used to send signals faster than light. According to the theory of relativity this would violate causality, leading to logical paradoxes such as the grandfather paradox. Tachyons would exhibit the unusual property of increasing in speed as their energy decreases, and would require infinite energy to slow down to the speed of light. No verifiable experimental evidence for the existence of such particles has been found. In the 1967 paper that coined the term, Gerald Feinberg proposed that tachyonic particles could be made from excitations of a quantum field with imaginary mass. However, it was soon realized that Feinberg's model did not in fact allow for superluminal (faster-than-light) particles or signals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
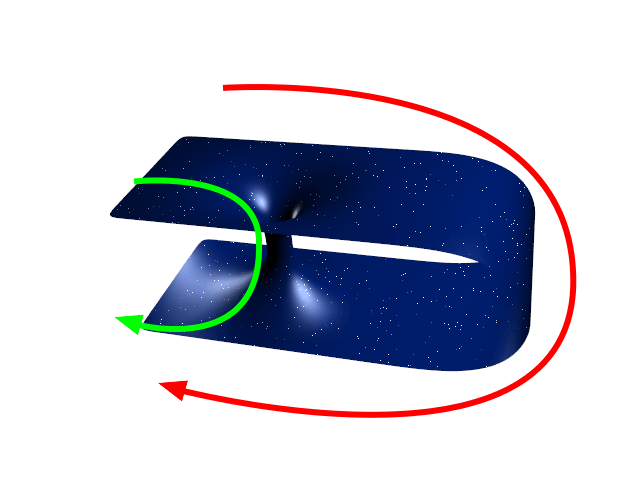
Traversable Wormhole
A wormhole (Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negative mass were generated in the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandfather Paradox
A temporal paradox, time paradox, or time travel paradox is a paradox, an apparent contradiction, or logical contradiction associated with the idea of time and time travel. The notion of time travel to the future complies with current understanding of physics via relativistic time dilation, temporal paradoxes arise from circumstances involving hypothetical time travel to the past and are often used to demonstrate its impossibility. In physics, temporal paradoxes fall into two broad groups: consistency paradoxes exemplified by the grandfather paradox; and causal loops. Other paradoxes associated with time travel are a variation of the Fermi paradox and paradoxes of free will that stem from causal loops such as Newcomb's paradox. Causal loop A causal loop is a paradox of time travel that occurs when a future event is the cause of a past event, which in turn is the cause of the future event. Both events then exist in spacetime, but their origin cannot be determined. A causal loop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-state Vector Formalism
The two-state vector formalism (TSVF) is a description of quantum mechanics in terms of a causal relation in which the present is caused by quantum states of the past and of the future taken in combination. Theory The two-state vector formalism is one example of a time-symmetric interpretation of quantum mechanics (see Interpretations of quantum mechanics). Time-symmetric interpretations of quantum mechanics were first suggested by Walter Schottky in 1921, and later by several other scientists. The two-state vector formalism was first developed by Satosi Watanabe in 1955, who named it the Double Inferential state-Vector Formalism (DIVF). Watanabe proposed that information given by forwards evolving quantum states is not complete; rather, both forwards and backwards evolving quantum states are required to describe a quantum state: a first state vector that evolves from the initial conditions towards the future, and a second state vector that evolves backwards in time from future ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. The idea of a time machine was popularized by H. G. Wells' 1895 novel ''The Time Machine''. It is uncertain if time travel to the past is physically possible, and such travel, if at all feasible, may give rise to questions of causality. Forward time travel, outside the usual sense of the perception of time, is an extensively observed phenomenon and well-understood within the framework of special relativity and general relativity. However, making one body advance or delay more than a few milliseconds compared to another body is not feasible with current technology. As for backward time travel, it is possible to find solutions in general relativity that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary ( macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (wave–particle duality); and there are limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology Protection Conjecture
The chronology protection conjecture is a hypothesis first proposed by Stephen Hawking that laws of physics beyond those of standard general relativity prevent time travel on all but microscopic scales - even when the latter theory states that it should be possible (such as in scenarios where faster than light travel is allowed). The permissibility of time travel is represented mathematically by the existence of closed timelike curves in some solutions to the field equations of general relativity. The chronology protection conjecture should be distinguished from chronological censorship under which every closed timelike curve passes through an event horizon, which might prevent an observer from detecting the causal violation (also known as chronology violation). Etymology In a 1992 paper, Hawking uses the metaphorical device of a "Chronology Protection Agency" as a personification of the aspects of physics that make time travel impossible at macroscopic scales, thus apparently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Defect
A topological soliton occurs when two adjoining structures or spaces are in some way "out of phase" with each other in ways that make a seamless transition between them impossible. One of the simplest and most commonplace examples of a topological soliton occurs in old-fashioned coiled telephone handset cords, which are usually coiled clockwise. Years of picking up the handset can end up coiling parts of the cord in the opposite counterclockwise direction, and when this happens there will be a distinctive larger loop that separates the two directions of coiling. This odd looking transition loop, which is neither clockwise nor counterclockwise, is an excellent example of a topological soliton. No matter how complex the context, anything that qualifies as a topological soliton must at some level exhibit this same simple issue of reconciliation seen in the twisted phone cord example. Topological solitons arise with ease when creating the crystalline semiconductors used in modern elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exotic Matter
There are several proposed types of exotic matter: * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have "exotic" physical properties that would violate known laws of physics, such as a particle having a negative mass. * Hypothetical particles and states of matter that have not yet been encountered, but whose properties would be within the realm of mainstream physics if found to exist. * Several particles whose existence has been experimentally confirmed that are conjectured to be exotic hadrons and within the Standard Model. * States of matter that are not commonly encountered, such as Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, nuclear matter, quantum spin liquid, string-net liquid, supercritical fluid, color-glass condensate, quark–gluon plasma, Rydberg matter, Rydberg polaron, photonic matter, and time crystal but whose properties are entirely within the realm of mainstream physics. * Forms of matter that are poorly understood, such as dark matter and mirror ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Strings
Cosmic strings are hypothetical 1-dimensional topological defects which may have formed during a symmetry-breaking phase transition in the early universe when the topology of the vacuum manifold associated to this symmetry breaking was not simply connected. Their existence was first contemplated by the theoretical physicist Tom Kibble in the 1970s. The formation of cosmic strings is somewhat analogous to the imperfections that form between crystal grains in solidifying liquids, or the cracks that form when water freezes into ice. The phase transitions leading to the production of cosmic strings are likely to have occurred during the earliest moments of the universe's evolution, just after cosmological inflation, and are a fairly generic prediction in both quantum field theory and string theory models of the early universe. Theories containing cosmic strings In string theory, the role of cosmic strings can be played by the fundamental strings (or F-strings) themselves that define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |