|
Retinal Bipolar Cell
As a part of the retina, bipolar cells exist between photoreceptors (rod cells and cone cells) and ganglion cells. They act, directly or indirectly, to transmit signals from the photoreceptors to the ganglion cells. Structure Bipolar cells are so-named as they have a central body from which two sets of processes arise. They can synapse with either rods or cones (rod/cone mixed input BCs have been found in teleost fish but not mammals), and they also accept synapses from horizontal cells. The bipolar cells then transmit the signals from the photoreceptors or the horizontal cells, and pass it on to the ganglion cells directly or indirectly (via amacrine cells). Unlike most neurons, bipolar cells communicate via graded potentials, rather than action potentials. Function Bipolar cells receive synaptic input from either rods or cones, or both rods and cones, though they are generally designated rod bipolar or cone bipolar cells. There are roughly 10 distinct forms of cone bipolar ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible for the perception of colour through the use of a range of opsins, as well as high-acuity vision used for task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa, as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the production of radiation. The concentration gradients of the charges directly determine this energy requirement. For the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential, normally given in units of milli volts and denoted as mV, range from –80 mV to –40 mV. All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Transmembrane proteins, also known as ion transporter or ion pump proteins, actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Receptor
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord. The sensory information travels on the afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve, to the brain via the spinal cord. The stimulus can come from ''exteroreceptors'' outside the body, for example those that detect light and sound, or from ''interoreceptors'' inside the body, for example those that are responsive to blood pressure or the sense of body position. Types and function Different types of sensory neurons have different sensory receptors that respond to different kinds of stimuli. There are at least six external and two internal sensory receptors: External receptors External receptors that respond to stimuli from outside the body are called ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionotropic
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter. When a presynaptic neuron is excited, it releases a neurotransmitter from vesicles into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter then binds to receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron. If these receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, a resulting conformational change opens the ion channels, which leads to a flow of ions across the cell membrane. This, in turn, results in either a depolarization, for an excitatory receptor response, or a hyperpolarization, for an inhibitory response. These receptor proteins are typically composed of at least two different domains: a transmembrane domain which includes the ion pore, and an extracellular domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabotropic
A metabotropic receptor, also referred to by the broader term G-protein-coupled receptor, is a type of membrane receptor that initiates a number of metabolic steps to modulate cell activity. The nervous system utilizes two types of receptors: metabotropic and ionotropic receptors. While ionotropic receptors form an ion channel pore, metabotropic receptors are indirectly linked with ion channels through signal transduction mechanisms, such as G proteins. Both receptor types are activated by specific chemical ligands. When an ionotropic receptor is activated, it opens a channel that allows ions such as Na+, K+, or Cl− to flow. In contrast, when a metabotropic receptor is activated, a series of intracellular events are triggered that can also result in ion channels opening or other intracellular events, but involve a range of second messenger chemicals. Mechanism Chemical messengers bind to metabotropic receptors to initiate a diversity of effects caused by biochemical sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoreceptor Cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential. There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes: rods, cones, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form an image of the environment, sight. Rods primarily mediate scotopic vision (dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate to photopic vision (bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. A third class of mammalian photoreceptor cell was discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina Amacrine Cell
Amacrine cells are interneurons in the retina. They are named from the Greek roots ''a–'' ("non"), ''makr–'' ("long") and ''in–'' ("fiber"), because of their short neuronal processes. Amacrine cells are inhibitory neurons, and they project their dendritic arbors onto the inner plexiform layer (IPL), they interact with retinal ganglion cells and/or bipolar cells. Structure Amacrine cells operate at inner plexiform layer (IPL), the second synaptic retinal layer where bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells form synapses. There are at least 33 different subtypes of amacrine cells based just on their dendrite morphology and stratification. Like horizontal cells, amacrine cells work laterally, but whereas horizontal cells are connected to the output of rod and cone cells, amacrine cells affect the output from bipolar cells, and are often more specialized. Each type of amacrine cell releases one or several neurotransmitters where it connects with other cells. They are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
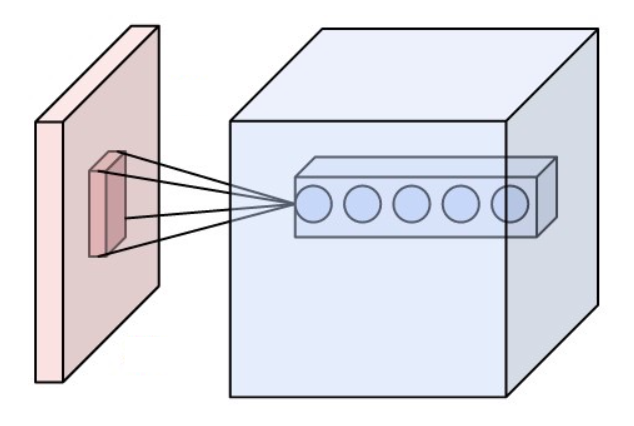
Receptive Field
The receptive field, or sensory space, is a delimited medium where some physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response in specific organisms. Complexity of the receptive field ranges from the unidimensional chemical structure of odorants to the multidimensional spacetime of human visual field, through the bidimensional skin surface, being a receptive field for touch perception. Receptive fields can positively or negatively alter the membrane potential with or without affecting the rate of action potentials. A sensory space can be dependent of an animal's location. For a particular sound wave traveling in an appropriate transmission medium, by means of sound localization, an auditory space would amount to a reference system that continuously shifts as the animal moves (taking into consideration the space inside the ears as well). Conversely, receptive fields can be largely independent of the animal's location, as in the case of place cells. A sensory space can also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Inhibition
In neurobiology, lateral inhibition is the capacity of an excited neuron to reduce the activity of its neighbors. Lateral inhibition disables the spreading of action potentials from excited neurons to neighboring neurons in the lateral direction. This creates a contrast in stimulation that allows increased sensory perception. It is also referred to as lateral antagonism and occurs primarily in visual processes, but also in tactile, auditory, and even olfactory processing. Cells that utilize lateral inhibition appear primarily in the cerebral cortex and thalamus and make up lateral inhibitory networks (LINs). Artificial lateral inhibition has been incorporated into artificial sensory systems, such as vision chips, hearing systems, and optical mice. An often under-appreciated point is that although lateral inhibition is visualised in a spatial sense, it is also thought to exist in what is known as "lateral inhibition across abstract dimensions." This refers to lateral inhibition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine Receptor
The glycine receptor (abbreviated as GlyR or GLR) is the receptor of the amino acid neurotransmitter glycine. GlyR is an ionotropic receptor that produces its effects through chloride current. It is one of the most widely distributed inhibitory receptors in the central nervous system and has important roles in a variety of physiological processes, especially in mediating inhibitory neurotransmission in the spinal cord and brainstem. The receptor can be activated by a range of simple amino acids including glycine, β-alanine and taurine, and can be selectively blocked by the high-affinity competitive antagonist strychnine. Caffeine is a competitive antagonist of GlyR. Gephyrin has been shown to be necessary for GlyR clustering at inhibitory synapses. GlyR is known to colocalize with the GABAA receptor on some hippocampal neurons. Nevertheless, some exceptions can occur in the central nervous system where the GlyR α1 subunit and gephyrin, its anchoring protein, are not foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina Amacrine Cell
Amacrine cells are interneurons in the retina. They are named from the Greek roots ''a–'' ("non"), ''makr–'' ("long") and ''in–'' ("fiber"), because of their short neuronal processes. Amacrine cells are inhibitory neurons, and they project their dendritic arbors onto the inner plexiform layer (IPL), they interact with retinal ganglion cells and/or bipolar cells. Structure Amacrine cells operate at inner plexiform layer (IPL), the second synaptic retinal layer where bipolar cells and retinal ganglion cells form synapses. There are at least 33 different subtypes of amacrine cells based just on their dendrite morphology and stratification. Like horizontal cells, amacrine cells work laterally, but whereas horizontal cells are connected to the output of rod and cone cells, amacrine cells affect the output from bipolar cells, and are often more specialized. Each type of amacrine cell releases one or several neurotransmitters where it connects with other cells. They are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |