|
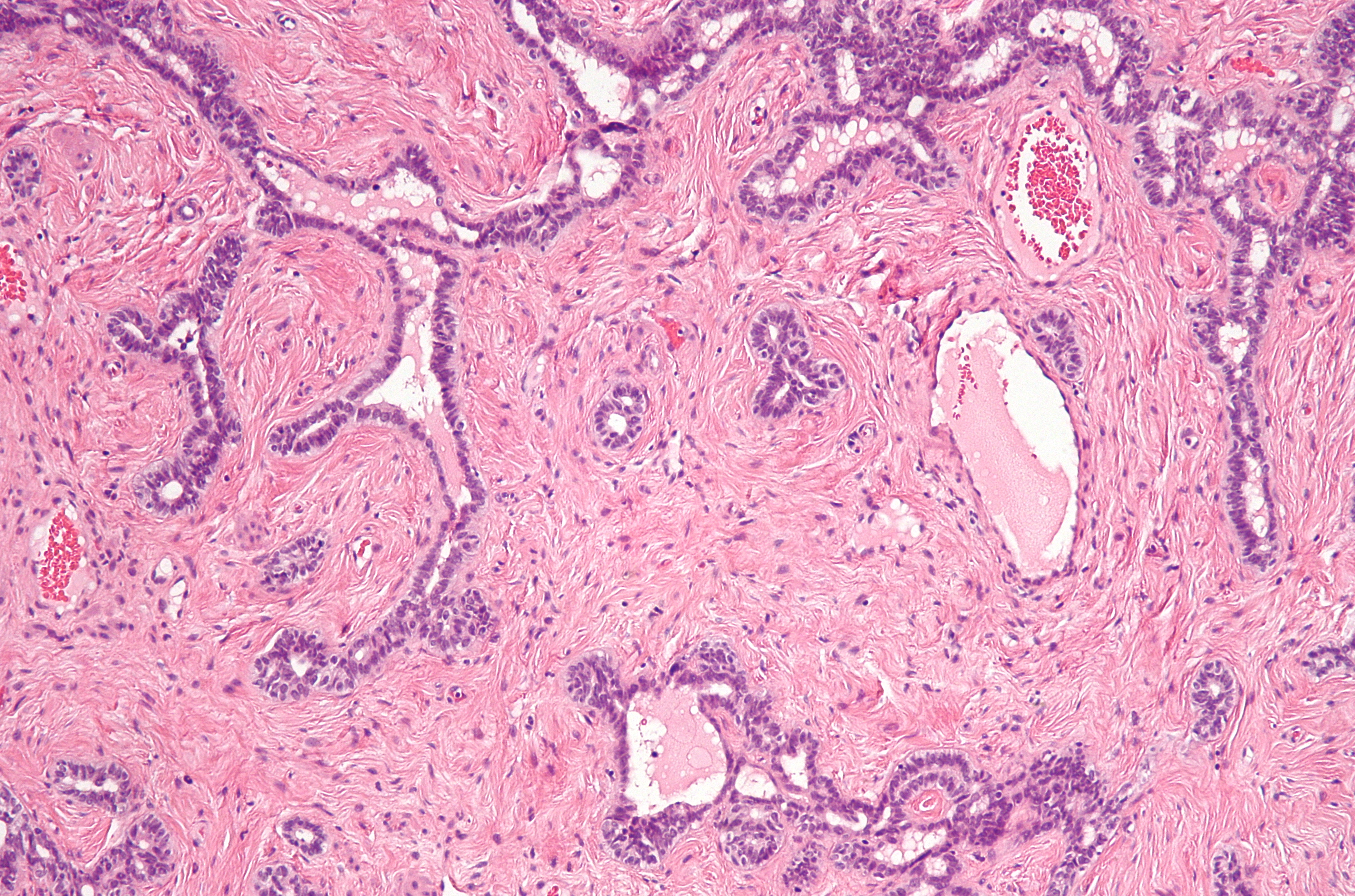
Rete Ovarii
The rete ovarii is a structure formed from the primary sex cords in females. It is the counterpart of the rete testis in males. It is a narrow hilus, at which nerves and vessels enter the ovary. In the medulla of the mammalian ovary near the hilus are small masses of blind tubules or solid cords—the rete ovarii—which are homologous (i.e., of the same embryonic origin) with the rete testis in the male. The microscopic right ovary of birds Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ... usually consists only of medullary tissue. References Embryology of urogenital system {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Cord
In embryogenesis, the sex cords (primitive sex cords, primitive seminiferous cords, or gonadal cords) are structures that develop from the genital ridges that further differentiate based on an embryo's sex. After sexual differentiation, at day 49, the sex cords in females become the cortical cords, also called secondary cords. After further development, they become the ovarian follicles. The sex cords in males become the testis cords by the action of the testis-determining factor protein, which helps to develop and nourish the Sertoli cells. The testis cords are precursors to the rete testis. They play several different roles in the development of the male genitals. The primitive sex cords originate from the proliferation of the epithelium of the two genital ridges. These epithelial cells (from the genital ridges) penetrate and invade the underlying mesenchyme to form the primitive sex cords. This occurs shortly before and during the arrival of the primordial germ cells (PGCs) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rete Testis
The rete testis ( ) is an anastomosing network of delicate tubules located in the hilum of the testicle (mediastinum testis) that carries sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts. It is the counterpart of the rete ovarii in females. Its function is to provide a site for fluid reabsorption. Structure The rete testis is the network of interconnecting tubules where the straight seminiferous tubules (the terminal part of the seminiferous tubules) empty. It is located within a highly vascular connective tissue in the mediastinum testis. The epithelial cells form a single layer that lines the inner surface of the tubules. These cells are cuboidal, with microvilli and a single cilium on their surface. Development In the development of the urinary and reproductive organs, the testis is developed in much the same way as the ovary, originating from mesothelium as well as mesonephros. Like the ovary, in its earliest stages it consists of a central mass covered by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilum (anatomy)
In human anatomy, the hilum (; plural hila), sometimes formerly called a hilus (; plural hili), is a depression or fissure where structures such as blood vessels and nerves enter an organ. Examples include: * Hilum of kidney, admits the renal artery, vein, ureter, and nerves * Splenic hilum, on the surface of the spleen, admits the splenic artery, vein, lymph vessels, and nerves * Hilum of lung, a triangular depression where the structures which form the root of the lung enter and leave the viscus * Hilum of lymph node, the portion of a lymph node where the efferent vessels exit * Hilus of dentate gyrus, part of hippocampus The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic syste ... that contains the mossy cells. {{Authority control Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes. Structure The ovaries are considered the female gonads. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Of Ovary
The medulla of ovary (or Zona vasculosa of Waldeyer) is a highly vascular stroma in the center of the ovary. It forms from embryonic mesenchyme and contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. This stroma forms the tissue of the hilum by which the ovarian ligament is attached, and through which the blood vessels enter: it does not contain any ovarian follicle An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. At the time of puberty, women have approximately 200,000 to 300,000 follicles, each with ...s. References External links * - "Female Reproductive System: ovary, medulla and cortex" * Mammal female reproductive system {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla ( hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla (cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora ( cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubule
In biology, a tubule is a general term referring to small tube or similar type of structure. Specifically, tubule can refer to: * a small tube or fistular structure * a minute tube lined with glandular epithelium * any hollow cylindrical body structure * a minute canal found in various structures or organs of the body * a slender elongated anatomical channel * a minute tube, especially as an anatomical structure. Examples of tubules * Collecting tubules: terminal channels of the nephrons * Cuvierian tubules: clusters of sticky tubules located at the base of the respiratory tree, which may be discharged by some sea cucumbers ( holothurians) when mechanically stimulated (i.e. being threatened by a predator) * Dentinal tubules or dental canaliculi: minute channels in the dentine of a tooth that extend from the pulp cavity to the cementum or the enamel * Distal convoluted tubule: the convoluted portion of the vertebrate nephron that lies between the loop of Henle and the nonsecret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)