|
Retained Antrum Syndrome
Retained antrum syndrome or retained gastric antrum syndrome is one of the rare postgastrectomy syndromes. It happens after Billroth II surgery and the mechanism involved is the inadequate removal of the distal antrum and pylorus during resection of the antrum and gastrojejunostomy. Lack of the usual acid-secreting gastric glands makes the antral segment continually exposed to the alkaline environment of the duodenum, which causes it to secrete excessive acid and be prone to form ulcers An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o .... References Gastrointestinal tract disorders {{disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bowel dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrectomy
A gastrectomy is a partial or total surgical removal of the stomach. Indications Gastrectomies are performed to treat stomach cancer and perforations of the stomach wall. In severe duodenal ulcers it may be necessary to remove the lower portion of the stomach called the pylorus and the upper portion of the small intestine called the duodenum. If there is a sufficient portion of the upper duodenum remaining a Billroth I procedure is performed, where the remaining portion of the stomach is reattached to the duodenum before the bile duct and the duct of the pancreas. If the stomach cannot be reattached to the duodenum a Billroth II is performed, where the remaining portion of the duodenum is sealed off, a hole is cut into the next section of the small intestine called the jejunum and the stomach is reattached at this hole. As the pylorus is used to grind food and slowly release the food into the small intestine, removal of the pylorus can cause food to move into the small intes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billroth II
Billroth II, more formally Billroth's operation II, is an operation in which a partial gastrectomy (removal of the stomach) is performed and the cut end of the stomach is closed. The greater curvature of the stomach (not involved with the previous closure of the stomach) is then connected to the first part of the jejunum in end-to-side anastomosis. The Billroth II always follows resection of the lower part of the stomach (antrum). The surgical procedure is called a partial gastrectomy and gastrojejunostomy. The Billroth II is often indicated in refractory peptic ulcer disease and gastric adenocarcinoma. Robinson, JO. The History of Gastric Surgery. Postgraduate Medical Journal. Dec 1960, p 706-713. Over the years, the Billroth II operation has been colloquially referred to as any partial removal of the stomach with an end to side connection to the stomach as shown in the picture; however, technically, this picture is a modification of Billroth's operation called a partial gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends as the ''pyloric orifice'', which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the ''pyloric sphincter''. The word ''pylorus'' comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word ''pylorus'' in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" ( el, pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word " pylon". Structure The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the ''antrum'', which connects to the body of the stomach, and the ''pyloric canal'', which connects to the duodenum. Antrum The ''pyloric antrum'' is the initial portion of the pylorus. It is near the bottom of the stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pylorus
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends as the ''pyloric orifice'', which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the ''pyloric sphincter''. The word ''pylorus'' comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word ''pylorus'' in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" ( el, pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word " pylon". Structure The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the ''antrum'', which connects to the body of the stomach, and the ''pyloric canal'', which connects to the duodenum. Antrum The ''pyloric antrum'' is the initial portion of the pylorus. It is near the bottom of the stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterostomy
A gastroenterostomy is the surgical creation of a connection between the stomach and the jejunum. The operation can sometimes be performed at the same time as a partial gastrectomy (the removal of part of the stomach). Gastroenterostomy was in the past typically performed to treat peptic ulcers, but today it is usually carried out to enable food to pass directly to the middle section of the small intestine when it is necessary to bypass the first section (the duodenum) because of duodenal damage. The procedure is still being used to treat gastroparesis that is refractory to other treatments, but it is now rarely used to treat peptic ulcers because most cases thereof are bacterial in nature (due to ''Helicobacter pylori'') and there are many new drugs available to treat the gastric reflux often experienced with peptic ulcer disease. Reported cure rates for ''H. pylori'' infection range from 70% to 90% after antibiotic treatment. See also * List of surgeries by type Many surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands. There are two types of gland in the stomach, the oxyntic gland, and the pyloric gland. The major type of gastric gland is the oxyntic gland that is present in 80 per cent of the stomach, and is often referred to simply as the ''gastric gland''. The oxyntic gland is an exocrine gland and contains the parietal cells that produce hydrochloric acid, and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. The other type of gland in the stomach is the pyloric gland found in the pyloric region taking up the remaining 20 per cent of the stomach area. The pyloric gland secretes gastrin from its G cells. Pyloric glands are similar in structure to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas. Gastrin binds to cholecystokinin B receptors to stimulate the release of histamines in enterochromaffin-like cells, and it induces the insertion of K+/H+ ATPase pumps into the apical membrane of parietal cells (which in turn increases H+ release into the stomach cavity). Its release is stimulated by peptides in the Lumen (anatomy), lumen of the stomach. Physiology Genetics In humans, the ''GAS'' gene is located on the long arm of the seventeenth chromosome (17q21). Synthesis Gastrin is a linear peptide hormone produced by G cells of the duodenum and in the pyloric antrum of the stomach. It is secreted into the bloodstream. The encoded polypeptide is preprogastrin, which is cleaved by enzymes in posttranslational modification to produce progastr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
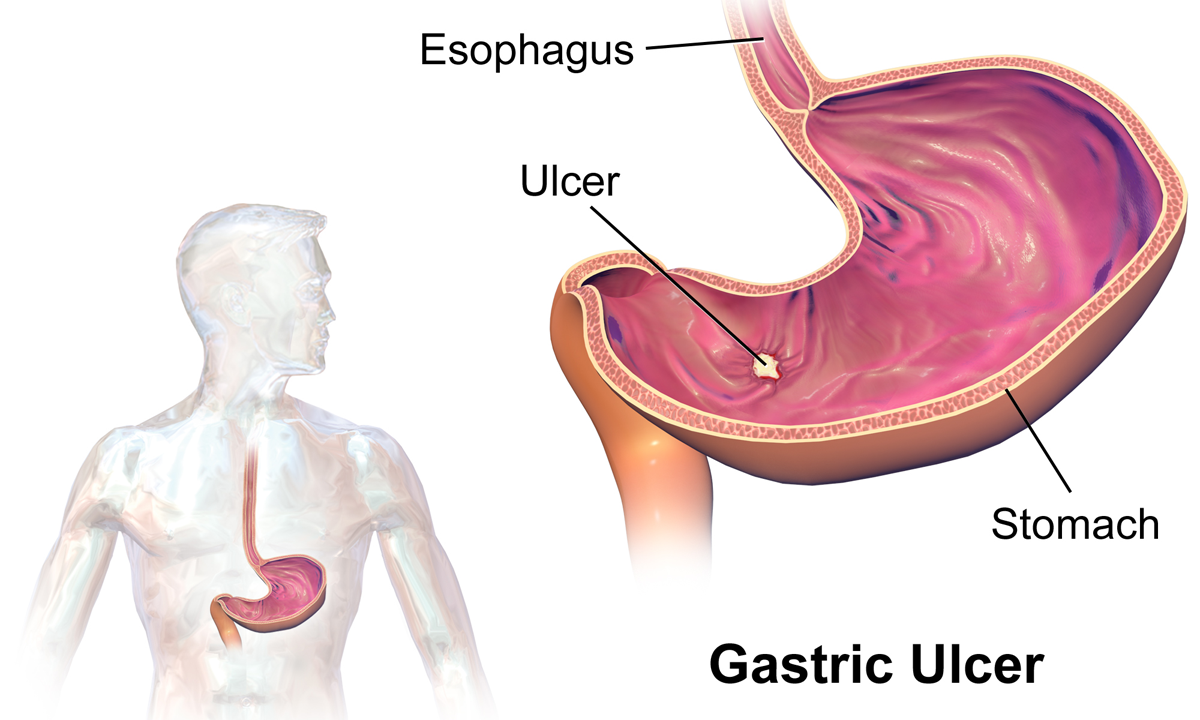
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |