|
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:"It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores." For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
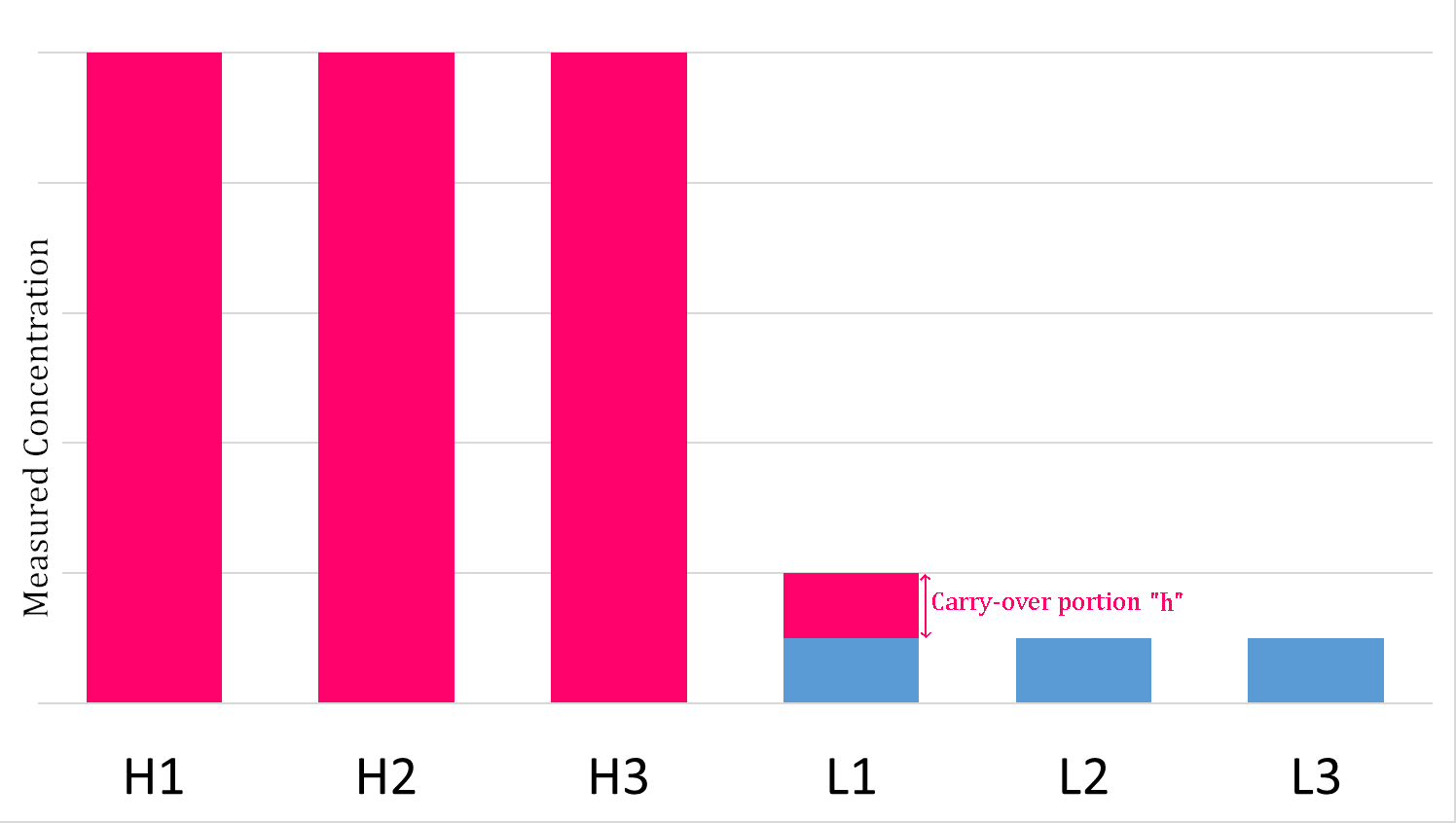
Carryover Effect
The carryover effect is a term used in clinical chemistry to describe the transfer of unwanted material from one container or mixture to another. It describes the influence of one sample upon the following one. It may be from a specimen, or a reagent, or even the washing medium. The significance of carry over is that even a small amount can lead to erroneous results. Carryover effect in clinical laboratory Carryover experiments are widely used for clinical chemistry and immunochemistry analyzers to evaluate and validate carryover effects. The pipetting and washing systems in an automated analyzer are designed to continuously cycle between the aspiration of patient specimens and cleaning. An obvious concern is a potential for carryover of analyte from one patient specimen into one or more following patient specimens, which can falsely increase or decrease the measured analyte concentration. Specimen carryover is typically addressed by judicious choice of probe material, probe de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Validity (statistics)
Validity is the main extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and likely corresponds accurately to the real world. The word "valid" is derived from the Latin validus, meaning strong. The validity of a measurement tool (for example, a test in education) is the degree to which the tool measures what it claims to measure. Validity is based on the strength of a collection of different types of evidence (e.g. face validity, construct validity, etc.) described in greater detail below. In psychometrics, validity has a particular application known as test validity: "the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores" ("as entailed by proposed uses of tests"). It is generally accepted that the concept of scientific validity addresses the nature of reality in terms of statistical measures and as such is an epistemological and philosophical issue as well as a question of measurement. The use of the term in logic is narrower, relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproducibility
Reproducibility, also known as replicability and repeatability, is a major principle underpinning the scientific method. For the findings of a study to be reproducible means that results obtained by an experiment or an observational study or in a statistical analysis of a data set should be achieved again with a high degree of reliability when the study is replicated. There are different kinds of replication but typically replication studies involve different researchers using the same methodology. Only after one or several such successful replications should a result be recognized as scientific knowledge. With a narrower scope, ''reproducibility'' has been introduced in computational sciences: Any results should be documented by making all data and code available in such a way that the computations can be executed again with identical results. In recent decades, there has been a rising concern that many published scientific results fail the test of reproducibility, evoking a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the prediction, prevention and man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Theory
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance, repair and operations, maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accuracy And Precision
Accuracy and precision are two measures of '' observational error''. ''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their '' true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other. In other words, ''precision'' is a description of '' random errors'', a measure of statistical variability. ''Accuracy'' has two definitions: # More commonly, it is a description of only ''systematic errors'', a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this ''trueness''. # Alternatively, ISO defines accuracy as describing a combination of both types of observational error (random and systematic), so high accuracy requires both high precision and high trueness. In the first, more common definition of "accuracy" above, the concept is independent of "precision", so a particular set of data can be said to be accurate, precise, both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levels Of Measurement
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and is widely criticized by scholars in other disciplines. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 ''Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales that he called "nominal", "ordinal", "interval", and "ratio", unifying both "qualitative" (which are described by his "nominal" type) and "quantitative" (to a different degree, all the rest of his scales). The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity (statistics)
In statistics, homogeneity and its opposite, heterogeneity, arise in describing the properties of a dataset, or several datasets. They relate to the validity of the often convenient assumption that the statistical properties of any one part of an overall dataset are the same as any other part. In meta-analysis, which combines the data from several studies, homogeneity measures the differences or similarities between the several studies (see also Study heterogeneity). Homogeneity can be studied to several degrees of complexity. For example, considerations of homoscedasticity examine how much the variability of data-values changes throughout a dataset. However, questions of homogeneity apply to all aspects of the statistical distributions, including the location parameter. Thus, a more detailed study would examine changes to the whole of the marginal distribution. An intermediate-level study might move from looking at the variability to studying changes in the skewness. In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistency (statistics)
In statistics, consistency of procedures, such as computing confidence intervals or conducting hypothesis tests, is a desired property of their behaviour as the number of items in the data set to which they are applied increases indefinitely. In particular, consistency requires that the outcome of the procedure with unlimited data should identify the underlying truth.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. (entries for consistency, consistent estimator, consistent test) Use of the term in statistics derives from Sir Ronald Fisher in 1922. Use of the terms ''consistency'' and ''consistent'' in statistics is restricted to cases where essentially the same procedure can be applied to any number of data items. In complicated applications of statistics, there may be several ways in which the number of data items may grow. For example, records for rainfall within an area might increase in three ways: records for additional time periods; records for additiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
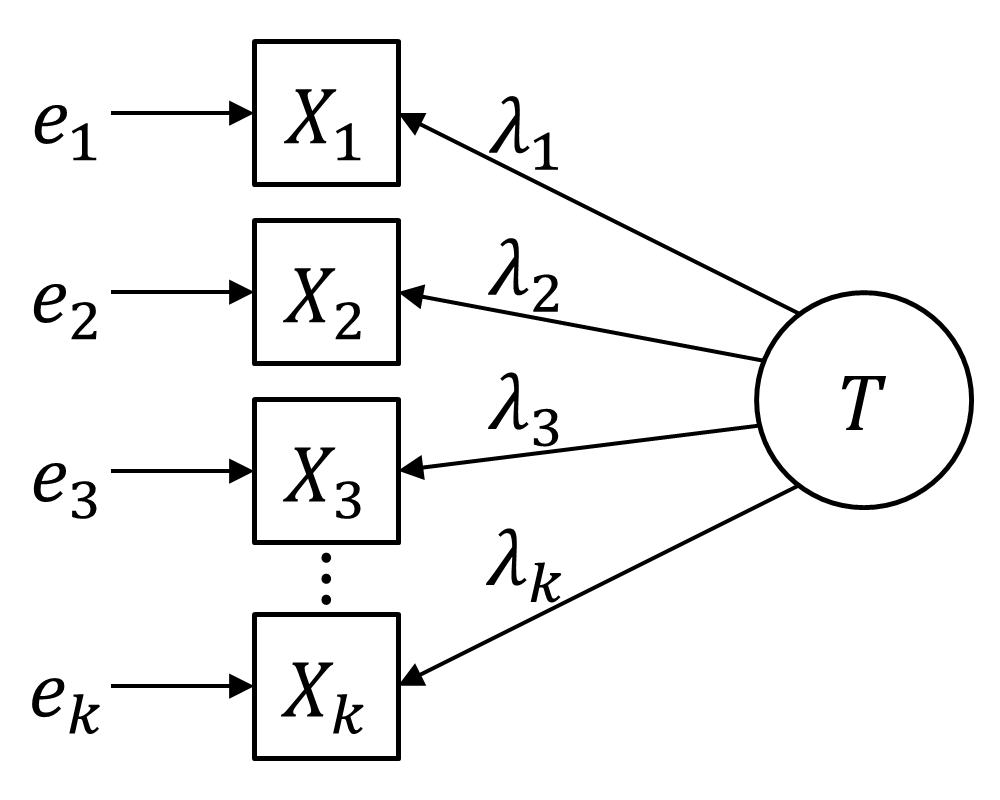
Congeneric Reliability
In statistical models applied to psychometrics, congeneric reliability \rho_C ("rho C")Cho, E. (2016). Making reliability reliable: A systematic approach to reliability coefficients. Organizational Research Methods, 19(4), 651–682. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428116656239 a single-administration test score reliability (i.e., the reliability of persons over items holding occasion fixed coefficient, commonly referred to as composite reliability, construct reliability, and coefficient omega. \rho_C is a structural equation model(SEM)-based reliability coefficients and is obtained from on a unidimensional model. \rho_C is the second most commonly used reliability factor after tau-equivalent reliability(\rho_T), and is often recommended as its alternative. Formula and calculation Systematic and conventional formula Let X_i denote the observed score of item i and X(=X_1 + X_2 + \cdots + X_k) denote the sum of all items in a test consisting of k items. It is assumed that each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Variation
In probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation (CV), also known as relative standard deviation (RSD), is a standardized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution or frequency distribution. It is often expressed as a percentage, and is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation \sigma to the mean \mu (or its absolute value, The CV or RSD is widely used in analytical chemistry to express the precision and repeatability of an assay. It is also commonly used in fields such as engineering or physics when doing quality assurance studies and ANOVA gauge R&R, by economists and investors in economic models, and in neuroscience. Definition The coefficient of variation (CV) is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation \ \sigma to the mean \ \mu , c_ = \frac. It shows the extent of variability in relation to the mean of the population. The coefficient of variation should be computed only for data measured on scales that have a meaningfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |