|
Relaxed Selection
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of change occurring in processes investigated by evolutionary biology, but the formal concept is often extended to other areas of research. In population genetics, selective pressure is usually expressed as a selection coefficient. Amino acids selective pressure It has been shown that putting an amino acid bio-synthesizing gene like ''HIS4'' gene under amino acid selective pressure in yeast causes enhancement of expression of adjacent genes which is due to the transcriptional co-regulation of two adjacent genes in Eukaryota. Antibiotic resistance Drug resistance in bacteria is an example of an outcome of natural selection. When a drug is used on a species of bacteria, those that cannot resist die and do not produce offspring, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the Cell (biology), cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
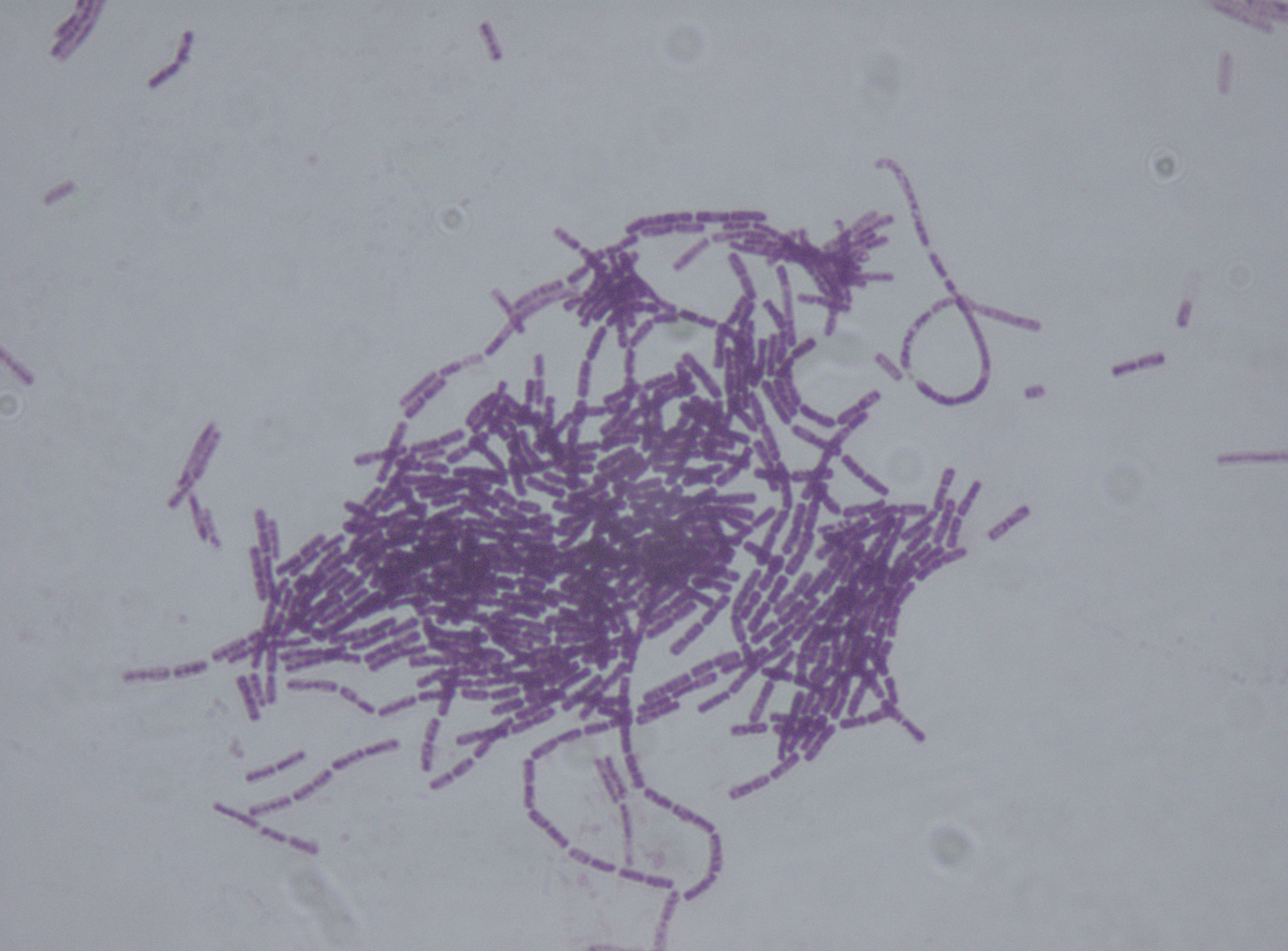
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaranthus Palmeri
''Amaranthus palmeri'' is a species of edible flowering plant in the amaranth genus. It has several common names, including carelessweed, dioecious amaranth, Palmer's amaranth, Palmer amaranth, and Palmer's pigweed. It is native to most of the southern half of North America. Populations in the eastern United States are probably naturalized. It has also been introduced to Europe, Australia, and other areas. The plant is fast-growing and highly competitive. Uses The leaves, stems and seeds of Palmer amaranth, like those of other amaranths, are edible and highly nutritious. Palmer amaranth was once widely cultivated and eaten by Native Americans across North America, both for its abundant seeds and as a cooked or dried green vegetable. Other related ''Amaranthus'' species have been grown as crops for their greens and seeds for thousands of years in Mexico, South America, the Caribbean, Africa, India, and China. The plant can be toxic to livestock animals due to the presence of nit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts. The mosquito life cycle consists of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Eggs are laid on the water surface; they hatch into motile larvae that feed on aquatic algae and organic material. These larvae are important food sources for many freshwater animals, such as dragonfly nymphs, many fish, and some birds such as ducks. The adult females of most species have tube-like mouthparts (called a proboscis) that can pierce the skin of a host and feed on blood, which contains protein and iron needed to produce eggs. Thousands of mosquito species feed on the blood of various hosts � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bt Corn
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both traits are now in use in multiple countries. GM maize has also caused controversy with respect to possible health effects, impact on other insects and impact on other plants via gene flow. One strain, called Starlink, was approved only for animal feed in the US but was found in food, leading to a series of recalls starting in 2000. Marketed products Herbicide-resistant maize Corn varieties resistant to glyphosate herbicides were first commercialized in 1996 by Monsanto, and are known as "Roundup Ready Corn". They tolerate the use of Roundup. Bayer CropScience developed "Liberty Link Corn" that is resistant to glufosinate. Pioneer Hi-Bred has developed and markets corn hybrids with tolerance to imidazoline herbicides under the trademark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamondback Moth
The diamondback moth (''Plutella xylostella''), sometimes called the cabbage moth, is a moth species of the family Plutellidae and genus '' Plutella''. The small, grayish-brown moth sometimes has a cream-colored band that forms a diamond along its back. The species may have originated in Europe, South Africa, or the Mediterranean region, but it has now spread worldwide. The moth has a short life cycle (14 days at 25 °C), is highly fecund, and is capable of migrating long distances. Diamondback moths are considered pests as they feed on the leaves of cruciferous crops and plants that produce glucosinolates. However, not all of these plants are equally useful as hosts to the moth. Because of this, studies have suggested using wintercress as a trap crop around agricultural fields because diamondback moths are highly attracted to that plant but their larvae fail to survive when eggs are laid on it. Originally, pesticides were used to kill the moths but diamondbacks have de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malathion
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. In the USSR, it was known as carbophos, in New Zealand and Australia as maldison and in South Africa as mercaptothion. Pesticide use Malathion is a pesticide that is widely used in agriculture, residential landscaping, public recreation areas, and in public health pest control programs such as mosquito eradication. In the US, it is the most commonly used organophosphate insecticide. A malathion mixture with corn syrup was used in the 1980s in Australia and California to combat the Mediterranean fruit fly. In Canada and the US starting in the early 2000s, malathion was sprayed in many cities to combat west Nile virus. Malathion was used over the last couple of decades on a regular basis during summer months to kill mosquitoes, but homeowners were allowed to exempt their properties if they chose.. Mechanism of action Malathion is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, a diverse family of chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell Anaemia
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of blood disorders typically inherited from a person's parents. The most common type is known as sickle cell anaemia. It results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to a rigid, sickle-like shape under certain circumstances. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis), anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections and stroke. Long-term pain may develop as people get older. The average life expectancy in the developed world is 40 to 60 years. Sickle cell disease occurs when a person inherits two abnormal copies of the β-globin gene (''HBB'') that makes haemoglobin, one from each parent. This gene occurs in chromosome 11. Several subtypes exist, depending on the exact mutation in each haemoglobin gene. An attack can be set off by tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |