|
Regulatory Feedback
There are many types of artificial neural networks (ANN). Artificial neural networks are computational models inspired by biological neural networks, and are used to approximate functions that are generally unknown. Particularly, they are inspired by the behaviour of neurons and the electrical signals they convey between input (such as from the eyes or nerve endings in the hand), processing, and output from the brain (such as reacting to light, touch, or heat). The way neurons semantically communicate is an area of ongoing research. Most artificial neural networks bear only some resemblance to their more complex biological counterparts, but are very effective at their intended tasks (e.g. classification or segmentation). Some artificial neural networks are adaptive systems and are used for example to model populations and environments, which constantly change. Neural networks can be hardware- (neurons are represented by physical components) or software-based (computer models), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a ''weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
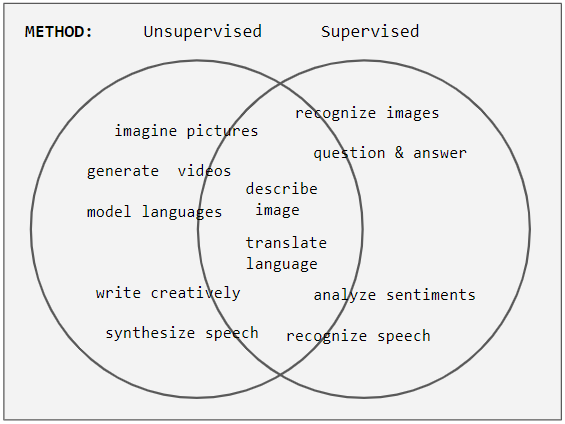
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a type of algorithm that learns patterns from untagged data. The hope is that through mimicry, which is an important mode of learning in people, the machine is forced to build a concise representation of its world and then generate imaginative content from it. In contrast to supervised learning where data is tagged by an expert, e.g. tagged as a "ball" or "fish", unsupervised methods exhibit self-organization that captures patterns as probability densities or a combination of neural feature preferences encoded in the machine's weights and activations. The other levels in the supervision spectrum are reinforcement learning where the machine is given only a numerical performance score as guidance, and semi-supervised learning where a small portion of the data is tagged. Neural networks Tasks vs. methods Neural network tasks are often categorized as discriminative (recognition) or generative (imagination). Often but not always, discriminative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeepDream
DeepDream is a computer vision program created by Google engineer Alexander Mordvintsev that uses a convolutional neural network to find and enhance patterns in images via algorithmic pareidolia, thus creating a dream-like appearance reminiscent of a psychedelic experience in the deliberately overprocessed images. Google's program popularized the term (deep) "dreaming" to refer to the generation of images that produce desired activations in a trained deep network, and the term now refers to a collection of related approaches. History The DeepDream software, originated in a deep convolutional network codenamed "Inception" after the film of the same name, was developed for the ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) in 2014 and released in July 2015. The dreaming idea and name became popular on the internet in 2015 thanks to Google's DeepDream program. The idea dates from early in the history of neural networks, and similar methods have been used to synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsule Neural Network
A capsule neural network (CapsNet) is a machine learning system that is a type of artificial neural network (ANN) that can be used to better model hierarchical relationships. The approach is an attempt to more closely mimic biological neural organization. The idea is to add structures called “capsules” to a convolutional neural network (CNN), and to reuse output from several of those capsules to form more stable (with respect to various perturbations) representations for higher capsules. The output is a vector consisting of the probability of an observation, and a pose for that observation. This vector is similar to what is done for example when doing ''classification with localization'' in CNNs. Among other benefits, capsnets address the "Picasso problem" in image recognition: images that have all the right parts but that are not in the correct spatial relationship (e.g., in a "face", the positions of the mouth and one eye are switched). For image recognition, capsnets exploi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yann LeCun
Yann André LeCun ( , ; originally spelled Le Cun; born 8 July 1960) is a French computer scientist working primarily in the fields of machine learning, computer vision, mobile robotics and computational neuroscience. He is the Silver Professor of the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences at New York University and Vice-President, Chief AI Scientist at Meta. He is well known for his work on optical character recognition and computer vision using convolutional neural networks (CNN), and is a founding father of convolutional nets. He is also one of the main creators of the DjVu image compression technology (together with Léon Bottou and Patrick Haffner). He co-developed the Lush programming language with Léon Bottou. LeCun received the 2018 Turing Award (often referred to as " Nobel Prize of Computing"), together with Yoshua Bengio and Geoffrey Hinton, for their work on deep learning. The three are sometimes referred to as the "Godfathers of AI" and "Godfathers of Deep Lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point. The equivalent concept for optical instruments and image sensors is the field of view (FOV). In optometry, ophthalmology, and neurology, a visual field test is used to determine whether the visual field is affected by diseases that cause local scotoma or a more extensive loss of vision or a reduction in sensitivity (increase in threshold). Normal limits The normal (monocular) human visual field extends to approximately 60 degrees nasally (toward the nose, or inward) from the vertical meridian in each eye, to 107 degrees temporally (away from the nose, or outwards) from the vertical meridian, and approximately 70 degrees above and 80 below the horizontal meridian. The binocular visual field is the superimposition of the two mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Pre-processing
Data preprocessing can refer to manipulation or dropping of data before it is used in order to ensure or enhance performance, and is an important step in the data mining process. The phrase "garbage in, garbage out" is particularly applicable to data mining and machine learning projects. Data-gathering methods are often loosely controlled, resulting in out-of-range values (e.g., Income: −100), impossible data combinations (e.g., Sex: Male, Pregnant: Yes), and missing values, etc. Analyzing data that has not been carefully screened for such problems can produce misleading results. Thus, the representation and quality of data is first and foremost before running any analysis. Often, data preprocessing is the most important phase of a machine learning project, especially in computational biology. If there is much irrelevant and redundant information present or noisy and unreliable data, then knowledge discovery during the training phase is more difficult. Data preparation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see commutativity). The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution (f*g) differs from cross-correlation (f \star g) only in that either or is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-correlation of and , or and . For complex-valued fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNNS
SNNS (Stuttgart Neural Network Simulator) is a neural network simulator originally developed at the University of Stuttgart. While it was originally built for X11 under Unix, there are Windows ports. Its successor JavaNNS never reached the same popularity. Features SNNS is written around a simulation kernel to which user written activation functions, learning procedures and output functions can be added. It has support for arbitrary network topologies and the standard release contains support for a number of standard neural network architectures and training algorithms. Status There is currently no ongoing active development of SNNS. In July 2008 the license was changed to the GNU LGPL. See also * Artificial neural network * Neural network software Neural network software is used to simulate, research, develop, and apply artificial neural networks, software concepts adapted from biological neural networks, and in some cases, a wider array of adaptive systems such as art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernel Fisher Discriminant Analysis
In statistics, kernel Fisher discriminant analysis (KFD), also known as generalized discriminant analysis and kernel discriminant analysis, is a kernelized version of linear discriminant analysis (LDA). It is named after Ronald Fisher. Linear discriminant analysis Intuitively, the idea of LDA is to find a projection where class separation is maximized. Given two sets of labeled data, \mathbf_1 and \mathbf_2, we can calculate the mean value of each class, \mathbf_1 and \mathbf_2, as : \mathbf_i = \frac\sum_^\mathbf_n^i, where l_i is the number of examples of class \mathbf_i. The goal of linear discriminant analysis is to give a large separation of the class means while also keeping the in-class variance small. This is formulated as maximizing, with respect to \mathbf, the following ratio: : J(\mathbf) = \frac, where \mathbf_B is the between-class covariance matrix and \mathbf_W is the total within-class covariance matrix: : \begin \mathbf_B & = (\mathbf_2-\mathbf_1)(\mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Graphical m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernel Density Estimation
In statistics, kernel density estimation (KDE) is the application of kernel smoothing for probability density estimation, i.e., a non-parametric method to estimate the probability density function of a random variable based on '' kernels'' as weights. KDE answers a fundamental data smoothing problem where inferences about the population are made, based on a finite data sample. In some fields such as signal processing and econometrics it is also termed the Parzen–Rosenblatt window method, after Emanuel Parzen and Murray Rosenblatt, who are usually credited with independently creating it in its current form. One of the famous applications of kernel density estimation is in estimating the class-conditional marginal densities of data when using a naive Bayes classifier, which can improve its prediction accuracy. Definition Let (''x''1, ''x''2, ..., ''xn'') be independent and identically distributed samples drawn from some univariate distribution with an unknown density ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


