|
Rectoprostatic Fascia
The rectoprostatic fascia (Denonvilliers' fascia) is a membranous partition at the lowest part of the rectovesical pouch. It separates the prostate and urinary bladder from the rectum. It consists of a single fibromuscular structure with several layers that are fused together and covering the seminal vesicles. It is also called ''Denonvilliers' fascia'' after French anatomist and surgeon Charles-Pierre Denonvilliers. The structure corresponds to the rectovaginal fascia The rectovaginal fascia (often called rectovaginal septum or sometimes fascia of Otto) is a thin structure separating the vagina and the rectum. This corresponds to the rectoprostatic fascia in the male. Clinical significance Perforations in i ... in the female. The rectoprostatic fascia also inhibits the posterior spread of prostatic adenocarcinoma; therefore invasion of the rectum is less common than is invasion of other contiguous structures. References Pelvis Prostate Fascia {{Anatomy-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectovesical Excavation
The rectovesical pouch is the pocket that lies between the rectum and the urinary bladder, bladder in Male, males in Human, humans and other mammals. It is lined by peritoneum. Structure The rectovesical pouch is a space between the rectum and the urinary bladder, bladder in Man, men. It lies above the seminal vesicles. It is lined by peritoneum and at its base is the rectoprostatic fascia (Denonvillier's fascia). When a man is upright or supine, it is the lowest part of his peritoneal cavity. It may contain parts of the ileum (lower small intestine) and the sigmoid colon. In Woman, women, the uterus lies between the rectum and the bladder. Therefore, women do not have a rectovesical pouch, but instead have a rectouterine pouch and vesicouterine pouch. After a hysterectomy in Woman, women, the remaining peritoneum may be referred to as a rectovesical pouch. Clinical significance When a man is upright or supine, the rectovesical pouch is the lowest part of his peritoneal cavit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
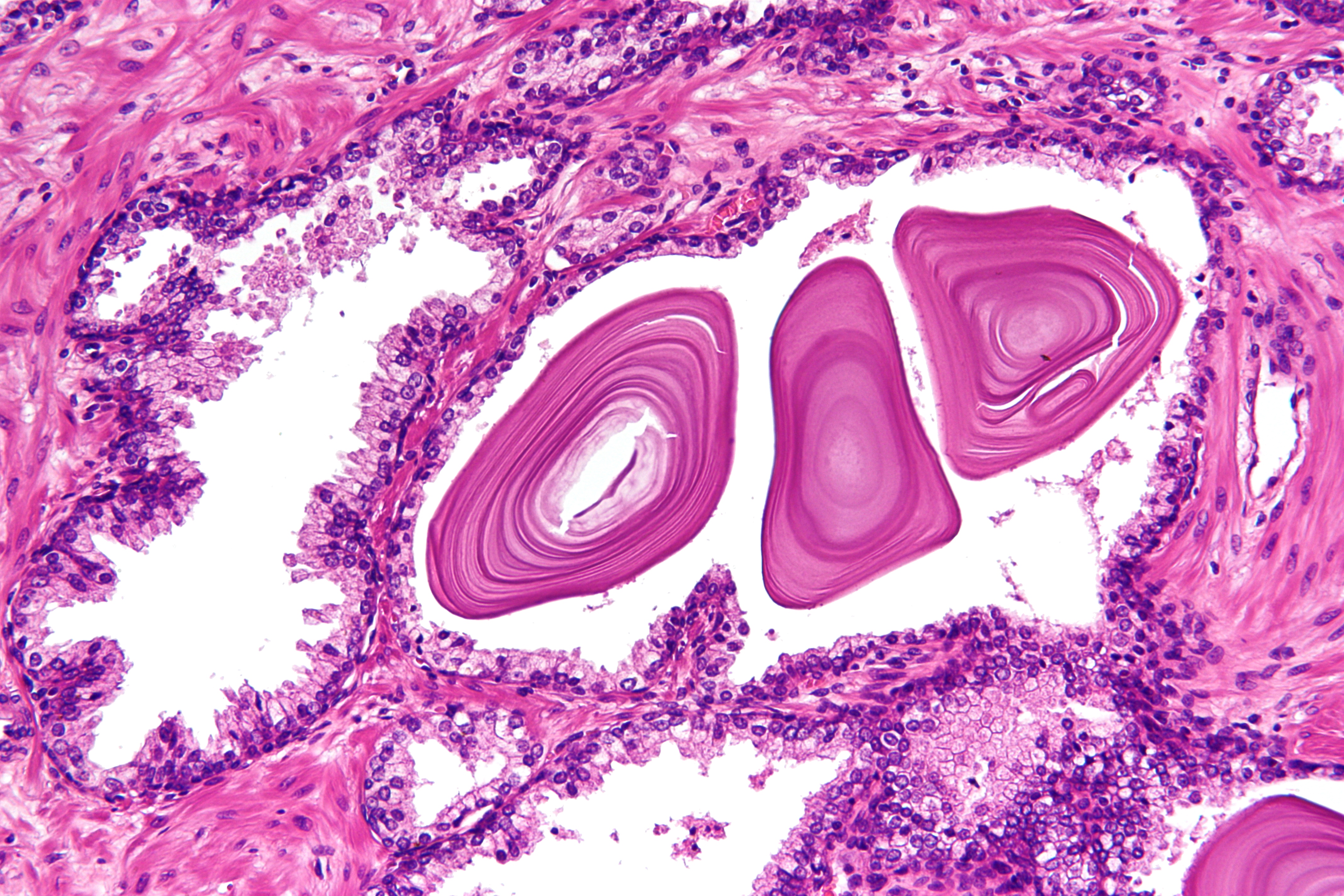
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the Gastrointestinal tract, gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring (the level of the puborectalis sling) or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal which is about long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin ''Wikt:rectum, rectum Wikt:intestinum, intestinum'', meaning ''straight intestine''. Structure The rectum is a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminal Vesicle
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands, or seminal glands) are a pair of two convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of some male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen. The vesicles are 5–10 cm in size, 3–5 cm in diameter, and are located between the bladder and the rectum. They have multiple outpouchings which contain secretory glands, which join together with the vas deferens at the ejaculatory duct. They receive blood from the vesiculodeferential artery, and drain into the vesiculodeferential veins. The glands are lined with column-shaped and cuboidal cells. The vesicles are present in many groups of mammals, but not marsupials, monotremes or carnivores. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is called seminal vesiculitis, most often is due to bacterial infection as a result of a sexually transmitted disease or following a surgical procedure. Seminal vesiculitis can cause pain in the lower abdomen, scrotum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Pierre Denonvilliers
Charles-Pierre Denonvilliers (4 February 1808 – 5 July 1872) was a French surgeon who was a native of Paris. In 1837 he received his medical doctorate, and later was a professor of surgery and anatomy in Paris. Denonvilliers was a pioneer of facial reconstructive surgery. In 1856 he independently performed the second Z-plasty operation for treatment of lower lid ectropion, after Horner in 1837. He is credited for providing the first description of the rectoprostatic fascia, which is sometimes called "Denonvilliers' fascia". Also, another name for the puboprostatic ligament is "Denonvilliers' ligament". With Auguste Bérard Auguste Bérard (1 August 1802 in Varrains – 16 October 1846 in Paris) was a French surgeon. He was the brother of physician Pierre Honoré Bérard (1797–1858). He is not to be confused with the French naval officer of the same name (1796– ... (1802-1846) and Léon Athanase Gosselin (1815-1887), he was co-author of the three-volume ''Compendiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectovaginal Fascia
The rectovaginal fascia (often called rectovaginal septum or sometimes fascia of Otto) is a thin structure separating the vagina and the rectum. This corresponds to the rectoprostatic fascia in the male. Clinical significance Perforations in it can lead to rectocele In gynecology, a rectocele ( ) or posterior vaginal wall prolapse results when the rectum bulges ( herniates) into the vagina. Two common causes of this defect are childbirth and hysterectomy. Rectocele also tends to occur with other forms of pe .... References External links * http://www.emedicinehealth.com/vaginal_prolapse/page18_em.htm Pelvis Fascia {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |