|
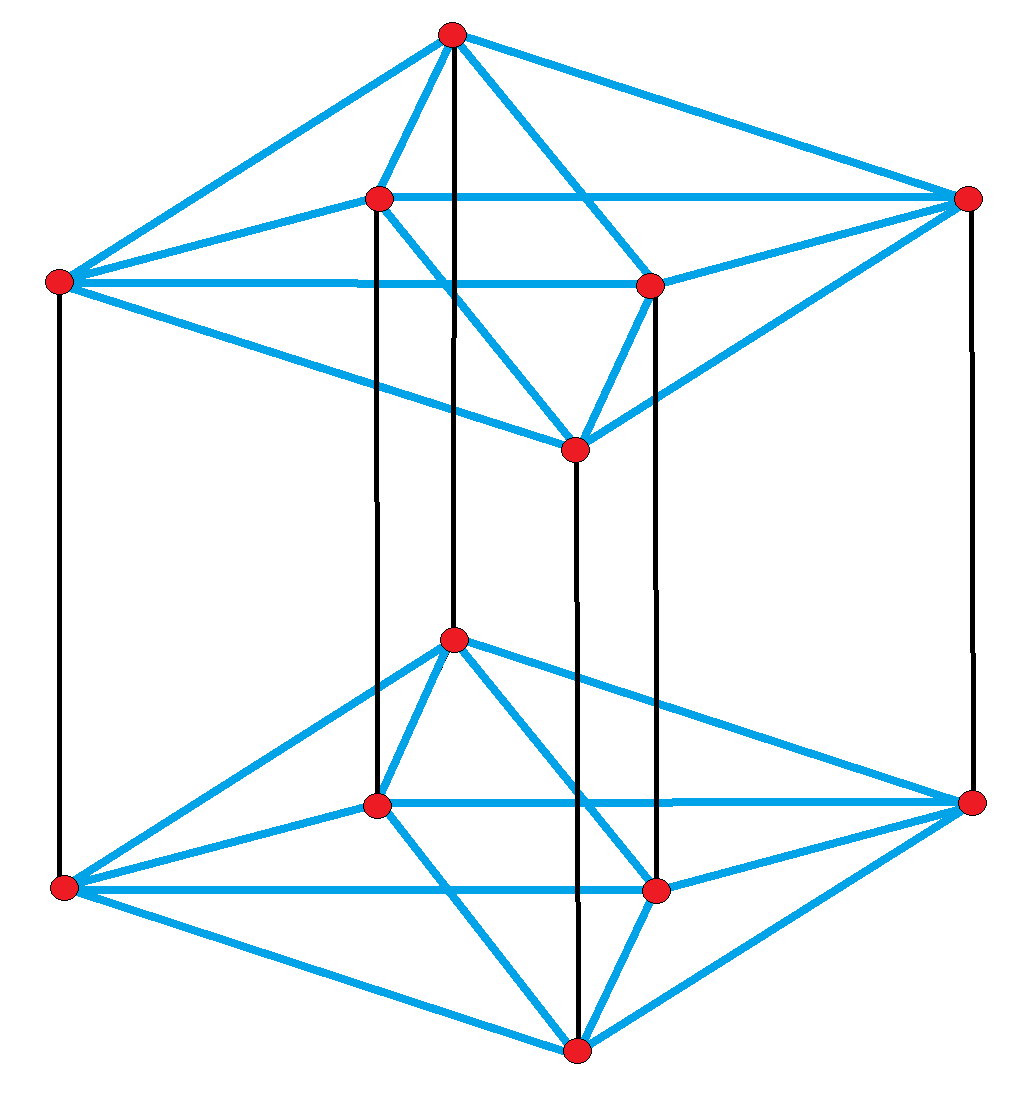
Rectified Pentacross
In five-dimensional geometry, a rectified 5-orthoplex is a convex uniform 5-polytope, being a rectification of the regular 5-orthoplex. There are 5 degrees of rectifications for any 5-polytope, the zeroth here being the 5-orthoplex itself, and the 4th and last being the 5-cube. Vertices of the rectified 5-orthoplex are located at the edge-centers of the 5-orthoplex. Vertices of the birectified 5-orthoplex are located in the triangular face centers of the 5-orthoplex. Rectified 5-orthoplex Its 40 vertices represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group D5. The vertices can be seen in 3 hyperplanes, with the 10 vertices rectified 5-cells cells on opposite sides, and 20 vertices of a runcinated 5-cell passing through the center. When combined with the 10 vertices of the 5-orthoplex, these vertices represent the 50 root vectors of the B5 and C5 simple Lie groups. E. L. Elte identified it in 1912 as a semiregular polytope, identifying it as Cr51 as a first rectification of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-cube T0
In five-dimensional geometry, a 5-cube is a name for a five-dimensional hypercube with 32 vertices, 80 edges, 80 square faces, 40 cubic cells, and 10 tesseract 4-faces. It is represented by Schläfli symbol or , constructed as 3 tesseracts, , around each cubic ridge. It can be called a penteract, a portmanteau of the Greek word , for 'five' (dimensions), and the word ''tesseract'' (the 4-cube). It can also be called a regular deca-5-tope or decateron, being a 5-dimensional polytope constructed from 10 regular facets. Related polytopes It is a part of an infinite hypercube family. The dual of a 5-cube is the 5-orthoplex, of the infinite family of orthoplexes. Applying an '' alternation'' operation, deleting alternating vertices of the 5-cube, creates another uniform 5-polytope, called a 5-demicube, which is also part of an infinite family called the demihypercubes. The 5-cube can be seen as an ''order-3 tesseractic honeycomb'' on a 4-sphere. It is related to the Euclide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified 5-cell
In four-dimensional geometry, the rectified 5-cell is a uniform 4-polytope composed of 5 regular tetrahedral and 5 regular octahedral cells. Each edge has one tetrahedron and two octahedra. Each vertex has two tetrahedra and three octahedra. In total it has 30 triangle faces, 30 edges, and 10 vertices. Each vertex is surrounded by 3 octahedra and 2 tetrahedra; the vertex figure is a triangular prism. Topologically, under its highest symmetry, ,3,3 there is only one geometrical form, containing 5 regular tetrahedra and 5 rectified tetrahedra (which is geometrically the same as a regular octahedron). It is also topologically identical to a tetrahedron-octahedron segmentochoron. The vertex figure of the ''rectified 5-cell'' is a uniform triangular prism, formed by three octahedra around the sides, and two tetrahedra on the opposite ends. Despite having the same number of vertices as cells (10) and the same number of edges as faces (30), the rectified 5-cell is not self-dual becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified 5-cell
In four-dimensional geometry, the rectified 5-cell is a uniform 4-polytope composed of 5 regular tetrahedral and 5 regular octahedral cells. Each edge has one tetrahedron and two octahedra. Each vertex has two tetrahedra and three octahedra. In total it has 30 triangle faces, 30 edges, and 10 vertices. Each vertex is surrounded by 3 octahedra and 2 tetrahedra; the vertex figure is a triangular prism. Topologically, under its highest symmetry, ,3,3 there is only one geometrical form, containing 5 regular tetrahedra and 5 rectified tetrahedra (which is geometrically the same as a regular octahedron). It is also topologically identical to a tetrahedron-octahedron segmentochoron. The vertex figure of the ''rectified 5-cell'' is a uniform triangular prism, formed by three octahedra around the sides, and two tetrahedra on the opposite ends. Despite having the same number of vertices as cells (10) and the same number of edges as faces (30), the rectified 5-cell is not self-dual becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplane
In geometry, a hyperplane is a subspace whose dimension is one less than that of its ''ambient space''. For example, if a space is 3-dimensional then its hyperplanes are the 2-dimensional planes, while if the space is 2-dimensional, its hyperplanes are the 1-dimensional lines. This notion can be used in any general space in which the concept of the dimension of a subspace is defined. In different settings, hyperplanes may have different properties. For instance, a hyperplane of an -dimensional affine space is a flat subset with dimension and it separates the space into two half spaces. While a hyperplane of an -dimensional projective space does not have this property. The difference in dimension between a subspace and its ambient space is known as the codimension of with respect to . Therefore, a necessary and sufficient condition for to be a hyperplane in is for to have codimension one in . Technical description In geometry, a hyperplane of an ''n''-dimensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Lie Group
In mathematics, a simple Lie group is a connected non-abelian Lie group ''G'' which does not have nontrivial connected normal subgroups. The list of simple Lie groups can be used to read off the list of simple Lie algebras and Riemannian symmetric spaces. Together with the commutative Lie group of the real numbers, \mathbb, and that of the unit-magnitude complex numbers, U(1) (the unit circle), simple Lie groups give the atomic "blocks" that make up all (finite-dimensional) connected Lie groups via the operation of group extension. Many commonly encountered Lie groups are either simple or 'close' to being simple: for example, the so-called "special linear group" SL(''n'') of ''n'' by ''n'' matrices with determinant equal to 1 is simple for all ''n'' > 1. The first classification of simple Lie groups was by Wilhelm Killing, and this work was later perfected by Élie Cartan. The final classification is often referred to as Killing-Cartan classification. Definition Unfortun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Polytope
A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set contained in the n-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^n. Most texts. use the term "polytope" for a bounded convex polytope, and the word "polyhedron" for the more general, possibly unbounded object. Others''Mathematical Programming'', by Melvyn W. Jeter (1986) p. 68/ref> (including this article) allow polytopes to be unbounded. The terms "bounded/unbounded convex polytope" will be used below whenever the boundedness is critical to the discussed issue. Yet other texts identify a convex polytope with its boundary. Convex polytopes play an important role both in various branches of mathematics and in applied areas, most notably in linear programming. In the influential textbooks of Grünbaum and Ziegler on the subject, as well as in many other texts in discrete geometry, convex polytopes are often simply called "polytopes". Grünbaum points out that this is solely to avoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter Group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H. S. M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of reflections (or kaleidoscopic mirrors). Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example. However, not all Coxeter groups are finite, and not all can be described in terms of symmetries and Euclidean reflections. Coxeter groups were introduced in 1934 as abstractions of reflection groups , and finite Coxeter groups were classified in 1935 . Coxeter groups find applications in many areas of mathematics. Examples of finite Coxeter groups include the symmetry groups of regular polytopes, and the Weyl groups of simple Lie algebras. Examples of infinite Coxeter groups include the triangle groups corresponding to regular tessellations of the Euclidean plane and the hyperbolic plane, and the Weyl groups of infinite-dimensional Kac–Moody algebras. Standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decagon
In geometry, a decagon (from the Greek δέκα ''déka'' and γωνία ''gonía,'' "ten angles") is a ten-sided polygon or 10-gon.. The total sum of the interior angles of a simple decagon is 1440°. A self-intersecting ''regular decagon'' is known as a decagram. Regular decagon A '' regular decagon'' has all sides of equal length and each internal angle will always be equal to 144°. Its Schläfli symbol is and can also be constructed as a truncated pentagon, t, a quasiregular decagon alternating two types of edges. Side length The picture shows a regular decagon with side length a and radius R of the circumscribed circle. * The triangle E_E_1M has to equally long legs with length R and a base with length a * The circle around E_1 with radius a intersects ]M\,E_ _in_a_point_P_(not_designated_in_the_picture)._ *_Now_the_triangle_\;_is_a_isosceles_triangle.html" ;"title="/math> in a point P (not designated in the picture). * Now the triangle \; is a isosceles triang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrie Polygon
In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of dimensions is a skew polygon in which every consecutive sides (but no ) belongs to one of the facets. The Petrie polygon of a regular polygon is the regular polygon itself; that of a regular polyhedron is a skew polygon such that every two consecutive sides (but no three) belongs to one of the faces. Petrie polygons are named for mathematician John Flinders Petrie. For every regular polytope there exists an orthogonal projection onto a plane such that one Petrie polygon becomes a regular polygon with the remainder of the projection interior to it. The plane in question is the Coxeter plane of the symmetry group of the polygon, and the number of sides, , is the Coxeter number of the Coxeter group. These polygons and projected graphs are useful in visualizing symmetric structure of the higher-dimensional regular polytopes. Petrie polygons can be defined more generally for any embedded graph. They form the faces of anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Prism
In geometry, an octahedral prism is a convex uniform 4-polytope. This 4-polytope has 10 polyhedral cells: 2 octahedra connected by 8 triangular prisms. Alternative names *Octahedral dyadic prism ( Norman W. Johnson) *Ope (Jonathan Bowers, for octahedral prism) *Triangular antiprismatic prism *Triangular antiprismatic hyperprism Coordinates It is a Hanner polytope with vertex coordinates, permuting first 3 coordinates: :( �1,0,0 ±1) Structure The octahedral prism consists of two octahedra connected to each other via 8 triangular prisms. The triangular prisms are joined to each other via their square faces. Projections The octahedron-first orthographic projection of the octahedral prism into 3D space has an octahedral envelope. The two octahedral cells project onto the entire volume of this envelope, while the 8 triangular prismic cells project onto its 8 triangular faces. The triangular-prism-first orthographic projection of the octahedral prism into 3D space has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectified Pentacross Verf
Rectification has the following technical meanings: Mathematics * Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points * Rectifiable curve, in mathematics * Rectifiable set, in mathematics Science * GHK flux equation#Rectification, in biology, a process in cell membranes Technology * Image rectification, adjustment of images to simplify stereo vision or to map images to a map coordinate system (GIS) * The function of a rectifier, a device that converts alternating electrical current to direct current * Rectified airspeed, a means of displaying the airspeed of high-speed aircraft * Rectification (chemical/process engineering), countercurrent distillation, a unit operation also used for the production of rectified spirit (see Distillation#Fractional distillation) Other uses * Rectification (law), an equitable legal remedy whereby a court orders a change in a written document to reflect what it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off. Definitions Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines across the connected faces, joining adjacent points around the face. When done, these lines form a complete circuit, i.e. a polygon, around the vertex. This polygon is the vertex figure. More precise formal definitions can vary quite widely, according to circumstance. For example Coxeter (e.g. 1948, 1954) varies his definition as convenient for the current area of discussion. Most of the following definitions of a vertex figure apply equally well to infinite tessellation, tilings or, by extension, to Honeycomb (geometry), space-filling tessellation with polytope Cell (geometry), cells and other higher-dimensional polytopes. As a flat slice Make a slice through the corner of the polyhedron, cutting through all the edges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |