|
Reaction Formation
In psychoanalytic theory, reaction formation (german: Reaktionsbildung) is a defense mechanism in which emotions and impulses which are anxiety-producing or perceived to be unacceptable are mastered by exaggeration of the directly opposing tendency. Charles Rycroft, ''A Critical Dictionary of Psychoanalysis'' (London, 2nd Edn, 1995) The reaction formations belong to Level 3 of neurotic defense mechanisms, which also include dissociation, displacement, intellectualization, and repression. Theory Reaction formation depends on the hypothesis that " e instincts and their derivatives may be arranged as pairs of opposites: life versus death, construction versus destruction, action versus passivity, dominance versus submission, and so forth. When one of the instincts produces anxiety by exerting pressure on the ego either directly or by way of the superego, the ego may try to sidetrack the offending impulse by concentrating upon its opposite. For example, if feelings of hate towards a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalytic Theory
Psychoanalytic theory is the theory of personality organization and the dynamics of personality development that guides psychoanalysis, a clinical method for treating psychopathology. First laid out by Sigmund Freud in the late 19th century, psychoanalytic theory has undergone many refinements since his work. The psychoanalytic theory came to full prominence in the last third of the twentieth century as part of the flow of critical discourse regarding psychological treatments after the 1960s, long after Freud's death in 1939. Freud had ceased his analysis of the brain and his physiological studies and shifted his focus to the study of the mind and the related psychological attributes making up the mind, and on treatment using free association and the phenomena of transference. His study emphasized the recognition of childhood events that could influence the mental functioning of adults. His examination of the genetic and then the developmental aspects gave the psychoanalytic theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
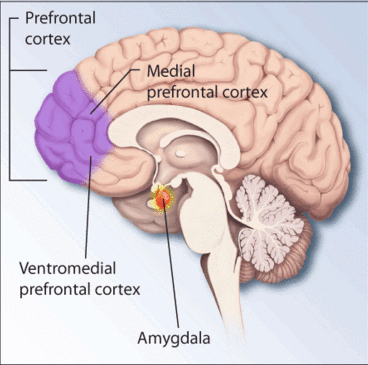
Phobia
A phobia is an anxiety disorder defined by a persistent and excessive fear of an object or situation. Phobias typically result in a rapid onset of fear and are usually present for more than six months. Those affected go to great lengths to avoid the situation or object, to a degree greater than the actual danger posed. If the object or situation cannot be avoided, they experience significant distress. Other symptoms can include fainting, which may occur in blood or injury phobia, and panic attacks, often found in agoraphobia. Around 75% of those with phobias have multiple phobias. Phobias can be divided into specific phobias, social anxiety disorder, and agoraphobia. Specific phobias are further divided to include certain animals, natural environment, blood or injury, and particular situations. The most common are fear of spiders, fear of snakes, and fear of heights. Specific phobias may be caused by a negative experience with the object or situation in early childhood. Soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streisand Effect
Attempts to hide, remove, or censor information often have the unintended consequence of increasing awareness of that information via the Internet. This is called the Streisand effect. It is named after American singer and actress Barbra Streisand, whose attempt to suppress the California Coastal Records Project's photograph of her cliff-top residence in Malibu, California, taken to document California coastal erosion, inadvertently drew greater attention to the photograph in 2003. Attempts to suppress information are often made through cease-and-desist letters, but instead of being suppressed, the information receives extensive publicity, as well as media extensions such as videos and spoof songs, which can be mirrored on the Internet or distributed on file-sharing networks. In addition, seeking or obtaining an injunction to prohibit something from being published or remove something that is already published can lead to increased publicity of the published work. The Streisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-hatred
Self-hatred is personal self-loathing or hatred of oneself, or low self-esteem which may lead to self-harm. In psychology and psychiatry The term "self-hatred" is used infrequently by psychologists and psychiatrists, who would usually describe people who hate themselves as "people with low self-esteem". Self-hatred, self-guilt and shame are important factors in some or many mental disorders, especially disorders that involve a perceived defect of oneself (e.g. body dysmorphic disorder). Self-hatred is also a symptom of many personality disorders, including borderline personality disorder, as well as mood disorders like depression. It can also be linked to guilt for someone's own actions that they view as wrongful, e.g., survivor guilt. In social groups Self-hatred by members of ethnic groups, gender groups, and religions is postulated to be a result of internalization of hatred of those groups from dominant cultures. African-Americans Racial stereotyping of African-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression (psychology)
Regression (german: Regression), according to psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud, is a defense mechanism leading to the temporary or long-term reversion of the ego to an earlier stage of development rather than handling unacceptable impulses more adaptively. In psychoanalytic theory, regression occurs when an individual's personality reverts to an earlier stage of development, adopting more childish mannerisms. Freud, regression, and neurosis Freud saw inhibited development, fixation, and regression as centrally formative elements in the creation of a neurosis. Arguing that 'the libidinal function goes through a lengthy development', he assumed that 'a development of this kind involves two dangers – first, of ''inhibition'', and secondly, of ''regression'' '. Inhibitions produced fixations; and the 'stronger the fixations on its path of development, the more readily will the function evade external difficulties by regressing to the fixations'. Neurosis for Freud was thus the product o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationalization (psychology)
Rationalization is a defense mechanism (ego defense) in which apparent logical reasons are given to justify behavior that is motivated by unconscious instinctual impulses. It is an attempt to find reasons for behaviors, especially one's own. Rationalizations are used to defend against feelings of guilt, maintain self-respect, and protect oneself from criticism. Rationalization happens in two steps: # A decision, action, judgement is made for a given reason, or no (known) reason at all. # A rationalization is performed, constructing a seemingly good or logical reason, as an attempt to justify the act after the fact (for oneself or others). Rationalization encourages irrational or unacceptable behavior, motives, or feelings and often involves ad hoc hypothesizing. This process ranges from fully conscious (e.g. to present an external defense against ridicule from others) to mostly unconscious (e.g. to create a block against internal feelings of guilt or shame). People rationalize fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Repression
Repression is a key concept of psychoanalysis, where it is understood as a defence mechanism that "ensures that what is unacceptable to the conscious mind, and would if recalled arouse anxiety, is prevented from entering into it." According to psychoanalytic theory, repression plays a major role in many mental illnesses, and in the psyche of the average person.Laplanche pp. 390, 392 There has been debate as to whether (or how often) memory repression really occurs and mainstream psychology holds that true memory repression occurs infrequently. American psychologists began to attempt to study repression in the experimental laboratory around 1930. However, psychoanalysts were at first uninterested in attempts to study repression in laboratory settings, and later came to reject them. Most psychoanalysts concluded that such attempts misrepresented the psychoanalytic concept of repression. Sigmund Freud's theory As Sigmund Freud moved away from hypnosis, and towards urging his patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Projection
Psychological projection is the process of misinterpreting what is "inside" as coming from "outside". It forms the basis of empathy by the projection of personal experiences to understand someone else's subjective world. In its malignant forms, it is a defense mechanism in which the ego defends itself against disowned and highly negative parts of the self by denying their existence in themselves and attributing them to others, breeding misunderstanding and causing untold interpersonal damage. A bully may project their own feelings of vulnerability onto the target, or a person who is confused may project feelings of confusion and inadequacy onto other people. Projection incorporates blame shifting and can manifest as shame dumping. Projection has been described as an early phase of introjection. Historical precursors A prominent precursor in the formulation of the projection principle was Giambattista Vico. In 1841, Ludwig Feuerbach was the first enlightenment thinker to employ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterphobic Attitude
Counterphobic attitude is a response to anxiety that, instead of fleeing the source of fear in the manner of a phobia, actively seeks it out, in the hope of overcoming the original anxiousness. Contrary to the avoidant personality disorder, the counterphobic represents the less usual, but not totally uncommon, response of seeking out what is feared: codependents may fall into a subcategory of this group, hiding their fears of attachment in over-dependency. Action Dare-devil activities are often undertaken in a counterphobic spirit, as a denial of the fears attached to them, which may be only partially successful. Acting out in general may have a counterphobic source, reflecting a false self over-concerned with compulsive doing to preserve a sense of power and control. Sex is a key area for counterphobic activity, sometimes powering hypersexuality in people who are actually afraid of the objects they believe they love. Adolescents, fearing sex play, may jump over to a kind of spu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panhandler
Begging (also panhandling) is the practice of imploring others to grant a favor, often a gift of money, with little or no expectation of reciprocation. A person doing such is called a beggar or panhandler. Beggars may operate in public places such as transport routes, urban parks, and markets. Besides money, they may also ask for food, drinks, cigarettes or other small items. Internet begging is the modern practice of asking people to give money to others via the Internet, rather than in person. Internet begging may encompass requests for help meeting basic needs such as medical care and shelter, as well as requests for people to pay for vacations, school trips, and other things that the beggar wants but cannot comfortably afford. Beggars differ from religious mendicants in that some mendicants do not ask for money. Their subsistence is reciprocated by providing society with various forms of religious service, moral education, and preservation of culture. History Beggars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm Syndrome
Stockholm syndrome is a condition in which hostages develop a psychological bond with their captors. It is supposed to result from a rather specific set of circumstances, namely the power imbalances contained in hostage-taking, kidnapping, and abusive relationships. Therefore, it is difficult to find a large number of people who experience Stockholm syndrome to conduct studies with any sort of power. This makes it hard to determine trends in the development and effects of the condition— and, in fact, it is a "contested illness" due to doubts about the legitimacy of the condition. Emotional bonds may be formed between captors and captives, during intimate time together, but these are generally considered irrational in light of the danger or risk endured by the victims. Stockholm syndrome has never been included in the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' or DSM, the standard tool for diagnosis of psychiatric illnesses and disorders in the US, mainly du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathexis
In psychoanalysis, cathexis (or emotional investment) is defined as the process of allocation of mental or emotional energy to a person, object, or idea. Origin of term The Greek term ''cathexis'' (κάθεξις) was chosen by James Strachey to render the German term ''Besetzung'' in his translation of Sigmund Freud's complete works. Freud himself used the word "interest" in English in an early letter to Ernest Jones. Peter Gay objected that Strachey's use of cathexis was an unnecessarily esoteric replacement for Freud's use of ''Besetzung'' – "a word from common German speech rich in suggestive meanings, among them 'occupation' (by troops) and 'charge' (of electricity)", of which the latter is an incorrect claim by Gay (as can be confirmed by looking in any German dictionary). Apparently Gay was confused by the common use of the English noun and verb "charge" to refer to both "allocation/allocating" and the "energy" allocated in cathexis, e.g. "emotional charge", "counter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |