|
Rap1
Rap1 (Ras-proximate-1 or Ras-related protein 1) is a small GTPase, which are small cytosolic proteins that act like cellular switches and are vital for effective signal transduction. There are two isoforms of the Rap1 protein, each encoded by a separate gene, RAP1A and RAP1B. Rap1 belongs to Ras-related protein family. GTPases are inactive when in their GDP-bound form, and become active when they bind to GTP. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) and guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) regulate small GTPases, with GAPs promoting the GDP-bound (inactive) form, and GEFs promoting the GTP-bound (active) form. When bound to GTP, small GTPases regulate myriad cellular processes. These proteins are divided into families depending on their protein structure, and the most well studied is the Ras superfamily, of which Rap1 is a member. Whereas Ras is known for its role in cell proliferation and survival, Rap1 is predominantly involved in cell adhesion and cell junction formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAP1B
Ras-related protein Rap-1b, also known as GTP-binding protein smg p21B, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAP1B'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAP1A
Ras-related protein Rap-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAP1A'' gene. Function The product of this gene belongs to the family of Ras-related proteins. These proteins share approximately 50% amino acid identity with the classical RAS proteins and have numerous structural features in common. The most striking difference between RAP proteins and RAS proteins resides in their 61st amino acid: glutamine in RAS is replaced by threonine in RAP proteins. The product of this gene counteracts the mitogenic function of RAS because it can interact with RAS GAPs and RAF in a competitive manner. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. Interactions RAP1A has been shown to interact with: * C-Raf, * MLLT4, * PDE6D, * RALGDS, * RAPGEF2, and * TSC2 Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2 (TSC2), also known as Tuberin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSC2'' gene. Function Mutations in this gene lead to tuberous sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transducing Adaptor Protein
Signal transducing adaptor proteins (STAPs) are proteins that are accessory to main proteins in a signal transduction pathway. Adaptor proteins contain a variety of protein-binding modules that link protein-binding partners together and facilitate the creation of larger signaling complexes. These proteins tend to lack any intrinsic enzymatic activity themselves, instead mediating specific protein–protein interactions that drive the formation of protein complexes. Examples of adaptor proteins include MYD88, Grb2 and SHC1. Signaling components Much of the specificity of signal transduction depends on the recruitment of several signalling components such as protein kinases and G-protein GTPases into short-lived active complexes in response to an activating signal such as a growth factor binding to its receptor. Domains Adaptor proteins usually contain several domains within their structure (e.g., Src homology 2 (SH2) and SH3 domains) that allow specific interactions with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APBB1IP
Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family B member 1-interacting protein (APBB1IP), also known as APBB1-interacting protein 1 or Rap1-GTP-interacting adapter molecule (RIAM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APBB1IP'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKD1
Polycystin 1 (often abbreviated to PC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PKD1'' gene. Mutations of ''PKD1'' are associated with most cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, a severe hereditary disorder of the kidneys characterised by the development of renal cysts and severe kidney dysfunction. Protein structure and function PC1 is a membrane-bound protein 4303 amino acids in length expressed largely upon the primary cilium, as well as apical membranes, adherens junctions, and desmosomes. It has 11 transmembrane domains, a large extracellular N-terminal domain, and a short (about 200 amino acid) cytoplasmic C-terminal domain. This intracellular domain contains a coiled-coil domain through which PC1 interacts with polycystin 2 (PC2), a membrane-bound Ca2+-permeable ion channel. PC1 has been proposed to act as a G protein–coupled receptor. The C-terminal domain may be cleaved in a number of different ways. In one instance, a ~35 kDa portion of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercellular Adhesion Molecule
In molecular biology, intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. They are important in inflammation, immune responses and in intracellular signalling events. The ICAM family consists of five members, designated ICAM-1 to ICAM-5. They are known to bind to leucocyte integrins CD11/CD18 such as LFA-1 and Macrophage-1 antigen, during inflammation and in immune responses. In addition, ICAMs may exist in soluble forms in human plasma, due to activation and proteolysis mechanisms at cell surfaces. Mammalian intercellular adhesion molecules include: * ICAM-1 * ICAM2 * ICAM3 * ICAM4 * ICAM5 Intercellular adhesion molecule 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ICAM5'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycopro ... References Cell biology Protein families {{Biochem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STK24
Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''STK24'' gene located in the chromosome 13, band q32.2. It is also known as Mammalian STE20-like protein kinase 3 (MST-3). The protein is 443 amino acids long and its mass is 49 kDa. Classification and discovery The yeast 'Sterile 20' gene (STE20) functions upstream of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. In mammals, protein kinases related to STE20 can be divided into 2 subfamilies based on their structure and regulation. Members of the PAK subfamily (see PAK3) contain a C-terminal catalytic domain and an N-terminal regulatory domain that has a CDC42-binding domain. In contrast, members of the GCK subfamily (MAP4K2), also called the Sps1 subfamily, have an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain without a CDC42-binding domain. STK24 belongs to the GCK subfamily of STE20-like kinases. The sterile 20 protein was first found in yeast. The MST-20 related kinases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MST1
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP), also known as hepatocyte growth factor-like protein (HLP, HGFL, or HGFLP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MST1'' (''macrophage-stimulating 1'') gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunological Synapse
In immunology, an immunological synapse (or immune synapse) is the interface between an antigen-presenting cell or target cell and a lymphocyte such as a T/B cell or Natural Killer cell. The interface was originally named after the neuronal synapse, with which it shares the main structural pattern. An immunological synapse consists of molecules involved in T cell activation, which compose typical patterns—activation clusters. Immunological synapses are the subject of much ongoing research. Structure and function The immune synapse is also known as the supramolecular activation cluster or SMAC. This structure is composed of concentric rings each containing segregated clusters of proteins—often referred to as the bull’s-eye model of the immunological synapse: * c-SMAC (central-SMAC) composed of the θ isoform of protein kinase C, CD2, CD4, CD8, CD28, Lck, and Fyn. * p-SMAC (peripheral-SMAC) within which the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) and the cytoskel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
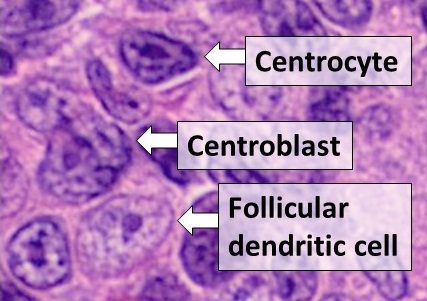
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |