|
Range Query
A range query is a common database operation that retrieves all records where some value is between an upper and lower boundary. For example, list all employees with 3 to 5 years' experience. Range queries are unusual because it is not generally known in advance how many entries a range query will return, or if it will return any at all. Many other queries, such as the top ten most senior employees, or the newest employee, can be done more efficiently because there is an upper bound to the number of results they will return. A query that returns exactly one result is sometimes called a singleton. Partial match query Match at least one of the requested keys. *B+ tree * k-d tree * R-tree See also * Range searching In computer science, the range searching problem consists of processing a set ''S'' of objects, in order to determine which objects from ''S'' intersect with a query object, called the ''range''. For example, if ''S'' is a set of points correspond ... References Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Row (database)
In a relational database, a row or " record" or " tuple", represents a single, implicitly structured data Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ... item in a table. A database table can be thought of as consisting of rows and columns. Cory Janssen, Techopedia, retrieved 27 June 2014 Each row in a table represents a set of related data, and every row in the table has the same structure. For example, in a table that represents companies, each row might represent a single company. Columns might represent things like company name, address, etc. In a table that represents ''the association'' of empl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable (from Latin language, Latin ) is a Mathematical symbol, symbol, typically a letter, that refers to an unspecified mathematical object. One says colloquially that the variable ''represents'' or ''denotes'' the object, and that any valid candidate for the object is the value (mathematics), value of the variable. The values a variable can take are usually of the same kind, often numbers. More specifically, the values involved may form a Set (mathematics), set, such as the set of real numbers. The object may not always exist, or it might be uncertain whether any valid candidate exists or not. For example, one could represent two integers by the variables and and require that the value of the square of is twice the square of , which in algebraic notation can be written . A definitive proof that this relationship is impossible to satisfy when and are restricted to integer numbers isn't obvious, but it has been known since ancient times and has had a big ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Singleton (mathematics)
In mathematics, a singleton (also known as a unit set or one-point set) is a set with exactly one element. For example, the set \ is a singleton whose single element is 0. Properties Within the framework of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, the axiom of regularity guarantees that no set is an element of itself. This implies that a singleton is necessarily distinct from the element it contains, thus 1 and \ are not the same thing, and the empty set is distinct from the set containing only the empty set. A set such as \ is a singleton as it contains a single element (which itself is a set, but not a singleton). A set is a singleton if and only if its cardinality is . In von Neumann's set-theoretic construction of the natural numbers, the number 1 is ''defined'' as the singleton \. In axiomatic set theory, the existence of singletons is a consequence of the axiom of pairing: for any set ''A'', the axiom applied to ''A'' and ''A'' asserts the existence of \, which is the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
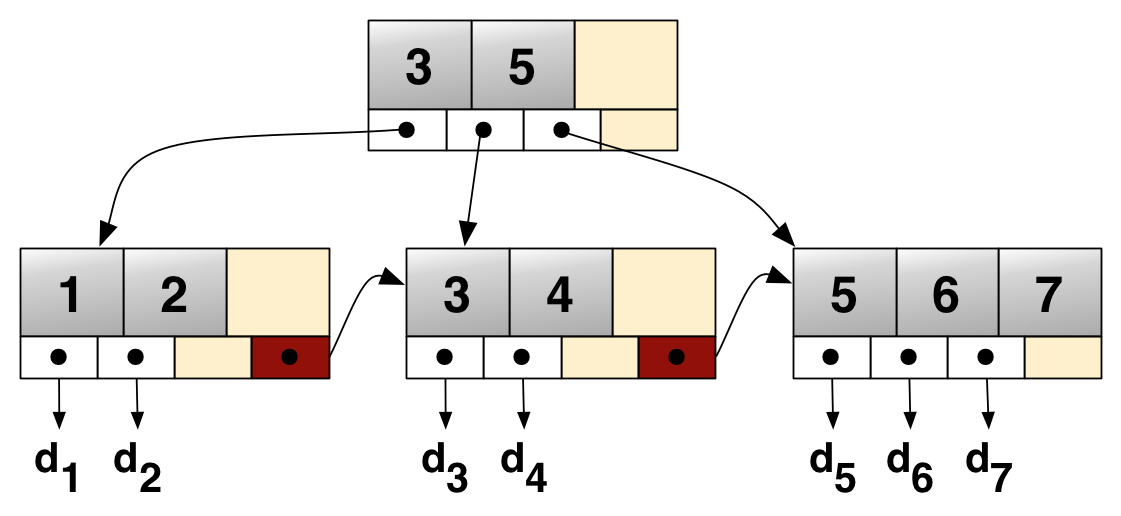
B+ Tree
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children. A B+ tree can be viewed as a B-tree in which each node contains only keys (not key–value pairs), and to which an additional level is added at the bottom with linked leaves. The primary value of a B+ tree is in storing data for efficient retrieval in a Block (data storage), block-oriented storage context—in particular, filesystems. This is primarily because unlike binary search trees, B+ trees have very high fanout (number of pointers to child nodes in a node, typically on the order of 100 or more), which reduces the number of I/O operations required to find an element in the tree. History There is no single paper introducing the B+ tree concept. Instead, the notion of maintaining all data in leaf nodes is repeatedly brought up as an interesting variant of the B- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
K-d Tree
In computer science, a ''k''-d tree (short for ''k-dimensional tree'') is a space-partitioning data structure for organizing points in a ''k''-dimensional space. K-dimensional is that which concerns exactly k orthogonal axes or a space of any number of dimensions. ''k''-d trees are a useful data structure for several applications, such as: * Searches involving a multidimensional search key (e.g. range searches and nearest neighbor searches) & * Creating point clouds. ''k''-d trees are a special case of binary space partitioning trees. Description The ''k''-d tree is a binary tree in which ''every'' node is a ''k''-dimensional point. Every non-leaf node can be thought of as implicitly generating a splitting hyperplane that divides the space into two parts, known as half-spaces. Points to the left of this hyperplane are represented by the left subtree of that node and points to the right of the hyperplane are represented by the right subtree. The hyperplane direction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
R-tree
R-trees are tree data structures used for spatial access methods, i.e., for indexing multi-dimensional information such as geographical coordinates, rectangles or polygons. The R-tree was proposed by Antonin Guttman in 1984 and has found significant use in both theoretical and applied contexts. A common real-world usage for an R-tree might be to store spatial objects such as restaurant locations or the polygons that typical maps are made of: streets, buildings, outlines of lakes, coastlines, etc. and then find answers quickly to queries such as "Find all museums within 2 km of my current location", "retrieve all road segments within 2 km of my location" (to display them in a navigation system) or "find the nearest gas station" (although not taking roads into account). The R-tree can also accelerate nearest neighbor search for various distance metrics, including great-circle distance. R-tree idea The key idea of the data structure is to group nearby objects and represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Range Searching
In computer science, the range searching problem consists of processing a set ''S'' of objects, in order to determine which objects from ''S'' intersect with a query object, called the ''range''. For example, if ''S'' is a set of points corresponding to the coordinates of several cities, find the subset of cities within a given range of latitudes and longitudes. The range searching problem and the data structures that solve it are a fundamental topic of computational geometry. Applications of the problem arise in areas such as Geographic information system, geographical information systems (GIS), computer-aided design (CAD) and databases. Variations There are several variations of the problem, and different data structures may be necessary for different variations. In order to obtain an efficient solution, several aspects of the problem need to be specified: * Object types: Algorithms depend on whether ''S'' consists of Point (geometry), points, line (geometry), lines, line seg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |