|
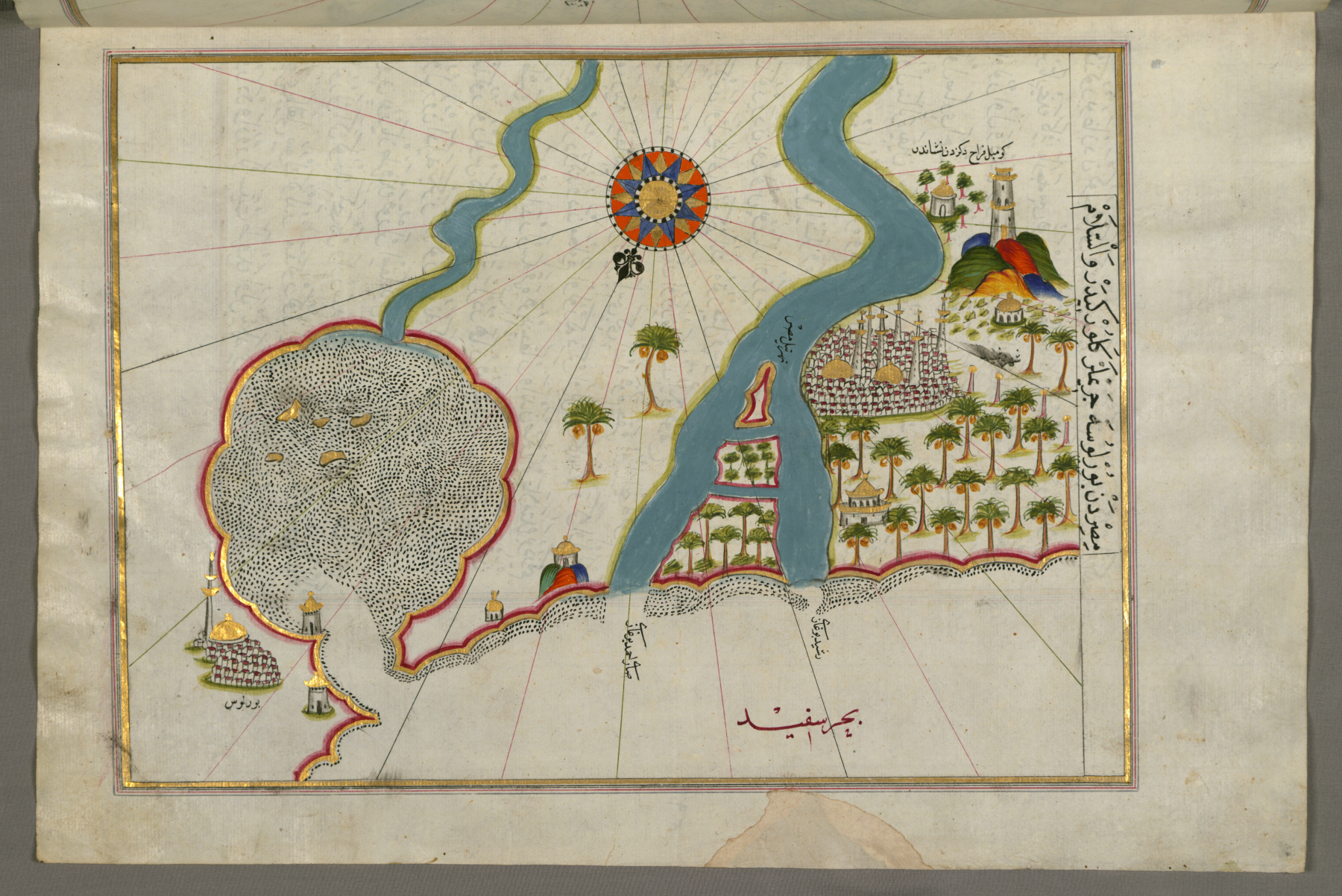
Rosette (Egypt)
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799. Founded around the 9th century on site of the ancient town Bolbitine, Rosetta boomed with the decline of Alexandria following the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517, only to wane in importance after Alexandria's revival. During the 19th century, it was a popular British tourist destination, known for its Ottoman mansions, citrus groves and relative cleanliness. Etymology The name of the town most likely comes from an Arabic name '' Rašīd'' (meaning "guide") and was transcribed and corrupted in numerous ways – the name ''Rexi'' was used by the Crusaders in Middle Ages and ''Rosetta'' or ''Rosette'' ("little rose" in Italian and French respectively) was used by the French at the time of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Egypt
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Julien
Fort Julien (or, in some sources, ''Fort Rashid'') (Arabic: طابية رشيد) is a fort located on the left or west bank of the Nile about north-west of Rashid (Rosetta) on the north coast of Egypt. It was originally built by the Ottoman Empire and occupied by the French during Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in Egypt and Syria between 1798 and 1801. The fort became famous as the place where the Rosetta Stone was found in 1799. Description and history The fort is a low, squat rectangular structure with a central blockhouse that overlooks the final few kilometres of the Nile before it joins the Mediterranean Sea. It was built around 1470 by the Mamluk Sultan Qait Bey, who also built the eponymous Citadel of Qaitbay in Alexandria. In 1516, Sultan Qansuh al-Ghuri reinforced it with a defensive wall. The fort subsequently fell into disrepair. The fort was built in part from stone looted from nearby ancient Egyptian sites; when Vivant Denon visited it in 1799, he noted that it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Hakim Bi-Amr Allah
Abū ʿAlī Manṣūr (13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Ḥākim bi-Amr Allāh ( ar, الحاكم بأمر الله, lit=The Ruler by the Order of God), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam (996–1021). Al-Hakim is an important figure in a number of Shia Ismaili sects, such as the world's 15 million Nizaris and 1–2 million Musta'lis, in addition to the 2 million Druze of the Levant. (''Which page?'') Histories of al-Hakim can prove controversial, as diverse views of his life and legacy exist. Historian Paul Walker writes: "Ultimately, both views of him, the mad and despotic tyrant (like Germanic and Roman despots) irrationally given to killing those around him on a whim, and the ideal supreme ruler, divinely ordained and chosen, whose every action was just and righteous, were to persist, the one among his enemies and those who rebelled against him, and the other in the hearts of true believers, who, while perhaps p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mutawakkil
Abū al-Faḍl Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad al-Muʿtaṣim bi-ʾllāh ( ar, جعفر بن محمد المعتصم بالله; March 822 – 11 December 861), better known by his regnal name Al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (, "He who relies on God") was the tenth Abbasid caliph. He succeeded his brother, al-Wathiq, and is known for expanding the empire to its maximum extent. He was deeply religious, and is remembered for discarding the Muʿtazila, ending the Mihna (a period of persecution of Islamic scholars), and releasing Ahmad ibn Hanbal. He is also known for his tough rule, especially with respect to non-Muslim subjects. He was assassinated on 11 December 861 by the Turkic guard with the support of his son, al-Muntasir, marking the beginning of the period of civil strife known as the "Anarchy at Samarra". Early life Al-Mutawakkil was born on February/March 822 to the Abbasid prince Abu Ishaq Muhammad (the future al-Mu'tasim) and a slave concubine from Khwarazm called Shuja. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian Empire, Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture and List of inventions in the medieval Islamic world, invention in what became known as the Islamic Golden Age, Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Coptic Encyclopedia
The ''Coptic Encyclopedia'' is an eight-volume work covering the history, theology, language, art, architecture, archeology and hagiography of Coptic Egypt. The encyclopedia was written by over 250 Western and Egyptian contributing experts in the field of Coptology, history, art and theology and was edited by Aziz Suryal Atiya. It was funded by Coptic Pope Shenouda III, the Rockefeller Foundation, the National Endowment for the Humanities, and others. Characteristics The ''Coptic Encyclopedia'' is the first Encyclopedia to focus on one of the Oriental Churches Cornelis Hulsman in ''Coptic Church Review'', Vol. 13, no. 3, Fall 1992 and since its publication in 1991 it has been used by many scholars and students in the West. The ''Encyclopedia'' is the fruit of the Coptic emigrant community in the West and the crown of the work of Aziz Suryal Atiya, who did not live to see his work carried into print. Atiya developed the vision to publish an encyclopedia during the years he t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashmuric Revolt
Bashmurian revolts (, ar, ثورة البشموريين) were a series of revolts by the Egyptians in the Bashmur region in the north of the Nile Delta against the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates in the eighth and ninth centuries. Exactly how many revolts there were cannot be determined, but the major military conflicts took place in 749, 767 and 831–832. The Bashmurian revolts are known from Coptic and Arabic sources. They did not become known in Europe until the early nineteenth century. Both Coptic and Arabic sources attribute them to oppressive taxation and the unjust treatment of Christians by the Arab governors. Location The exact boundaries of Bashmur varied over time depending on where the Bashmurians were settled. At the time of the revolts, it seems to have lain across the northern Delta just south of the Mediterranean from Fuwwa in the west to Ashmun al-Rumman in the east. By the thirteenth century, the Bashmurians seem to have been confined to the eastern Delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayya ibn Abd Shams, Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Mu'awiya I, Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Syria (region), Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuwwah
Fuwwah ( ar, فوه; ) is a city in the Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, Egypt. Name The name of the town is attested in and , although it's also claimed that the name is derived from the Arabic word for saffron, ''fuwwa''. History Medieval Fuwwah grew to become one of the most important cities in al-Dimashqi's time, when he compared its size to that of Cairo. Fuwwah's prosperity owed largely to the decline of Rosetta at that time. Fuwwah was the capital of a province variously called ''Fuwwah'' or '' Al-Muzahamiyatayn''. Fuwwah's Christian bishopric remained active through the late thirteenth century, indicating the presence of a large Christian population at the time. Its location on the Rosetta branch of the Nile meant that residents could easily travel by boat, the main mode of transport in the Nile Delta at the time - overland travel was potentially dangerous, as evidenced by the inability of Yusab, the bishop of Fuwwah, to travel to the Synod of 1250 due to Bedouin raids. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damietta
Damietta ( arz, دمياط ' ; cop, ⲧⲁⲙⲓⲁϯ, Tamiati) is a port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt, a former bishopric and present multiple Catholic titular see. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, about north of Cairo. Damietta joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities. Etymology The modern name of the town comes from its Coptic name Tamiati ( cop, ⲧⲁⲙⲓⲁϯ} Late Coptic: ), which in turn most likely comes from Ancient Egyptian ("harbour, port"), although al-Maqrizi suggested a Syriac etymology. History Mentioned by the 6th-century geographer Stephanus Byzantius, it was called ''Tamiathis'' () in the Hellenistic period. Under Caliph Omar (579–644), the Arabs took the town and successfully resisted the attempts by the Byzantine Empire to recover it, especially in 739, 821, 921 and 968. The Abbasids used Alexandria, Damietta, Aden and Siraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)