|
Ron Herron
Ronald James Herron () was an English architect and teacher. He is perhaps best known for his work with the seminal experimental architecture collective Archigram, which was formed in London in the early 1960s. Herron was the creator of one of the group's best known and celebrated projects, the Walking City. Early life and education Ron Herron was born in London on 12 August 1930, to a leather-working family. He studied draughtsmanship at the Brixton School of Building and architecture at the Regent Street Polytechnic in London. Academic career Herron taught at the Architectural Association in London from 1965 until 1993, when he was appointed as professor and Head of the School of Architecture at the University of East London. Professional career Herron formed Herron Associates with his sons Andrew and Simon in 1981. The firm built the acclaimed Imagination Headquarters in London and were involved in the design for Canada Water station. Archigram Shortly after finishing his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Westminster
, mottoeng = The Lord is our Strength , type = Public , established = 1838: Royal Polytechnic Institution 1891: Polytechnic-Regent Street 1970: Polytechnic of Central London 1992: University of Westminster , endowment = £5.1 million , budget = £205.1 million , chancellor = Lady Sorrell , vice_chancellor = Peter Bonfield , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = London , country = United Kingdom , colours = Royal blue, Fuchsia , website www.westminster.ac.uk, logo = Navbar-westminster-logo.svg , affiliations = The University of Westminster is a public university based in London, United Kingdom. Founded in 1838 as the Royal Polytechnic Institution, it was the first polytechnic to open in London. The Polytechnic formally received a Royal charter in August 1839, and became the University of Westminster in 1992. Westminster has its main campus in Regent Street in central London, with additional campuses in Fitzrovia, Marylebone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theo Crosby
Theo Crosby (3 April 1925 – 12 September 1994) was an architect, editor, writer and sculptor, engaged with major developments in design across four decades. He was also an early vocal critic of modern urbanism. He is best remembered as a founding partner of the international design partnership Pentagram (design studio), Pentagram, and as architect for the reconstruction of Shakespeare's Globe in London. However, his role as ''éminence grise'' in British architecture and design from 1950 to 1990 helped effect much broader changes. Crosby's archive is located at the University of Brighton Design Archives. 1940s and 1950s: architecture and sculpture Crosby studied architecture under Rex Martienssen, an acolyte of Le Corbusier, at Witwatersrand University Johannesburg. From 1944 he participated in the Allied invasion of Italy. His post-VE day travels around that country introduced him to a world—of urbanity and cultural generosity—which he had never experienced in South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academics Of The University Of East London
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architects From London
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that have human occupancy or use as their principal purpose. Etymologically, the term architect derives from the Latin ''architectus'', which derives from the Greek (''arkhi-'', chief + ''tekton'', builder), i.e., chief builder. The professional requirements for architects vary from place to place. An architect's decisions affect public safety, and thus the architect must undergo specialized training consisting of advanced education and a ''practicum'' (or internship) for practical experience to earn a license to practice architecture. Practical, technical, and academic requirements for becoming an architect vary by jurisdiction, though the formal study of architecture in academic institutions has played a pivotal role in the development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artists From London
An artist is a person engaged in an activity related to creating art, practicing the arts, or demonstrating an art. The common usage in both everyday speech and academic discourse refers to a practitioner in the visual arts only. However, the term is also often used in the entertainment business, especially in a business context, for musicians and other performers (although less often for actors). "Artiste" (French for artist) is a variant used in English in this context, but this use has become rare. Use of the term "artist" to describe writers is valid, but less common, and mostly restricted to contexts like used in criticism. Dictionary definitions The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' defines the older broad meanings of the term "artist": * A learned person or Master of Arts. * One who pursues a practical science, traditionally medicine, astrology, alchemy, chemistry. * A follower of a pursuit in which skill comes by study or practice. * A follower of a manual art, such as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1994 Deaths
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson Mandela casts his vote in the 1994 South African general election, in which he was elected South Africa's first president, and which effectively brought Apartheid to an end; NAFTA, which was signed in 1992, comes into effect in Canada, the United States, and Mexico; The first passenger rail service to utilize the newly-opened Channel tunnel; The 1994 FIFA World Cup is held in the United States; Skulls from the Rwandan genocide, in which over half a million Tutsi people were massacred by Hutus., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 1994 Winter Olympics rect 200 0 400 200 Northridge earthquake rect 400 0 600 200 Sinking of the MS Estonia rect 0 200 300 400 Rwandan genocide rect 300 200 600 400 Nelson Mandela rect 0 400 200 600 1994 FIFA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930 Births
Year 193 ( CXCIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sosius and Ericius (or, less frequently, year 946 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 193 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 1 – Year of the Five Emperors: The Roman Senate chooses Publius Helvius Pertinax, against his will, to succeed the late Commodus as Emperor. Pertinax is forced to reorganize the handling of finances, which were wrecked under Commodus, to reestablish discipline in the Roman army, and to suspend the food programs established by Trajan, provoking the ire of the Praetorian Guard. * March 28 – Pertinax is assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard, who storm the imperial palace. The Empire is auctioned o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodford Green
Woodford Green is an area of Woodford in north-east London, England, within the London Borough of Redbridge. It adjoins Buckhurst Hill to the north, Woodford Bridge to the east, South Woodford to the south, and Chingford to the west. Epping Forest runs through Woodford Green in the west of the area, north-east of Charing Cross. It was a hamlet in the ancient civil parish of Woodford St Mary, in the historic county of Essex, becoming an urban district in 1894. For administrative purposes, this merged with the Wanstead Urban District to form the Wanstead and Woodford Urban District in 1934. In 1965, the urban district became part of the London Borough of Redbridge. Politics Woodford Green is part of the Parliamentary Constituency of Chingford and Woodford Green, represented since its creation in 1997 by Iain Duncan Smith, leader of the Conservative Party from 2001 to 2003. He was Secretary of State for Work and Pensions from 2010 to 2016. Duncan Smith is a successor of Sir W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20th centuries. There has been a settlement in this location since the Mesolithic era. A nunnery was founded by Eanswith, granddaughter of Æthelberht of Kent in the 7th century, who is still commemorated as part of the town's culture. During the 13th century it subsequently developed into a seaport and the harbour developed during the early 19th century to provide defence against a French invasion. Folkestone expanded further west after the arrival of the railway in 1843 as an elegant coastal resort, thanks to the investment of the Earl of Radnor under the urban plan of Decimus Burton. In its heyday - during the Edwardian era - Folkestone was considered the most fashionable resort of the time, visited by royalties - amongst them Queen Victo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
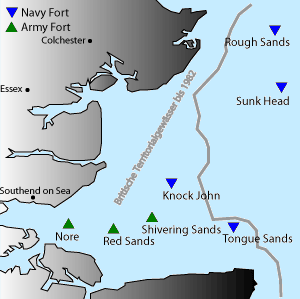
Maunsell Forts
The Maunsell Forts are armed towers built in the Thames and Mersey estuaries during the Second World War to help defend the United Kingdom. They were operated as army and navy forts, and named after their designer, Guy Maunsell. The forts were decommissioned in the late 1950s and later used for other activities including pirate radio broadcasting. One of the forts is managed by the unrecognised Principality of Sealand; boats visit the remaining forts occasionally, and a consortium called Project Redsands is planning to conserve the fort situated at Red Sands. In the summers of 2007 and 2008 Red Sands Radio, a station commemorating the pirate radio stations of the 1960s, operated from the Red Sands fort on 28-day Restricted Service Licences. The fort was subsequently declared unsafe, and Red Sands Radio has moved its operations ashore to Whitstable. Forts had been built in river mouths and similar locations to defend against ships, such as the Grain Tower Battery at the mouth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technological Utopianism
Technological utopianism (often called techno-utopianism or technoutopianism) is any ideology based on the premise that advances in science and technology could and should bring about a utopia, or at least help to fulfill one or another utopian ideal. A techno-utopia is therefore an ideal society, in which laws, government, and social conditions are solely operating for the benefit and well-being of all its citizens, set in the near- or far-future, as advanced science and technology will allow these ideal living standards to exist; for example, post-scarcity, transformations in human nature, the avoidance or prevention of suffering and even the end of death. Technological utopianism is often connected with other discourses presenting technologies as agents of social and cultural change, such as technological determinism or media imaginaries. A tech-utopia does not disregard any problems that technology may cause, but strongly believes that technology allows mankind to make so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)