|
Rhoptry
A rhoptry is a specialized secretory organelle. They are club-shaped organelles connected by thin necks to the extreme apical pole of the parasite. These organelles, like micronemes, are characteristic of the motile stages of Apicomplexa protozoans. They can vary in number and shape and contain numerous enzymes that are released during the penetration process. The proteins they contain are important in the interaction between the host and the parasite, including the formation of the parasitophorous vacuole The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) is a structure produced by apicomplexan parasites in the cells of its host. The PV allows the parasite to develop while protected from the phagolysosomes of the host cell. The PV is a bubble-like compartment ma .... References Organelles {{Cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitophorous Vacuole
The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) is a structure produced by apicomplexan parasites in the cells of its host. The PV allows the parasite to develop while protected from the phagolysosomes of the host cell. The PV is a bubble-like compartment made of plasma membrane; the compartment contains cytoplasm and the parasite. The PV allows the parasite to exist and grow within the cell while protecting the parasite from the host cell defense mechanisms. The PV prevents the acidification of the compartment, the mechanism by which the lysosomes of the host cell would normally destroy an invading parasite. Parasites that form a parasitophorous vacuole as part of their infection process include '' Plasmodium falciparum'', which causes malaria and ''Toxoplasma gondii'', which causes toxoplasmosis. The parasitophorous vacuole is formed during cell invasion, when the parasite uses part of the membrane of the host cell to form a parasitophorous vacuolar membrane (PVM). The PVM surrounds the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microneme
Micronemes are secretory organelles, possessed by parasitic apicomplexans. Micronemes are located on the apical third of the protozoan body. They are surrounded by a typical unit membrane. On electron microscopy they have an electron-dense matrix due to the high protein content. They are specialized secretory organelles important for host-cell invasion and gliding motility. These organelles secrete several proteins such as the '' Plasmodium falciparum'' apical membrane antigen-1, or PfAMA1, and Erythrocyte family antigen, or EBA, family proteins. These proteins specialize in binding to erythrocyte surface receptors and facilitating erythrocyte entry. Only by this initial chemical exchange can the parasite enter into the erythrocyte via actin-myosin motor complex. It has been posited that this organelle works cooperatively with its counterpart organelle, the rhoptry, which also is a secretory organelle. It is possible that, while the microneme initiates erythrocyte-binding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis ('' Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis ('' Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis ('' Cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
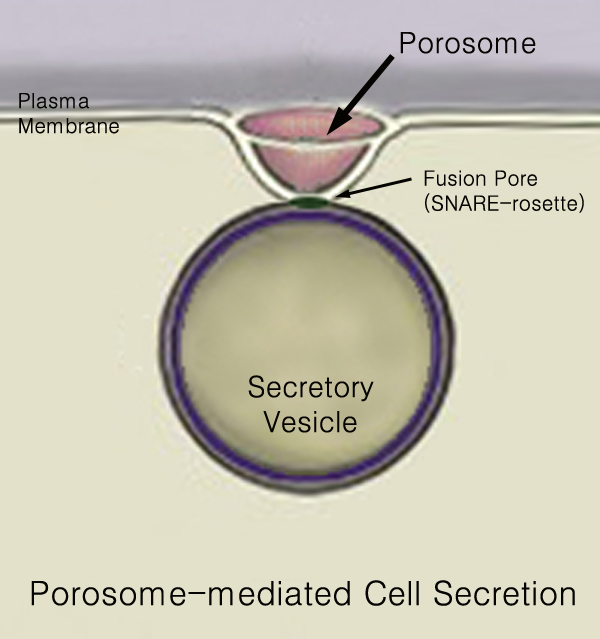
Secretion
440px Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules for example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. '' Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' the suffix ''-elle'' being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers (also called membrane-bound organelles) or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer (non-membrane bound organelles). Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst. Organelles are identified by microscopy, and can also be purified by cell fractionation. There are many types of organelles, particularly in eukaryotic cells. They include structures that make up the endomembrane system (such as the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require ... [...More Info...] |