|
Rhizoxin
Rhizoxin is an antimitotic agent with anti-tumor activity. It is isolated from a pathogenic plant fungus ('' Rhizopus microsporus'') which causes rice seedling blight. Biosynthesis Rhizoxin is biosynthesised by ''Burkholderia rhizoxinica'', a bacterial endosymbiont of the fungus ''Rhizopus microsporus''. It is one of a large group of rhizoxin-like compounds produced by the bacteria. The bacterial endosymbiont can be grown independently in culture. This may allow easy harvesting of rhizoxin and the related compounds avoiding total chemical synthesis, although total chemical synthesis is possible. Cytotoxic function Rhizoxin binds beta tubulin in eukaryotic cells disrupting microtubule formation. This, in turn, prevents formation of the mitotic spindle inhibiting cell division. Additionally rhizoxin can depolymerise assembled microtubules.Erratum in J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)., 40 (4), following 565. (1987) The function of rhizoxin is similar to ''Vinca'' alkaloids. Rhizoxin has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizopus Microsporus
''Rhizopus microsporus '' is a fungal plant pathogen infecting maize, sunflower, and rice. A domesticated variant of this species is used in the preparation of traditional soy fermentation such as tempeh and sufu (see ''Rhizopus oligosporus''). It can also cause a nosocomial infection and necrosis to the infected area, particularly prevalent in pre-term infants. This fungus contains the bacterial endosymbiont '' Burkholderia rhizoxinica'' that produces the antitumor drug rhizoxin. Hosts and symptoms Certain strains of ''Rhizopus microsporus'' use agricultural rice as a host, causing the disease Rice Seedling Blight. This infection is first observed by the fast swelling of seedling roots, but displays no further signs of infection. The main causal agent of Rice Seedling Blight is attributed to the endosymbiotic relationship with ''Burkholderia'' sp. The production of rhizoxin by the bacteria inhibits the ability of rice plant cells to perform mitosis, dramatically weakening ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia
''Burkholderia'' is a genus of Pseudomonadota whose pathogenic members include the ''Burkholderia cepacia'' complex, which attacks humans and ''Burkholderia mallei'', responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; '' Burkholderia pseudomallei'', causative agent of melioidosis; and ''Burkholderia cepacia'', an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). ''Burkholderia'' species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized ''Burkholderia cepacia'' from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. The ''Burkholderia'' (previously part of '' Pseudomonas'') genus name refers to a group of virtually ubiquitous Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that are motile by means of single or multiple polar flagella, with the exception of ''Burkholderia mallei'', which is nonmotile. Members belonging to the genus do not produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimitotic
A mitotic inhibitor is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cells are able to grow and eventually spread through the body (metastasize) through continuous mitotic division. Thus, cancer cells are more sensitive to inhibition of mitosis than normal cells. Mitotic inhibitors are also used in cytogenetics (the study of chromosomes), where they stop cell division at a stage where chromosomes can be easily examined. Mitotic inhibitors are derived from natural substances such as plant alkaloids, and prevent cells from undergoing mitosis by disrupting microtubule polymerization, thus preventing cancerous growth. Microtubules are long, ropelike proteins that extend through the cell and move cellular components around. Microtubules are long polymers made of smaller units (monomers) of the protein tubulin. Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolymerise
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them. In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur via a variety of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and their inherent steric effects. In more straightforward polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize. Alkanes can also be polymerized, but only with the help of strong acids. As alkenes can polymerize in somewhat straightforward radical reactions, they form useful compounds such as polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
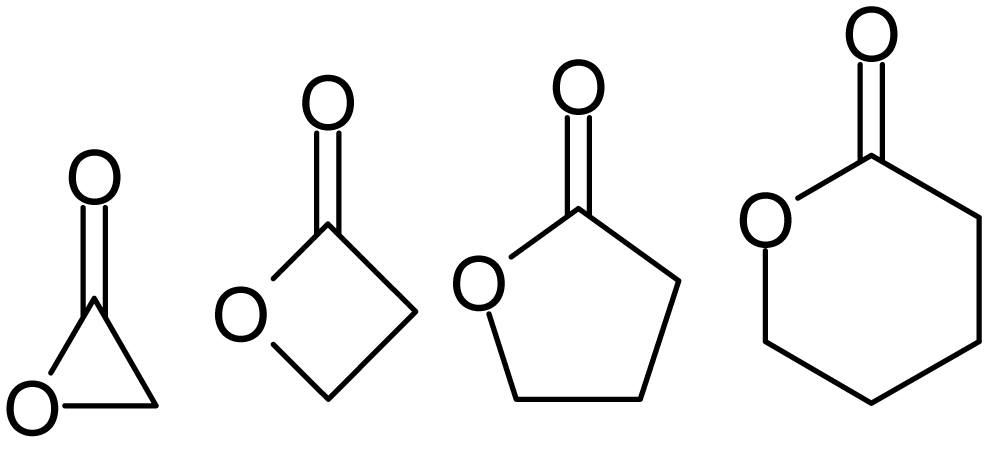
Epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy'', but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrolides
The Macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Rapamycin is also a macrolide and was originally developed as an antifungal, but is now used as an immunosuppressant drug and is being investigated as a potential longevity therapeutic. Macrolides are bacteriostatic in that they suppress or inhibit bacterial growth rather than killing bacteria completely. Definition In general, any macrocyclic lactone having greater than 8-membered rings are candidates for this class. The macrocycle may contain amino nitrogen, amide nitrogen (but should be differentiated from cyclopeptides), an oxazole ring, or a thiazole ring. Benzene rings are exclud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazoles
Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a p''K''a of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole. Preparation Classical oxazole synthetic methods in organic chemistry are * the Robinson–Gabriel synthesis by dehydration of 2-acylaminoketones * the Fischer oxazole synthesis from cyanohydrins and aldehydes * the Bredereck reaction with α-haloketones and formamide * the Van Leusen reaction with aldehydes and TosMIC Other methods: * Oxazolines can also be obtained from cycloisomerization of certain propargyl amides. In one study oxazoles were prepared via a one-pot synthesis consisting of the condensation of propargyl amine and benzoyl chloride to the amide, followed by a Sonogashira coupling of the terminal alkyne end with another equivalent of benzoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsaturated Compound
In chemistry, a saturated compound is a chemical compound (or ion) that resists the addition reactions, such as hydrogenation, oxidative addition, and binding of a Lewis base. The term is used in many contexts and for many classes of chemical compounds. Overall, saturated compounds are less reactive than unsaturated compounds. Saturation is derived from the Latin word ''saturare'', meaning 'to fill'. Organic chemistry Unsaturated compounds generally carry out typical addition reactions that are not possible with saturated compounds such as alkanes. A saturated organic compound has only single bonds between carbon atoms. An important class of saturated compounds are the alkanes. Many saturated compounds have functional groups, e.g., alcohols. Unsaturated organic compounds The concept of saturation can be described using various naming systems, formulas, and analytical tests. For instance, IUPAC nomenclature is a system of naming conventions used to describe the type and loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxazole
Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon. Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a p''K''a of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole. Preparation Classical oxazole synthetic methods in organic chemistry are * the Robinson–Gabriel synthesis by dehydration of 2-acylaminoketones * the Fischer oxazole synthesis from cyanohydrins and aldehydes * the Bredereck reaction with α-haloketones and formamide * the Van Leusen reaction with aldehydes and TosMIC Other methods: * Oxazolines can also be obtained from cycloisomerization of certain propargyl amides. In one study oxazoles were prepared via a one-pot synthesis consisting of the condensation of propargyl amine and benzoyl chloride to the amide, followed by a Sonogashira coupling of the terminal alkyne end with another equivalent of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)