|
Rhinelandic
Rhinelandic is a term occasionally used for linguistic varieties of a region on both sides of the Middle and Lower Rhine river in Central West Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. It has at least two distinct meanings which often can only be determined from the fine grain context in which the term is used. (This could be complicated at times since in German publications, local languages of villages or cities are commonly referred to as "the dialects" or "dialect", whereas the regiolects, which are dialects of Low German or High German in a linguistic sense, are hardly called so, but referred to using terms like "Rhinelandic", "Hessian," or "Bavarian", etc., that also name large compounds of related local languages ) One of the meanings of ''Rhinelandic'' is that of a group of local languages in an area called the Rhineland. Another meaning is that of the regiolect being used by the people approximately of the same area. Rhinelandic Local Languages ''Rhinelandic'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinelandic Regiolect
The terms Rhinelandic, Rhenish, and Rhinelandic regiolect refer to the vernacular lect spoken in the so-called Rhineland of West Germany. This linguistic region is approximately formed of the West of North Rhine-Westphalia, the North of Rhineland-Palatinate and several smaller adjacent areas, including some areas in neighbouring countries. Although there is such a thing as a Rhinelandic accent, and the regiolect uses it, the Rhinelandic variety is not simply German spoken with an accent. Indeed, it differs from Standard German in several thousand commonly used additional words, phrases, and idioms, and some grammatical constructions. Like other German regiolects, there is not a strict definition of what constitutes Rhinelandic; it can be spoken in a way very close to the standard idiom, but if locals talk to each other, it is mostly unintelligible to inhabitants of other German-speaking regions. Linguists classify the Rhinelandic regiolect as a dialectal variety of Standard Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
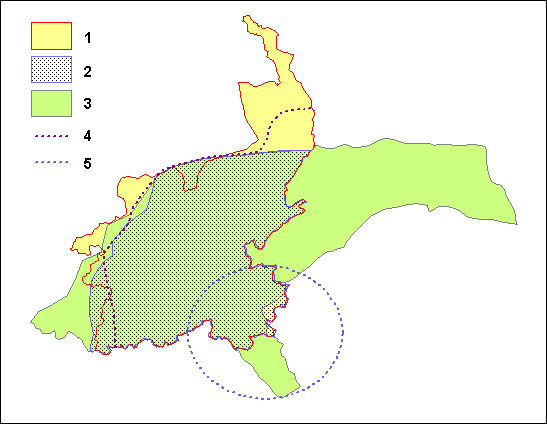
Ripuarian Language
Ripuarian ( ; also ''Ripuarian Franconian''; german: Ripuarisch, , ''ripuarische Mundart, ripuarischer Dialekt, ripuarisch-fränkische Mundart, Ribuarisch'', nl, Ripuarisch , ''Noordmiddelfrankisch'') is a German dialect group, part of the West Central German language group. Together with the Moselle Franconian which includes the Luxembourgish language, Ripuarian belongs to the larger Central Franconian dialect family and also to the Rhinelandic linguistic continuum with the Low Franconian languages. It is spoken in the Rhineland south of the Benrath line — from northwest of Düsseldorf and Cologne to Aachen in the west and to Waldbröl in the east. The language area also comprises the north of the German-speaking Community of Belgium as well as the southern edge of the Limburg province of the Netherlands, especially Kerkrade (''Kirchroa''), where it is perceived as a variety of Limburgish and legally treated as such. The name derives from the Ripuarian Franks (''Rheinfra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative Dictionary Of The Rhinelandic Colloquial Language
The Cooperative Dictionary of the Rhinelandic Colloquial Language, (') is a website that both documents and collects data on the current distinct variety of German used colloquially in the Rhineland region - where some 15 million speakers live. It is run by the Landschaftsverband Rheinland (LVR), a public body of municipal self governance of the Rhineland in West of North Rhine-Westphalia in Western Germany, under the auspices of the Bureau of Research and Documentation of the Rhineland ( Amt für rheinische Landeskunde); and is the first of its kind - replacing interviews with individual speakers, or questionnaires, by an interactive web application quasi anonymously collecting scientific evidence about a contemporary language. The Project started the interactive World Wide Web site towards the end of February 2007. Website The cooperative dictionary website has several pages describing what it is all about, how to use it, and such. It has an editorial-like "featured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergish Dialects
Bergish is a collective name for a group of West Germanic dialects spoken in the Bergisches Land region east of the Rhine in western Germany. The name is commonly used among its speakers, but is not of much linguistic relevance, because the varieties belong to several quite distinct groups inside the continental West Germanic dialect continuum. As usual inside a dialect continuum, neighbouring varieties have a high degree mutual intelligibility and share many similarities while the two more distant ones may be completely mutually unintelligible and considerably different. Therefore, speakers usually perceive the differences in their immediate neighbourhood as merely dialectal oddities of an otherwise larger, solid group or language that they are all part of, such as "Bergish". Bergish is itself commonly classified as a form of "Rhinelandic", which in turn is part of German. Bergish in a strict sense is the eastmost part of the Limburgish language group, which extends far beyond the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Bergish
South Bergish (German: ') or Upper Bergish (German: ') is a group of German dialects of the Bergisches Land region East of the Rhine and approximately south of the Wupper and north of the Sieg. These dialects are part of the Ripuarian group and thus are also called East Ripuarian. Ripuarian dialects are also spoken west of the Rhine up to the German border, and in some small areas next to the respective borders in Belgium and in the Netherlands. Ripuarian Bergish dialects belong to the Middle German group, and thus are varieties of High German, where they belong to the northmost ones. In the North, they border to the Bergish dialects, which are part of the Low Franconian group like Dutch. Some of South Bergish is transitional with East Bergish. In popular view, rather than scientific, South Bergish dialects are often referred to as ''Bergish'' by locals, or as ''Rhinelandic'' by outsiders. See also * Meuse-Rhenish * Rheinischer Fächer (in the German Wikipedia) Literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Bergish
East Bergish is a group of dialects of the Bergisches Land Region in western Germany. It combines features of the Westphalian group, the South Guelderish or Cleverlands group, and (predominantly) the Limburgish group, of which some of it is part of. South Guelderish covers much of the Lower Rhine area in Germany and extends into the Central Netherlands. It is a Low Franconian group, whereas Westphalian belongs to the Low German group. It is also seen as part of the larger Meuse-Rhenish language group. East Bergish is called ' in German. Some East Bergish dialects are '' Bergish dialects. They are seen as ''Rhinelandic'' by outsiders. Literature * Georg Wenker Georg Wenker (January 25, 1852 – July 17, 1911) was a German linguist who began documenting German dialect geography during the late nineteenth century. He is considered a pioneer in this field and contributed several groundbreaking publica ...: ''Das rheinische Platt''. 1877. ** ''Das rheinische Platt'', (Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limburgish Language
Limburgish ( li, Limburgs or ; nl, Limburgs ; german: Limburgisch ; french: Limbourgeois ), also called Limburgan, Limburgian, or Limburgic, is a West Germanic language spoken in the Dutch and Belgian provinces of Limburg and in the neighbouring regions of Germany. It shares characteristics with both German and Dutch but has unique features such as tonality. Within the modern communities of the Belgian and Dutch provinces of Limburg, intermediate idiolects are also very common, which combine standard Dutch with the accent and some grammatical and pronunciation tendencies derived from Limburgish. This "Limburgish Dutch" is confusingly also often referred to simply as "Limburgish", although in Belgium such intermediate languages tend to be called ("in-between language"), no matter the exact dialect/language with which standard Dutch is combined. Although frequently misunderstood as such, Limburgish does not refer to the regional variation of Dutch spoken in Dutch Limburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinelandic Rhyming Bible
The Rhinelandic Rhyming Bible ( nl, Rijnlandse Rijmbijbel and german: Rheinische Reimbibel), or (erroneously) Central Franconian Rhyming Bible (german: Mittelfränkische Reimbibel), is a verse translation of biblical histories, attested only in a series of fragments, probably of early-twelfth-century date. It was likely composed in north-west Germany in the early 12th century, possibly in Werden Abbey, on the border of Old High German (Old Central Franconian), Old Low German (Old Low Saxon), and Old Dutch (Old Low Franconian). The recovered fragments come from three different manuscripts written in the three different language variants. They are currently referenced under the letters A, A *, B, B * and C. The fragments complement each other, although there is also a small overlap between the A and B versions. The A fragments can be clearly assigned to a Dutch Low Franconian writer, the B fragments and the C fragment would rather be of German Central Franconian origin, although other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiolect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, Walt and Schilling, Natalie. 2016. ''American English: Dial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine Province
The Rhine Province (german: Rheinprovinz), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg. Its capital was Koblenz and in 1939 it had 8 million inhabitants. The Province of Hohenzollern was militarily associated with the Oberpräsident of the Rhine Province. The Rhine Province was bounded on the north by the Netherlands, on the east by the Prussian provinces of Westphalia and Hesse-Nassau, and the grand duchy of Hesse-Darmstadt, on the southeast by the Palatinate (a district of the Kingdom of Bavaria), on the south and southwest by Lorraine, and on the west by Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands. The small exclave district of Wetzlar, wedged between the grand duchy states Hesse-Nassau and Hesse-Darmstadt was also part of the Rhine Province. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eifel
The Eifel (; lb, Äifel, ) is a low mountain range in western Germany and eastern Belgium. It occupies parts of southwestern North Rhine-Westphalia, northwestern Rhineland-Palatinate and the southern area of the German-speaking Community of Belgium. The Eifel is part of the Rhenish Massif; within its northern portions lies the Eifel National Park. Geography Location The Eifel lies between the cities of Aachen to the north, Trier to the south and Koblenz to the east. It descends in the northeast along a line from Aachen via Düren to Bonn into the Lower Rhine Bay. In the east and south it is bounded by the valleys of the Rhine and the Moselle. To the west it transitions in Belgium and Luxembourg into the geologically related Ardennes and the Luxembourg Ösling. In the north it is limited by the Jülich-Zülpicher Börde. Within Germany it lies within the states of Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia; in the Benelux the area of Eupen, St. Vith and Luxemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety of the German language used in formal contexts and for communication between different dialect areas. It is a pluricentric Dachsprache with three codified (or standardised) specific regional variants: German Standard German, Austrian Standard German and Swiss Standard German. Regarding the spelling and punctuation, a recommended standard is published by the Council for German Orthography which represents the governments of all majority and minority German-speaking countries and dependencies. Adherence is obligatory for government institutions, including schools. Regarding the pronunciation, although there is no official standards body, there is a long-standing ''de facto'' standard pronunciation (Bühnendeutsch), most commonly used in fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |