|
Resorption
Resorption is the absorption of cells or tissue into the circulatory system, usually by osteoclasts. Types of resorption include: * Bone resorption * Herniated Disc Resorption * Tooth resorption * Fetal resorption * Blood resorption See also * Nutrient resorption In plants Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plant ..., in plants References Set index articles {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Resorption
Resorption of the root of the tooth, or root resorption, is the progressive loss of dentin and cementum by the action of odontoclasts. Root resorption is a normal physiological process that occurs in the exfoliation of the primary dentition. However, pathological root resorption occurs in the permanent or secondary dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition. Causes While resorption of bone is a normal physiological response to stimuli throughout the body, root resorption in permanent dentition and sometimes in the primary dentition is pathological. The root is protected internally (endodontium) by pre-dentin and externally on the root surface by cementum and the periodontal ligament. Chronic stimuli that damage these protective layers expose underlying dentin to the action of osteoclasts. Root resorption most commonly occurs due to inflammation caused by: pulp necrosis, trauma, periodontal treatment, orthodontic tooth movement and tooth whitening. Less common causes incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Resorption
Bone resorption is resorption of bone tissue, that is, the process by which osteoclasts break down the tissue in bones and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone tissue to the blood. The osteoclasts are multi-nucleated cells that contain numerous mitochondria and lysosomes. These are the cells responsible for the resorption of bone. Osteoblasts are generally present on the outer layer of bone, just beneath the periosteum. Attachment of the osteoclast to the osteon begins the process. The osteoclast then induces an infolding of its cell membrane and secretes collagenase and other enzymes important in the resorption process. High levels of calcium, magnesium, phosphate and products of collagen will be released into the extracellular fluid as the osteoclasts tunnel into the mineralized bone. Osteoclasts are prominent in the tissue destruction found in psoriatic arthritis and rheumatological disorders. The human body is in a constant state of bone remod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
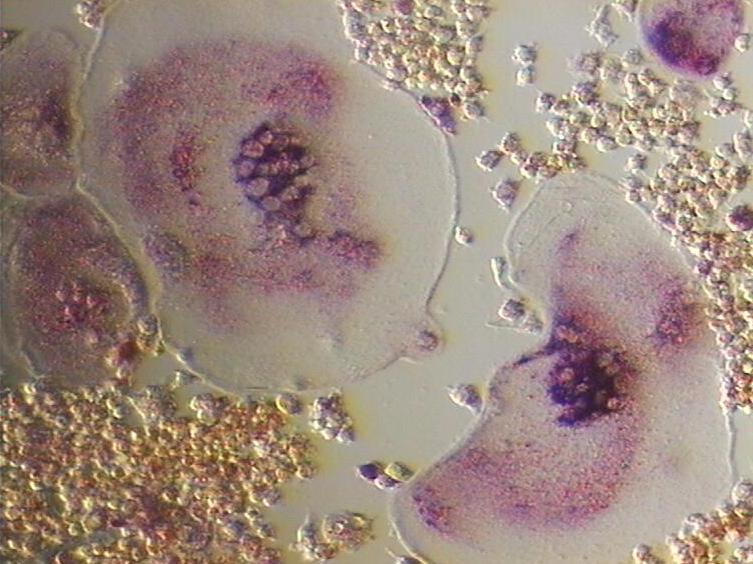
Osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as ''bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a resorption bay. The periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Resorption
Fetal resorption (also known as fetus resorption) is the disintegration and assimilation of one or more fetuses in the uterus at any stage after the completion of organogenesis, which, in humans, is after the ninth week of gestation. Before organogenesis, the process is called embryo loss. Resorption is more likely to happen early on in the gestation than later on; a later death of a fetus is likely to result in a miscarriage. In rodents Fetal resorption in rats is common and can be influenced by antioxidants. In canines In 1998, an ultrasound study found that the resorption of one or two conceptuses happen in up to 10% of all dog pregnancies, although many cases of assumed complete resorption of an entire litter are likely to have just been the bitch experiencing a pseudopregnancy. See also * Vanishing twin syndrome A vanishing twin, also known as twin resorption, is a fetus in a multigestation pregnancy that dies ''in utero ''and is then partially or completely reabso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Resorption
In plants Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ..., nutrient resorption is a process in which nutrients are withdrawn from senescing plant tissues. It acts as a nutrient conservation mechanism. It is influenced by several environmental and physiological processes. References External links Nutrient resorption or accumulation of desert plants with contrasting sodium regulation strategies Plant nutrition {{Plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reabsorption
In renal physiology, reabsorption or tubular reabsorption is the process by which the nephron removes water and solutes from the tubular fluid (pre-urine) and returns them to the circulating blood. It is called ''reabsorption'' (and not ''absorption'') because these substances have already been absorbed once (particularly in the intestines) and the body is reclaiming them from a postglomerular fluid stream that is on its way to becoming urine (that is, they will soon be lost to the urine unless they are reabsorbed from the tubule into the peritubular capillaries. This happens as a result of sodium transport from the lumen into the blood by the Na+/K+ATPase in the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cells. Thus, the glomerular filtrate becomes more concentrated, which is one of the steps in forming urine. Nephrons are divided into five segments, with different segments responsible for reabsorbing different substances. Reabsorption allows many useful solutes (primarily gluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The Closed circulatory system, circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Resorption
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |