|
Reminiscence
Reminiscence is the act of recollecting past experiences or events. An example of the typical use of reminiscence is when people share their personal stories with others or allows other people to live vicariously through stories of family, friends, and acquaintances while gaining an authentic meaningful relationship with the people. An example of reminiscence may be grandparents remembering past events with friends or their grandchildren, sharing their individual experience of what the past was like. Psychological usage Reminiscence therapy Reminiscence can be defined as the act or process of recalling past experiences, events, or memories. Anyone can reminiscence about the past or a certain event, but reminiscence is often used in the older population, particularly the elderly population with forms of dementia as a therapeutic tool. This type of reminiscence is called reminiscence therapy. Reminiscence therapy is a non-pharmacological intervention that improves self-esteem and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reminiscence Bump
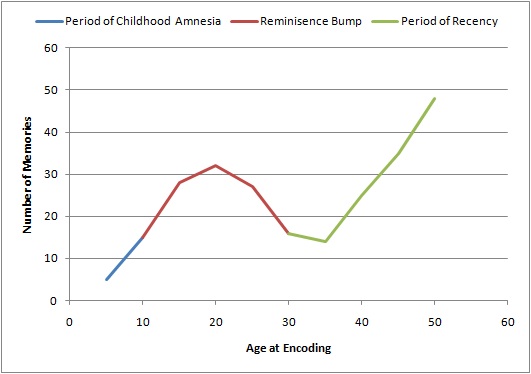
The reminiscence bump is the tendency for older adults (over forty) to have increased or enhanced recollection for events that occurred during their adolescence and early adulthood. It was identified through the study of autobiographical memory and the subsequent plotting of the age of encoding of memory, memories to form the lifespan retrieval curve. The ''lifespan retrieval curve'' is a graph that represents the number of autobiographical memories encoded at various ages during the life span. The lifespan retrieval curve contains three different parts. From birth to five years old is a period of childhood amnesia, from 16 to 25 years old is the reminiscence bump and last is a period of forgetting from the end of the reminiscence bump to present time. The reminiscence bump has been observed on the lifespan retrieval curve in multiple studies. Theorists have proposed several explanations, ranging from changes in brain biology to the type of events that typically occur during this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affects a person's ability to function and carry out everyday activities. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Consciousness is not affected. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning, and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging. Several diseases and injuries to the brain, such as a stroke, can give rise to dementia. However, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Term
Jargon is the specialized terminology associated with a particular field or area of activity. Jargon is normally employed in a particular communicative context and may not be well understood outside that context. The context is usually a particular occupation (that is, a certain trade, profession, vernacular or academic field), but any ingroup can have jargon. The main trait that distinguishes jargon from the rest of a language is special vocabulary—including some words specific to it and often different senses or meanings of words, that outgroups would tend to take in another sense—therefore misunderstanding that communication attempt. Jargon is sometimes understood as a form of technical slang and then distinguished from the official terminology used in a particular field of activity. The terms ''jargon'', ''slang,'' and ''argot'' are not consistently differentiated in the literature; different authors interpret these concepts in varying ways. According to one definition, j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into Causality, cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experiment, natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacing Effect
The spacing effect demonstrates that learning is more effective when study sessions are spaced out. This effect shows that more information is encoded into long-term memory by spaced study sessions, also known as ''spaced repetition'' or ''spaced presentation'', than by massed presentation (" cramming"). The phenomenon was first identified by Hermann Ebbinghaus, and his detailed study of it was published in the 1885 book (''Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology''), which suggests that active recall with increasing time intervals reduces the probability of forgetting information. This robust finding has been supported by studies of many explicit memory tasks such as free recall, recognition, cued-recall, and frequency estimation (for reviews see Crowder 1976; Greene, 1989). Researchers have offered several possible explanations of the spacing effect, and much research has been conducted that supports its impact on recall. In spite of these findings, the robustness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autobiographical Memory
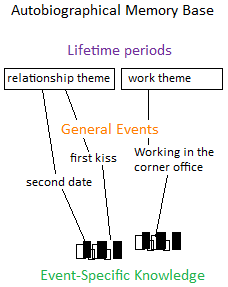
Autobiographical memory is a memory system consisting of episodes recollected from an individual's life, based on a combination of episodic (personal experiences and specific objects, people and events experienced at particular time and place) and semantic (general knowledge and facts about the world) memory.Williams, H. L., Conway, M. A., & Cohen, G. (2008). Autobiographical memory. In G. Cohen & M. A. Conway (Eds.), Memory in the Real World (3rd ed., pp. 21-90). Hove, UK: Psychology Press. It is thus a type of explicit memory. Formation Conway and Pleydell-Pearce (2000) proposed that autobiographical memory is constructed within a self-memory system (SMS), a conceptual model composed of an autobiographical knowledge base and the working self. Autobiographical knowledge base The autobiographical knowledge base contains knowledge of the self, used to provide information on what the self is, what the self was, and what the self can be. This information is categorized into three b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodic memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychotherapies
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase happiness, and overcome problems. Psychotherapy aims to improve an individual's well-being and mental health, to resolve or mitigate troublesome behaviors, beliefs, compulsions, thoughts, or emotions, and to improve relationships and social skills. Numerous types of psychotherapy have been designed either for individual adults, families, or children and adolescents. Certain types of psychotherapy are considered evidence-based for treating some diagnosed mental disorders; other types have been criticized as pseudoscience. There are hundreds of psychotherapy techniques, some being minor variations; others are based on very different conceptions of psychology. Most involve one-to-one sessions, between the client and therapist, but some are conducted with groups, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |