|
Reinstatement
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or recrudescence. In psychiatry, relapse or reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior, is the recurrence of pathological drug use, self harm or other symptoms after a period of recovery. Relapse is often observed in individuals who have developed a drug addiction or a form of drug dependence, as well as those who have a mental disorder. Risk factors Dopamine D2 receptor availability The availability of the dopamine receptor D2 plays a role in self-administration and the reinforcing effects of cocaine and other stimulants. The D2 receptor availability has an inverse relationship to the vulnerability of reinforcing effects of the drug. With the D2 receptors becoming limited, the user becomes more susceptible to the reinforcing effects of cocain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-administration
Self-administration is, in its medical sense, the process of a subject administering a pharmacological substance to themself. A clinical example of this is the subcutaneous "self-injection" of insulin by a diabetic patient. In animal experimentation, self-administration is a form of operant conditioning where the reward is a drug. This drug can be administered remotely through an implanted intravenous line or an intracerebroventricular injection. Self-administration of putatively addictive drugs is considered one of the most valid experimental models to investigate drug-seeking and drug-taking behavior. The higher the frequency with which a test animal emits the operant behavior, the more rewarding (and addictive), the test substance is considered. Self-administration of addictive drugs has been studied using humans, non-human primates, mice, invertebrates such as ants, and, most commonly, rats. Self-administration of heroin and cocaine is used to screen drugs for possible eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use often alters brain function in ways that perpetuate craving, and weakens (but does not completely negate) self-control. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological (and thus involuntary) factors that are implicated in addiction's development. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use despite negative consequences. Habits and patterns associated with addiction are typically characterized by immediate gratification (short-term reward), coupled with delayed deleterious effects (long-term costs). Examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstinence
Abstinence is a self-enforced restraint from indulging in bodily activities that are widely experienced as giving pleasure. Most frequently, the term refers to sexual abstinence, but it can also mean abstinence from alcohol, drugs, food, etc. Because the regimen is intended to be a conscious act, freely chosen to enhance life, abstinence is sometimes distinguished from the psychological mechanism of repression. The latter is an unconscious state, having unhealthy consequences. Abstinence in religion Abstinence may arise from an ascetic over indulgent, hasidic point of view in natural ways of procreation, present in most faiths, or from a subjective need for spiritual discipline. In its religious context, abstinence is meant to elevate the believer beyond the normal life of desire, to a chosen ideal, by following a path of renunciation. In Judaism, Christianity and Islam, amongst others, pre-marital sex is prohibited. Judaism For Jews, the principal day of fast is Yom Kippur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (psychological)
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excessive amounts of stress, however, can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, and mental illnesses such as depression and also aggravation of a pre-existing condition. Stress can be external and related to the environment, but may also be caused by internal perceptions that cause an individual to experience anxiety or other negative emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc., which they then deem stressful. Hans Selye (1974) proposed four variations of stress. On one axis he locates good stress (eustress) and bad stress (distress). On the other is over-stress (hyperstress) and understress (hypostress). Selye advocates balancing these: the ultimate goal would be to balance hyperstress and hypostres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Environment
The social environment, social context, sociocultural context or milieu refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. It includes the culture that the individual was educated or lives in, and the people and institutions with whom they interact. The interaction may be in person or through communication media, even anonymous or one-way, and may not imply equality of social status. The social environment is a broader concept than that of social class or social circle. The physical and social environment is a determining factor in active and healthy aging in place, being a central factor in the study of environmental gerontology. Solidarity People with the same social environment often develop a sense of social solidarity; people often tend to trust and help one another, and to congregate in social groups. They will often think in similar styles and patterns, even though the conclusions which they reach may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurochemistry
Neurochemistry is the study of chemicals, including neurotransmitters and other molecules such as psychopharmaceuticals and neuropeptides, that control and influence the physiology of the nervous system. This particular field within neuroscience examines how neurochemicals influence the operation of neurons, synapses, and neural networks. Neurochemists analyze the biochemistry and molecular biology of organic compounds in the nervous system, and their roles in such neural processes including cortical plasticity, neurogenesis, and neural differentiation. History While neurochemistry as a recognized science is relatively new, the idea behind neurochemistry has been around since the 18th century. Originally, the brain had been thought to be a separate entity apart from the peripheral nervous system. Beginning in 1856, there was a string of research that refuted that idea. The chemical makeup of the brain was nearly identical to the makeup of the peripheral nervous system. The first l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dose (biochemistry)
A dose is a measured quantity of a medicine, nutrient, or pathogen which is delivered as a unit. The greater the quantity delivered, the larger the dose. Doses are most commonly measured for compounds in medicine. The term is usually applied to the quantity of a drug or other agent administered for therapeutic purposes, but may be used to describe any case where a substance is introduced to the body. In nutrition, the term is usually applied to how much of a specific nutrient is in a person's diet or in a particular food, meal, or dietary supplement. For bacterial or viral agents, dose typically refers to the amount of the pathogen required to infect a host. For information on dosage of toxic substances, see Toxicology. For information on excessive intake of pharmaceutical agents, see Drug overdose. In clinical pharmacology, dose refers to dosage or amount of dose administered to a person, whereas exposure means the time-dependent concentration (often in the circulatory blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered to a living organism. The substances of interest include any chemical xenobiotic such as: pharmaceutical drugs, pesticides, food additives, cosmetics, etc. It attempts to analyze chemical metabolism and to discover the fate of a chemical from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics is the study of how an organism affects a drug, whereas pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of how the drug affects the organism. Both together influence dosing, benefit, and adverse effects, as seen in PK/PD models. Overview Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific xenobiotic/chemical after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
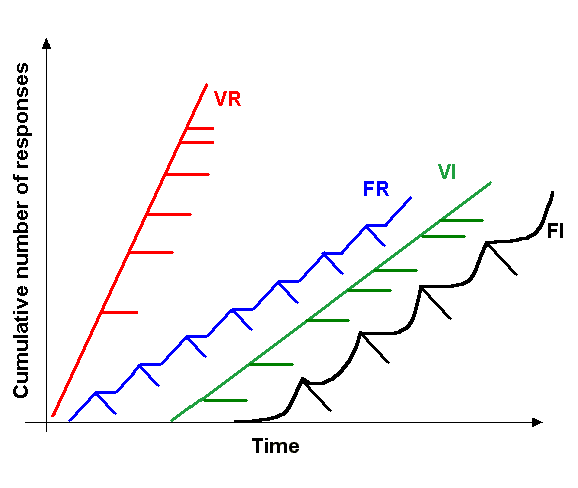
Reinforce
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Hierarchy
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and political). As such, stratification is the relative social position of persons within a social group, category, geographic region, or social unit. In modern Western societies, social stratification is typically defined in terms of three social classes: the upper class, the middle class, and the lower class; in turn, each class can be subdivided into the upper-stratum, the middle-stratum, and the lower stratum. Moreover, a social stratum can be formed upon the bases of kinship, clan, tribe, or caste, or all four. The categorization of people by social stratum occurs most clearly in complex state-based, polycentric, or feudal societies, the latter being based upon socio-economic relations among classes of nobility and classes of peasants. Whether social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance Hierarchy
In biology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social animal , social groups interact, creating a ranking system. A dominant higher-ranking individual is sometimes called an alpha, and the submissive lower-ranking individual a beta. Different types of interactions can result in dominance depending on the species, including ritualized displays of aggression or direct physical violence. In social living groups, members are likely to compete for access to limited resources and mating , mating opportunities. Rather than fighting each time they meet, relative rank is established between individuals of the same sex, with higher-ranking individuals often gaining more access to resources and mates. Based on repetitive interactions, a social order is created that is subject to change each time a dominant animal is challenged by a subordinate one. Definitions Dominance is an individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)