|
Regenerative Heat Exchanger
A regenerative heat exchanger, or more commonly a regenerator, is a type of heat exchanger where heat from the hot fluid is intermittently stored in a thermal storage medium before it is transferred to the cold fluid. To accomplish this the hot fluid is brought into contact with the heat storage medium, then the fluid is displaced with the cold fluid, which absorbs the heat. In regenerative heat exchangers, the fluid on either side of the heat exchanger can be the same fluid. The fluid may go through an external processing step, and then it is flowed back through the heat exchanger in the opposite direction for further processing. Usually the application will use this process cyclically or repetitively. Regenerative heating was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution when it was used in the hot blast process on blast furnaces. It was later used in glass melting furnaces and steel making, to increase the efficiency of open hearth furnaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement Image:Heat_exc_1-1.svg, Fig. 1: Shell and tube heat exchanger, single pass (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Concha
In anatomy, a nasal concha (), plural conchae (), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name (Latin ''concha'' from Greek ''κόγχη''). A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal passages in vertebrates.''Anatomy of the Human Body'' Gray, Henry (1918) The Nasal Cavity. In humans, the conchae divide the nasal airway into four groove-like air passages, and are responsible for forcing inhaled air to flow in a steady, regular pattern around the largest possible surface area of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Tech Briefs
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is required by its charter to report to industry any new, commercially significant technologies developed in the course of their R&D. Since the early 1960s, this has been accomplished primarily through the publication of ''NASA Tech Briefs''. ''NASA Tech Briefs'' were first published about 1963 by the Technology Utilization Office at NASA HQ (Washington DC) as single page documents. Over the years, hundreds of such documents were published and disseminated covering many areas of science and industry. The material for these documents was collected by TU offices in each of the NASA field centers, as well as from all of their contractors. Most work done under NASA contract was presumed to be the property of NASA and was freely disseminated to industry and the public. Compilations of these became available in the 1970s. Since then, it has been a joint publishing venture of NASA and Tech Briefs Media Group, a unit of SAE Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying (magazine)
''Flying'', sometimes styled ''FLYING'', is an aviation magazine published since 1927 and called ''Popular Aviation'' prior to 1942, as well as ''Aeronautics'' for a brief period. It is read by pilots, aircraft owners, aviation enthusiasts and aviation-oriented executives in business, commercial and general aviation markets worldwide. It has the largest paid subscription, newsstand, and international circulation of any U.S.-based aviation magazine, according to its former publisher the Bonnier Corporation, and is promoted as "the world's most widely read aviation magazine". It is owned by digital media entrepreneur Craig Fuller. History The magazine first began publishing in 1927 as ''Popular Aviation'' soon after Charles Lindbergh's historic transatlantic flight. It was given the name ''Aeronautics'' briefly from 1929–1930 and was changed back to ''Popular Aviation'' until 1942, when it became ''Flying''. In June 2009, ''Flying'' owner, Hachette Filipacchi Media U.S., s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Wheel
A thermal wheel, also known as a rotary heat exchanger, or rotary air-to-air enthalpy wheel, energy recovery wheel, or heat recovery wheel, is a type of energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of air-handling units or rooftop units or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the heat energy. Other variants include enthalpy wheels and desiccant wheels. A cooling-specific thermal wheel is sometimes referred to as a Kyoto wheel. Description A thermal wheel consists of a circular honeycomb matrix of heat-absorbing material, which is slowly rotated within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air-handling system. As the thermal wheel rotates, heat is captured from the exhaust air stream in one half of the rotation and released to the fresh air stream in the other half of the rotation. Thus waste heat energy from the exhaust air stream is transferred to the matrix material and then from the matrix material to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saltwater (especially sea water) is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Desalination is used on many seagoing ships and submarines. Most of the modern interest in desalination is focused on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few rainfall-independent water resources. Due to its energy consumption, desalinating sea water is generally more costly than fresh water from surface water or groundwater, water recycling and water conservation. However, these alternatives are not always available and depletion of reserves is a critical problem worldwide. Desalination processes are using eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recuperator
A recuperator is a special purpose counter-flow energy recovery heat exchanger positioned within the supply and exhaust air streams of an air handling system, or in the exhaust gases of an industrial process, in order to recover the waste heat. Generally, they are used to extract heat from the exhaust and use it to preheat air entering the combustion system. In this way they use waste energy to heat the air, offsetting some of the fuel, and thereby improve the energy efficiency of the system as a whole. Description In many types of processes, combustion is used to generate heat, and the recuperator serves to recuperate, or reclaim this heat, in order to reuse or recycle it. The term recuperator refers as well to liquid-liquid counterflow heat exchangers used for heat recovery in the chemical and refinery industries and in closed processes such as ammonia-water or LiBr-water absorption refrigeration cycle. Recuperators are often used in association with the burner portion of a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
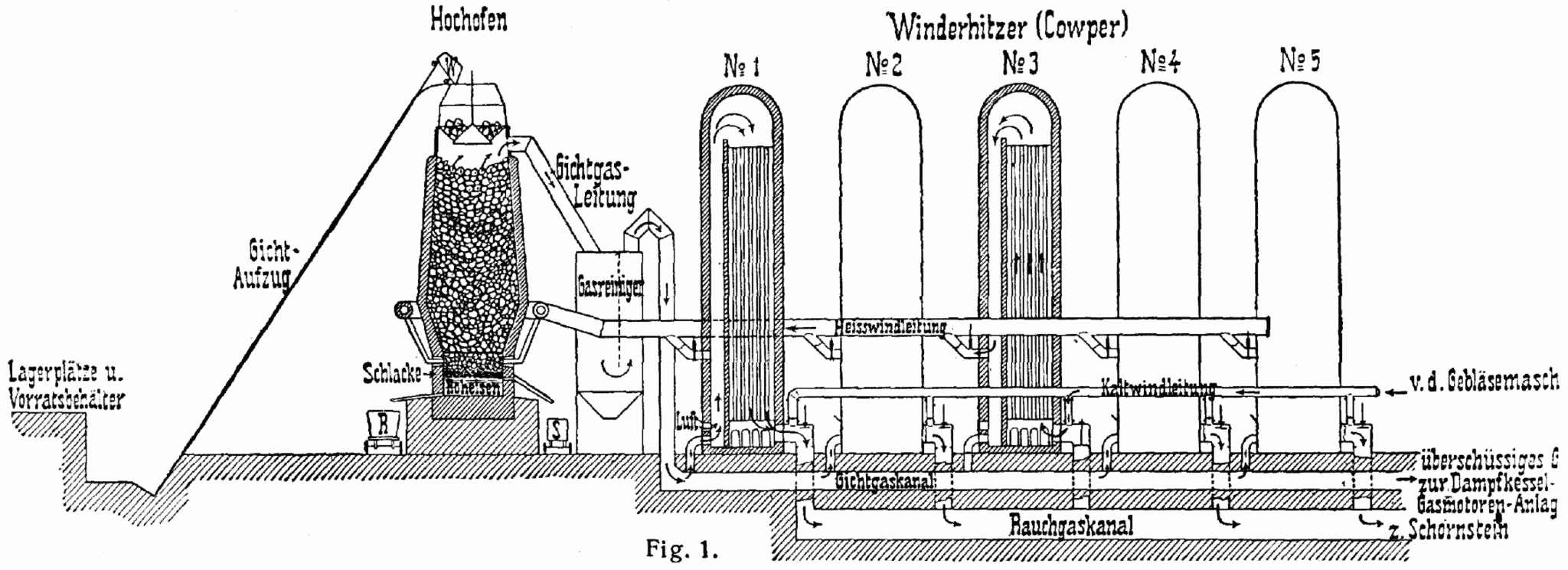
Hot Blast
Hot blast refers to the preheating of air blown into a blast furnace or other metallurgical process. As this considerably reduced the fuel consumed, hot blast was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution. Hot blast also allowed higher furnace temperatures, which increased the capacity of furnaces. As first developed, it worked by alternately storing heat from the furnace flue gas in a firebrick-lined vessel with multiple chambers, then blowing combustion air through the hot chamber. This is known as regenerative heating. Hot blast was invented and patented for iron furnaces by James Beaumont Neilson in 1828 at Wilsontown Ironworks in Scotland, but was later applied in other contexts, including late bloomeries. Later the carbon monoxide in the flue gas was burned to provide additional heat. History Invention and spread James Beaumont Neilson, previously foreman at Glasgow gas works, invented the system of preheating the blast for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement Image:Heat_exc_1-1.svg, Fig. 1: Shell and tube heat exchanger, single pass (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economizer
Economizers (US and Oxford spelling), or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger. Stirling engine Robert Stirling's innovative contribution to the design of hot air engines of 1816 was what he called the 'Economiser'. Now known as the regenerator, it stored heat from the hot portion of the engine as the air passed to the cold side, and released heat to the cooled air as it returned to the hot side. This innovation improved the efficiency of Stirling engine enough to make it commercially successful in particular applications, and has since been a component of every air engine that is called a Stirling engine. Boilers In boilers, economizers are heat exchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countercurrent Exchange
Countercurrent exchange is a mechanism occurring in nature and mimicked in industry and engineering, in which there is a crossover of some property, usually heat or some chemical, between two flowing bodies flowing in opposite directions to each other. The flowing bodies can be liquids, gases, or even solid powders, or any combination of those. For example, in a distillation column, the vapors bubble up through the downward flowing liquid while exchanging both heat and mass. The maximum amount of heat or mass transfer that can be obtained is higher with countercurrent than co-current (parallel) exchange because countercurrent maintains a slowly declining difference or gradient (usually temperature or concentration difference). In cocurrent exchange the initial gradient is higher but falls off quickly, leading to wasted potential. For example, in the adjacent diagram, the fluid being heated (exiting top) has a higher exiting temperature than the cooled fluid (exiting bottom) that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |