|
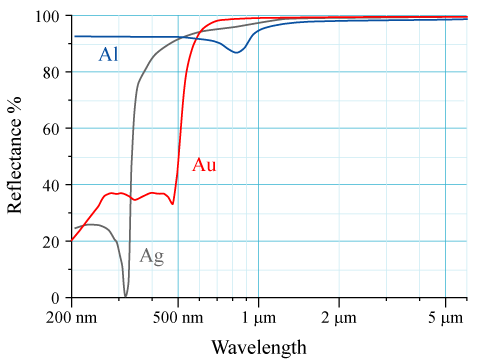
Reflectance Capture
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Reflection Coefficient
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, when no one realized that the waves were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index and a second medium with refractive index , both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel () who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, when no one realized that the waves were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the ''s'' and ''p'' polarizations incident upon a material interface. Overview When light strikes the interface between a medium with refractive index and a second medium with refractive index , both reflection and refraction of the light may occur. The Fresnel equations give the ratio of the ''reflected'' wave's electric field to the incident wave's electric field, and the ratio of the ''transmitted'' wave's electric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where is the wavelength of that light in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Reflectivity
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambertian Reflectance
Lambertian reflectance is the property that defines an ideal "matte" or diffusely reflecting surface. The apparent brightness of a Lambertian surface to an observer is the same regardless of the observer's angle of view. More precisely, the reflected radiant intensity obeys Lambert's cosine law, which makes the reflected radiance the same in all directions. Lambertian reflectance is named after Johann Heinrich Lambert, who introduced the concept of perfect diffusion in his 1760 book '' Photometria''. Examples Unfinished wood exhibits roughly Lambertian reflectance, but wood finished with a glossy coat of polyurethane does not, since the glossy coating creates specular highlights. Though not all rough surfaces are Lambertian, this is often a good approximation, and is frequently used when the characteristics of the surface are unknown. Spectralon is a material which is designed to exhibit an almost perfect Lambertian reflectance. Use in computer graphics In computer graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Of Incidence
In describing reflection and refraction in optics, the plane of incidence (also called the incidence plane or the meridional plane) is the plane which contains the surface normal and the propagation vector of the incoming radiation. (In wave optics, the latter is the k-vector, or wavevector, of the incoming wave.) When reflection is specular, as it is for a mirror or other shiny surface, the reflected ray also lies in the plane of incidence; when refraction also occurs, the refracted ray lies in the same plane. The condition of co-planarity among incident ray, surface normal, and reflected ray (refracted ray) is known as the first law of reflection (first law of refraction, respectively). Polarizations {{main, Polarization (waves)#s and p{{!''s'' and ''p'' polarizations The orientation of the incident light's polarization with respect to the plane of incidence has an important effect on the strength of the reflection. ''P-polarized'' light is incident linearly polarized l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffuse Reflection
Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light or other waves or particles from a surface such that a ray incident on the surface is scattered at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection. An ''ideal'' diffuse reflecting surface is said to exhibit Lambertian reflection, meaning that there is equal luminance when viewed from all directions lying in the half-space adjacent to the surface. A surface built from a non-absorbing powder such as plaster, or from fibers such as paper, or from a polycrystalline material such as white marble, reflects light diffusely with great efficiency. Many common materials exhibit a mixture of specular and diffuse reflection. The visibility of objects, excluding light-emitting ones, is primarily caused by diffuse reflection of light: it is diffusely-scattered light that forms the image of the object in an observer's eye over a wide range of angles of the observer with respect to the object. Mechanism Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection (physics), reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray (optics), ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. The earliest known description of this behavior was recorded by Hero of Alexandria (Anno Domini, AD c. 10–70). Later, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection. He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name Commission internationale de l'éclairage) is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces. It was established in 1913 as a successor to the Commission Internationale de Photométrie, which was founded in 1900, and is today based in Vienna, Austria. Organization The CIE has six active divisions, each of which establishes technical committees to carry out its program: * Division 1: Vision and Colour * Division 2: Physical Measurement of Light and Radiation * Division 3: Interior Environment and Lighting Design * Division 4: Transportation and Exterior Applications * Division 6: Photobiology and Photochemistry * Division 8: Image Technology Two divisions are no longer active. * Division 5: Exterior Lighting and Other Applications * Division 7: General Aspects of Lighting The President of the CIE from 2023 is Jennifer Veitch from Canada. CIE publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |