|
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including Vacuum tube#Diodes, vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium rectifier, selenium oxide plates, Diode#Semiconductor diodes, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a "Crystal detector#Cat whisker detector, cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector". Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury-arc Valve
A mercury-arc valve or mercury-vapor rectifier or (UK) mercury-arc rectifier is a type of electrical rectifier used for converting high-voltage or high- current alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is a type of cold cathode gas-filled tube, but is unusual in that the cathode, instead of being solid, is made from a pool of liquid mercury and is therefore self-restoring. As a result mercury-arc valves, when used as intended, are far more robust and durable and can carry much higher currents than most other types of gas discharge tube. Some examples have been in continuous service, rectifying 50-ampere currents, for decades. Invented in 1902 by Peter Cooper Hewitt, mercury-arc rectifiers were used to provide power for industrial motors, electric railways, streetcars, and electric locomotives, as well as for radio transmitters and for high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission. They were the primary method of high power rectification before the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
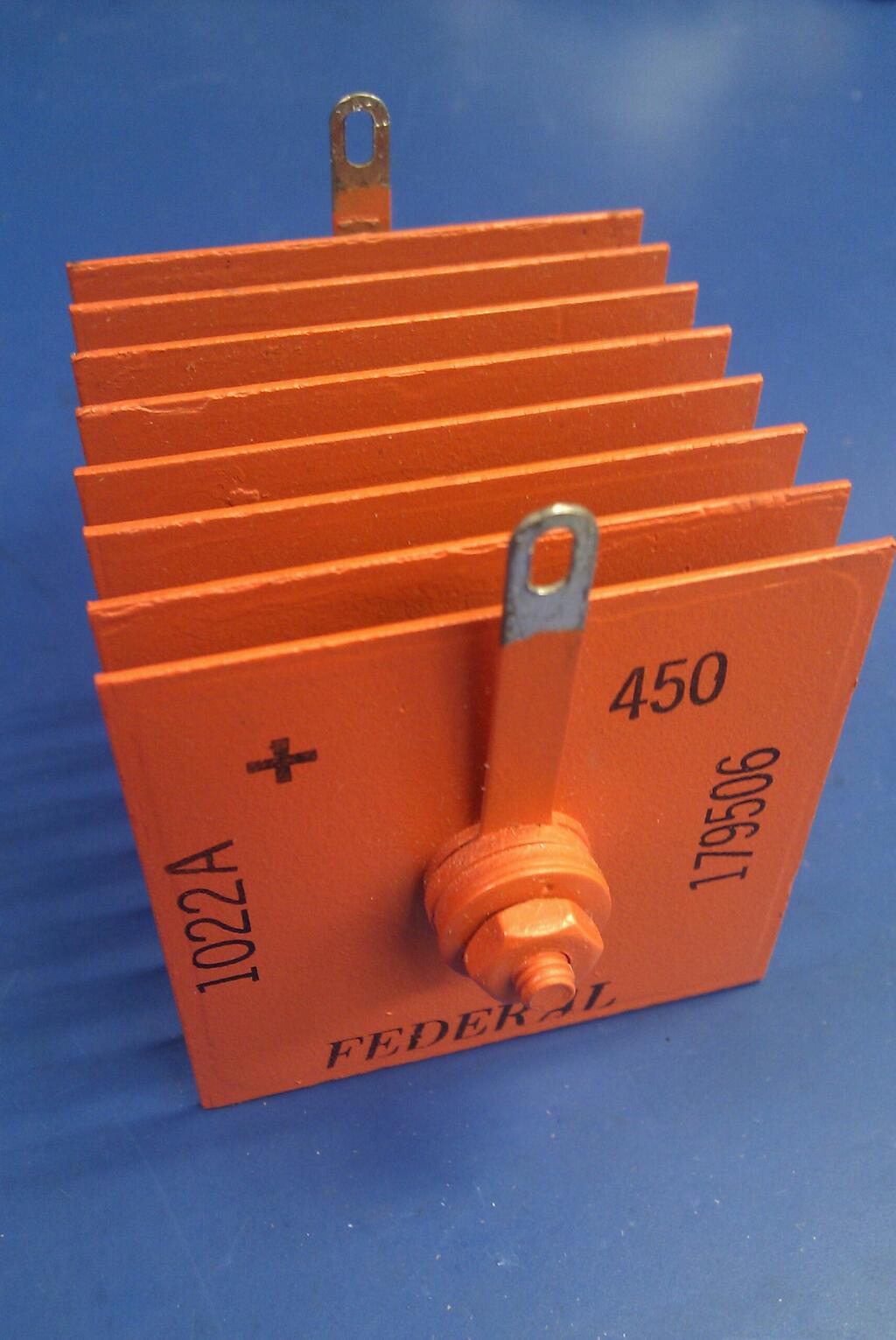
Metal Rectifier
A metal rectifier is an early type of semiconductor rectifier in which the semiconductor is copper oxide, germanium or selenium. They were used in power applications to convert alternating current to direct current in devices such as radios and battery chargers. Westinghouse Electric was a major manufacturer of these rectifiers since the late 1920s, under the trade name Westector (now used as a trade name for an overcurrent trip device by Westinghouse Nuclear). In some countries the term "metal rectifier" is applied to all such devices; in others the term "metal rectifier" normally refers to copper-oxide types, and " selenium rectifier" to selenium-iron types. Description Metal rectifiers consist of washer-like discs of different metals, either copper (with an oxide layer to provide the rectification) or steel or aluminium, plated with selenium. The discs are often separated by spacer sleeves to provide cooling. Mode of operation The principle of operation of a metal re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a Crystallinity, crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an Exponential function, exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first Semiconductor device, semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a Crystal, crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junction Diode
A diode is a two- terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance). It has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. The obsolete thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverter
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC. The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or maybe a combination of mechanical effects (such as a rotary apparatus) and electronic circuitry. Static inverters do not use moving parts in the conversion process. Power inverters are primarily used in electrical power applications where high currents and voltages are present; circuits that perform the same function for electronic signals, which usually have very low currents and vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon-controlled Rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier (SCR) is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of four-layer p–n–p–n switching was developed by Moll, Tanenbaum, Goldey, and Holonyak of Bell Laboratories in 1956. The practical demonstration of silicon controlled switching and detailed theoretical behavior of a device in agreement with the experimental results was presented by Dr Ian M. Mackintosh of Bell Laboratories in January 1958. The SCR was developed by a team of power engineers led by Gordon Hall and commercialized by Frank W. "Bill" Gutzwiller in 1957. Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers and thyristors as synonymous while other sources define silicon-controlled rectifiers as a proper subset of the set of thyristors; the latter being devices with at least four layers of alternating n- and p-type mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless and metal rectifiers used in early power applications can be considered primitive Schottky diodes. When sufficient forward voltage is applied, a current flows in the forward direction. A silicon p–n diode has a typical forward voltage of 600–700 mV, while the Schottky's forward voltage is 150–450 mV. This lower forward voltage requirement allows higher switching speeds and better system efficiency. Construction A metal–semiconductor junction is formed between a metal and a semiconductor, creating a Schottky barrier (instead of a semiconductor–semiconductor junction as in conventional diodes). Typical metals used ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-voltage Direct Current
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems. Most HVDC links use voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV. HVDC lines are commonly used for long-distance power transmission, since they require fewer conductors and incur less power loss than equivalent AC lines. HVDC also allows power transmission between AC transmission systems that are not synchronized. Since the power flow through an HVDC link can be controlled independently of the phase angle between source and load, it can stabilize a network against disturbances due to rapid changes in power. HVDC also allows the transfer of power between grid systems running at different frequencies, such as 50 and 60 Hz. This improves the stability and economy of each grid, by allowing the exchange of power between previously incompatible networks. The modern form o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Detector
A crystal detector is an obsolete electronic component used in some early 20th century radio receivers. It consists of a piece of crystalline mineral that rectifies an alternating current radio signal. It was employed as a detector ( demodulator) to extract the audio modulation signal from the modulated carrier, to produce the sound in the earphones. It was the first type of semiconductor diode, and one of the first semiconductor electronic devices. The most common type was the so-called cat's whisker detector, which consisted of a piece of crystalline mineral, usually galena ( lead sulfide), with a fine wire touching its surface. Greenleaf Whittier Pickard, ''Detector for Wireless Telegraphy and Telephony'', filed: 21 June 1911, granted: 21 July 1914 The "asymmetric conduction" of electric current across electrical contacts between a crystal and a metal was discovered in 1874 by Karl Ferdinand Braun. Crystals were first used as radio wave detectors in 1894 by Jagad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |