|
Recrudescence
Recrudescence is the recurrence of an undesirable condition. In medicine, it is usually defined as the recurrence of symptoms after a period of remission or quiescence, in which sense it can sometimes be synonymous with relapse. In a narrower sense, it can also be such a recurrence with higher severity than before the remission. "Relapse" conventionally has a specific (albeit somewhat illogical) meaning when used in relation to malaria (see below). Malaria In malaria, recurrence can take place due to ''recrudescence''; or ''relapse''; or ''re-infection'' (via mosquito transmission). ''Relapse'' means that a recurrence has been precipitated by a dormant stage in the liver called a "hypnozoite". Thus, ''relapse'' is applied only for those plasmodial species that have hypnozoites in the life cycle, such as ''Plasmodium vivax'' and '' P. ovale''. On the other hand, ''recrudescence'' means that circulating, multiplying parasites are detected after having persisted in the bloodstream ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melioidosis
Melioidosis is an infectious disease caused by a gram-negative bacterium called ''Burkholderia pseudomallei''. Most people exposed to ''B. pseudomallei'' experience no symptoms, but complications can range from fever and skin changes to pneumonia, abscesses, and septic shock, which can be fatal. Approximately 10% of people with melioidosis develop symptoms that last longer than two months, termed "chronic melioidosis". Prior to the Vietnam war less than a handful of patients had diagnosed in the United States in the twentieth century. In 1966, Spotnitz et al discovered that a number of servicemen with delayed onset of pulmonary infections had previously been deployed in Vietnam. Spotnitz coined the term “Vietnam Time Bomb” highlighting the fact that Burkholderia pseudomallei could remain dormant for years.The term gained traction as subsequent studies revealed latent infections in Vietnam veterans with estimates suggesting up to 250,000 U.S. soldiers were exposed. Spotnitz w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
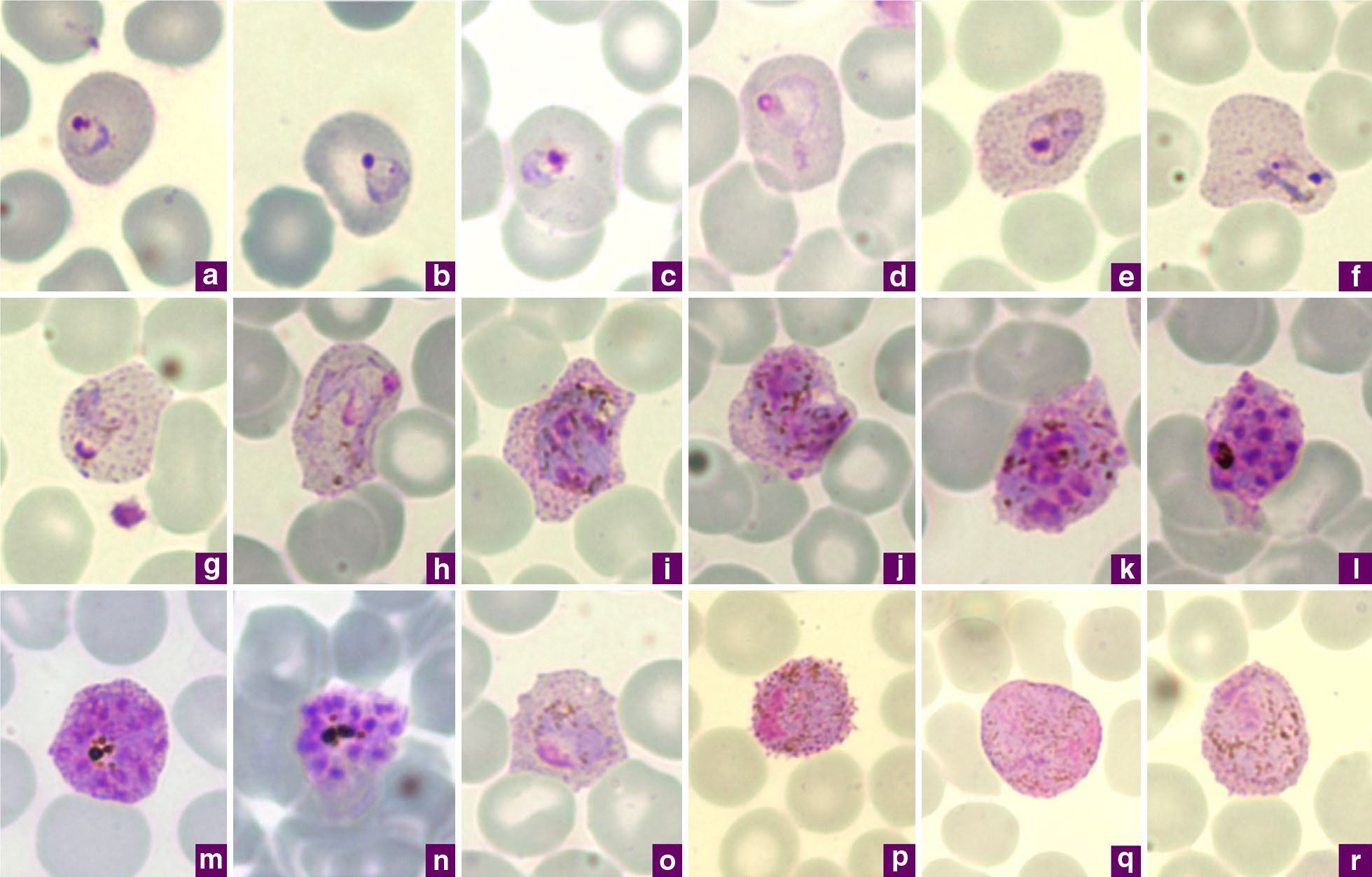
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female ''Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptom
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or recrudescence. In psychiatry, relapse or reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior, is the recurrence of pathological drug use, self harm or other symptoms after a period of recovery. Relapse is often observed in individuals who have developed a drug addiction or a form of drug dependence, as well as those who have a mental disorder. Risk factors Dopamine D2 receptor availability The availability of the dopamine receptor D2 plays a role in self-administration and the reinforcing effects of cocaine and other stimulants. The D2 receptor availability has an inverse relationship to the vulnerability of reinforcing effects of the drug. With the D2 receptors becoming limited, the user becomes more susceptible to the reinforcing effects of coc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cure
A cure is a substance or procedure that resolves a medical condition. This may include a medication, a surgery, surgical operation, a lifestyle change, or even a philosophical shift that alleviates a person's suffering or achieves a state of healing. The medical condition can be a disease, mental illness, genetic disorder, or a condition considered socially undesirable, such as baldness or insufficient breast tissue. An incurable disease is not necessarily a terminal illness, and conversely, a curable illness can still be fatal. The cure fraction or cure rate—the proportion of people with a disease who are cured by a given treatment—is determined by comparing disease-free survival in treated individuals against a matched control group without the disease. Another method for determining the cure fraction and/or "cure time" involves measuring when the hazard rate in a diseased group returns to the hazard rate observed in the general population. The concept of a cure inherently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quiescence
Quiescence (/kwiˈɛsəns/) is a state of quietness or inactivity. It may refer to: * Quiescence search, in game tree searching (adversarial search) in artificial intelligence, a quiescent state is one in which a game is considered stable and unlikely to change drastically the next few plays * Seed dormancy, a form of delayed seed germination * Quiescence, a type of dormancy in trees * Quiescent phase, the first part of the first stage of childbirth * The G0 phase of a cell in the cell cycle; quiescence is the state of a cell when it is not dividing * Quiescent current A low-dropout regulator (LDO regulator) is a type of a DC linear regulator, linear voltage regulator circuit that can operate even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage. The advantages of an LDO regulator over other DC-to-D ... (biasing) in an electronic circuit * Quiescent consistency is one of the safety properties for concurrent data structures See also * Rest (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia Pseudomallei
''Burkholderia pseudomallei'' (also known as ''Pseudomonas pseudomallei'') is a Gram-negative, bipolar, aerobic, motile rod-shaped bacterium. It is a soil-dwelling bacterium endemic in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, particularly in Thailand and northern Australia. It was reported in 2008 that there had been an expansion of the affected regions due to significant natural disasters, and it could be found in Southern China, Hong Kong, and countries in the Americas. ''B. pseudomallei'', amongst other pathogens, has been found in monkeys imported into the United States from Asia for laboratory use, posing a risk that the pathogen could be introduced into the country. Although it is mainly a soil-dwelling bacterium, one study showed that ''Burkholderia pseudomallei'' survived in distilled water for 16 years, demonstrating that it is capable of living in water if a specific environment is provided. It is resistant to a variety of harsh conditions including nutrient defici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Virus Diarrhea
Bovine viral diarrhea (BVD), bovine viral diarrhoea (UK English) or mucosal disease, previously referred to as bovine virus diarrhea (BVD), is an economically significant disease of cattle that is found in the majority of countries throughout the world. Worldwide reviews of the economically assessed production losses and intervention programs (e.g. eradication programs, vaccination strategies and biosecurity measures) incurred by BVD infection have been published. The causative agent, bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), is a member of the genus '' Pestivirus'' of the family Flaviviridae. BVD infection results in a wide variety of clinical signs, due to its immunosuppressive effects, as well as having a direct effect on respiratory disease and fertility. In addition, BVD infection of a susceptible dam during a certain period of gestation can result in the production of a persistently infected (PI) fetus. PI animals recognise intra-cellular BVD viral particles as ‘self’ and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster or zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be paresthesia, tingling or local pain in the area. Other common symptoms are fever, headache, and tiredness. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks, but some people develop ongoing neuropathy, nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with Immunosuppression, poor immune function the #Disseminated shingles, rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken Pox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella ( ), is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the chest, back, and face. It then spreads to the rest of the body. The rash and other symptoms, such as fever, tiredness, and headaches, usually last five to seven days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, and bacterial skin infections. The disease is usually more severe in adults than in children. Chickenpox is an airborne disease which easily spreads via human-to-human transmission, typically through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. The incubation period is 10–21 days, after which the characteristic rash appears. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |