|
Recombination Line , the time at which protons and electrons formed neutral hydrogen in the timeli ...
Recombination may refer to: *Carrier generation and recombination, in semiconductors, the cancellation of mobile charge carriers (electrons and holes) *Crossover (genetic algorithm), also called recombination *Genetic recombination, the process by which genetic material is broken and joined to other genetic material **Bacterial recombination **Homologous recombination *Plasma recombination, the formation of neutral atoms from the capture of free electrons by the cations in a plasma *Recombination (chemistry), the opposite of dissociation *Cage effect, a special kind of recombination reaction that appears in condensed phases *Recombination (cosmology) In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch during which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms. Recombination occurred about 370,000 yearsRecombination time frames: * Edward L. Wright'Jav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
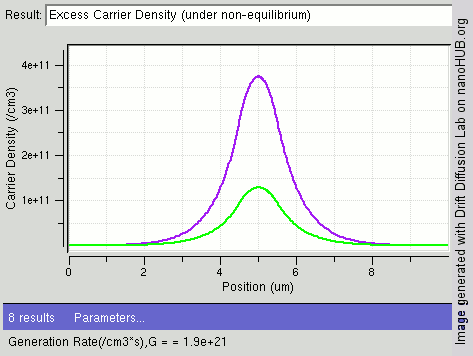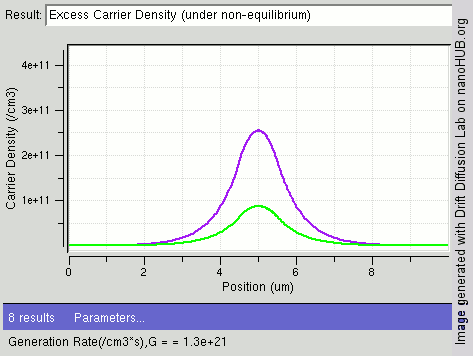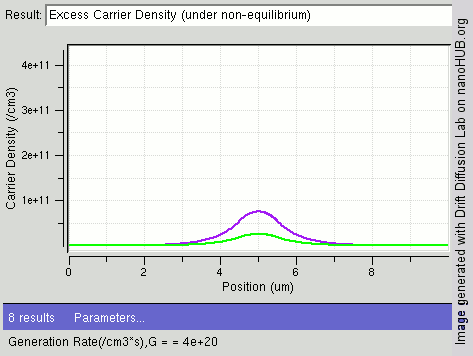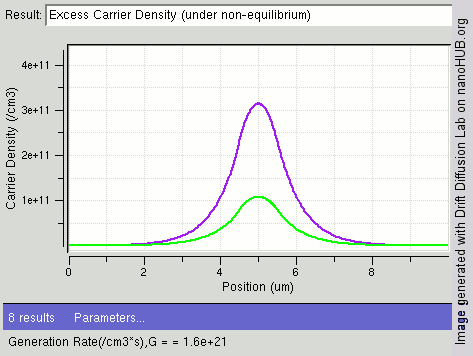
Carrier Generation And Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossover (genetic Algorithm)
In genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation, crossover, also called recombination, is a genetic operator used to combine the genetic information of two parents to generate new offspring. It is one way to stochastically generate new solutions from an existing population, and is analogous to the crossover that happens during sexual reproduction in biology. Solutions can also be generated by cloning an existing solution, which is analogous to asexual reproduction. Newly generated solutions are typically mutated before being added to the population. Different algorithms in evolutionary computation may use different data structures to store genetic information, and each genetic representation can be recombined with different crossover operators. Typical data structures that can be recombined with crossover are bit arrays, vectors of real numbers, or trees. Examples Traditional genetic algorithms store genetic information in a chromosome represented by a bit array. Crossover m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Recombination
Bacterial recombination is a type of genetic recombination in bacteria characterized by DNA transfer from one organism called donor to another organism as recipient. This process occurs in three main ways: * Transformation, the uptake of exogenous DNA from the surrounding environment. * Transduction, the virus-mediated transfer of DNA between bacteria. * Conjugation, the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another via cell-to-cell contact. The final result of conjugation, transduction, and/or transformation is the production of genetic recombinants, individuals that carry not only the genes they inherited from their parent cells but also the genes introduced to their genomes by conjugation, transduction, and/or transformation. Recombination in bacteria is ordinarily catalyzed by a RecA type of recombinase. These recombinases promote repair of DNA damages by homologous recombination. The ability to undergo natural transformation is present in at least 67 bacterial specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in cellular organisms but may be also RNA in viruses). Homologous recombination is widely used by cells to accurately DNA repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks (DSB), in a process called homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses. Horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Recombination
Plasma recombination is a process by which positive ions of a plasma capture a free (energetic) electron and combine with electrons or negative ions to form new neutral atoms (gas). Recombination is an exothermic reaction, meaning heat releasing reaction. Except for plasma composed of pure hydrogen (or its isotopes), there may also be multiple charged ions. Therefore, a single electron capture results in decrease of the ion charge, but not necessarily in a neutral atom or molecule. Recombination usually takes place in the whole volume of a plasma (volume recombination), although in some cases it is confined to some special region of it. Each kind of reaction is called a recombining mode and their individual rates are strongly affected by the properties of the plasma such as its energy (heat), density of each species, pressure and temperature of the surrounding environment. Uses An everyday example of rapid plasma recombination occurs when a fluorescent lamp is switched off. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombination (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry is a general process in which molecules (or ionic compounds such as salts, or complexes) separate or split into other things such as atoms, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner. For instance, when an acid dissolves in water, a covalent bond between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom is broken by heterolytic fission, which gives a proton (H+) and a negative ion. Dissociation is the opposite of association or recombination. Dissociation constant For reversible dissociations in a chemical equilibrium :AB A + B the dissociation constant ''K''d is the ratio of dissociated to undissociated compound :K_d = \mathrm where the brackets denote the equilibrium concentrations of the species. Dissociation degree The dissociation degree \alpha is the fraction of original solute molecules that have dissociated. It is usually indicated by the Greek symbol α. More accurately, degree of dissociation refers to the amount of solute dissociated int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cage Effect
In chemistry, the cage effect (also known as geminate recombination) describes how the properties of a molecule are affected by its surroundings. First introduced by Franck and Rabinowitch in 1934, the cage effect suggests that instead of acting as an individual particle, molecules in solvent are more accurately described as an encapsulated particle. The encapsulated molecules or radicals are called cage pairs or geminate pairs. In order to interact with other molecules, the caged particle must diffuse from its solvent cage. The typical lifetime of a solvent cage is 10 seconds. Many manifestations of the cage effect exist. In free radical polymerization, radicals formed from the decomposition of an initiator molecule are surrounded by a cage consisting of solvent and/or monomer molecules. Within the cage, the free radicals undergo many collisions leading to their recombination or mutual deactivation. This can be described by the following reaction: : R\!-\!R \;\;\unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Phase
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |